 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 18(3); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
There is an emergent need for imaging methods to better triage patients with acute stroke for tissue-plasminogen activator (tPA)-mediated thrombolysis or endovascular clot retrieval by directly visualizing the size and distribution of cerebral thromboemboli. Currently, magnetic resonance (MR) or computed tomography (CT) angiography visualizes the obstruction of blood flow within the vessel lumen rather than the thrombus itself. The present visualization method, which relies on observation of the dense artery sign (the appearance of cerebral thrombi on a non-enhanced CT), suffers from low sensitivity. When translated into the clinical setting, direct thrombus imaging is likely to enable individualized acute stroke therapy by allowing clinicians to detect the thrombus with high sensitivity, assess the size and nature of the thrombus more precisely, serially monitor the therapeutic effects of thrombolysis, and detect post-treatment recurrence. This review is intended to provide recent updates on stroke-related direct thrombus imaging using MR imaging, positron emission tomography, or CT.
It is estimated that one-sixth of the population will have a stroke during their lifetime. In the United States, a stroke occurs every 40 seconds, with someone dying of stroke every 4 minutes [1]. Moreover, stroke is the leading cause of long-term disability; about two-thirds of stroke survivors have permanent disability [1,2], and many become completely dependent on their caregivers. Stroke-related therapy is estimated to cost ~$33 billion each year in the United States [1].
Approximately 80% of strokes are infarction, which is typically caused by atherothrombosis [1]. The only FDA-approved thrombolytic drug for acute cerebral infarction is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) [3], which is a fibrinolytic agent with limited efficacy and a narrow therapeutic index [4]. Moreover, tPA has a short half-life and often leads to hemorrhagic complications [5]. Thus, despite the proven efficacy of tPA to improve stroke outcomes, ~60% of patients with stroke die or become functionally dependent despite adequate treatment [2]. This emphasizes the need for improvement in our current therapeutic regimens for stroke [6].
Current clinical guidelines recommend intravenous administration of a fixed dose of tPA (0.9 mg/kg) for acute stroke treatment [3]. Without an in vivo imaging tool to provide clinicians with critical information on the size, distribution, and nature of thrombi in individual patients, the tPA dosage could be insufficient in some patients or excessive in others, resulting in either decreased rates of thrombolysis or increased rates of hemorrhagic complications, respectively [7].
Present thrombolysis guidelines are based on the results of previous studies [3] conducted before advanced imaging modalities were available to determine thrombus location and size. Recently, the Enhanced Control of Hypertension and Thrombolysis Stroke Study (ENCHANTED trial) [8] failed to prove the non-inferiority of low-dose tPA compared to that of standard-dose tPA with respect to the primary outcome (death and disability at 90 days), albeit by a narrow margin (53.2% vs. 51.1%, respectively). However, the study reported significantly fewer symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhages with low-dose tPA administration. Thus, we believe that prompt characterization of the thrombus burden and composition can potentially guide thrombolytic therapy by enabling clinicians to reduce tPA dose for smaller fragile thrombi and perform endovascular clot retrieval for bigger compact thrombi that are likely to be resistant to conventional tPA doses, at an early stage (or even directly at the beginning).
Current methods such as magnetic resonance (MR) or computed tomography (CT) angiography (with or without contrast agents) allow indirect visualization of thrombi by confirming the obstruction of arterial blood flow and not by directly visualizing the obstructing thrombus itself [9]. Therefore, these techniques are not suitable for reliable assessment of the size and nature of the thrombus and cannot easily track scattered cerebral thromboemboli. In addition, they pose difficulties in distinguishing between thrombi and underlying atheromas [10], both of which constitute atherothrombotic steno-occlusion.
Consequently, there is a growing need to develop direct thrombus imaging techniques that allow us to identify and triage patients suited for thrombolysis [7,10-12]. Based on the imaging assessment of thrombus size and nature, thrombi expected to be resistant to dissolution with tPA could either receive higher doses or be considered for mechanical thrombolysis [7,10]. Thus, direct thrombus imaging is likely to provide opportunities for individuals to receive personalized thrombolytic therapy and appropriate withholding of unnecessary or potentially dangerous therapies [10,11].
Acute ischemic stroke occurs due to a sudden interruption of blood supply to the brain. However, an established thrombus could form before days or weeks of stroke onset, with fresh occlusive thrombi latching on to the already formed older thrombi [13]. Moreover, a post-treatment residual thrombus increases the risk of additional thrombotic events [14]. Residual thrombus impedes blood flow and serves as a potent prothrombotic factor, posing a risk for thrombus growth or subsequent rethrombosis [15]. Even after aggressive anti-thrombotic therapy, residual thrombus could be highly thrombogenic, reinitiating the thrombotic cascade and leading to arterial re-occlusion. Recently, Ahn et al. [16] showed that after thrombectomy in patients with ST-segment elevation-related myocardial infarction, residual thrombi indicated a higher occurrence of the no-reflow phenomenon, which is associated with adverse clinical outcomes. Therefore, in addition to the initial burden and location of thrombi, the presence of residual thrombi or distal embolization can affect vascular outcomes [17-19], including stroke. Direct thrombus imaging will also help visualize such residual thrombi or distal thromboemboli in addition to fresh but partially occlusive thrombus [7,10,20,21], thereby reducing the risk of treatment failure or stroke occurrence itself.
This review focuses on stroke-related direct thrombus imaging (Table 1) using MR imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), or CT. The authors apologize to many researchers whose studies were not cited because of the assigned scope and space limitation.
Plaque rupture exposes collagen and lipid core to the circulating blood. This initiates platelet adhesion and aggregation at the injury site and activates the coagulation cascade that leads to thrombus formation [22]. Due to the loss of non-thrombogenic properties of the endothelium, platelets adhere to the exposed subendothelial tissues. Binding of collagen to platelet receptor glycoprotein (GP) VI induces the release of activating factors (e.g., thrombin, adenosine diphosphate, thromboxane A2, serotoinin, and epinephrine), which, in turn, stimulates platelet activation and promotes further recruitment of circulating platelets. During the activation process, platelets undergo morphological changes (pseudopod formation), begin expressing proinflammatory molecules, and show procoagulant activity. Conformational changes in the platelet receptor GP IIb/IIIa allow it to bind to vWF and fibrinogen, thereby creating a bridge linking individual platelets into larger aggregates. The activating factors also release the platelet granule contents to induce activation/aggregation of platelets and the activation of coagulation. Plaque rupture also exposes subendothelial tissue factor (TF). TF forms a complex with factor VIIa to initiate a coagulation cascade, which culminates in the formation of the prothrombinase complex that catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin subsequently converts fibrinogen to fibrin, forming a fibrin clot stabilized by factor IIIa that crosslinks fibrin strands. Promising molecular targets should allow for high sensitivity and specificity in visualizing thrombus or its components.
MRI provides outstanding spatial resolution, and molecular MR imaging technologies allow for direct correlation among anatomy, function, and biological composition in both animals and humans. The intensity of MR images depends on both the concentration and relaxivity of MR probes at the site of interest, thereby making the optimization of target-to-background signal ratio necessary. There are two key disadvantages to using MRI for patients with acute stroke: i) relatively long acquisition times (compared to CT), and ii) susceptibility to motion artifacts.
Many ischemic strokes are attributable to plaque rupture in arteries with stenosis ≤50%, highlighting the importance of plaque ruptures [23-25] as a causative mechanism. Rupture-prone vulnerable plaques are not well-identified by conventional anatomy-based imaging techniques such as routine angiography or duplex ultrasonography, which provide minimal information about arterial wall pathology including plaque size and morphology [26-28]. Atherosclerotic vessels can preserve lumen diameter by compensatory arterial remodeling, thereby disguising the severity of atherosclerotic plaque burden [29]. While duplex ultrasonography can characterize unstable carotid plaques as heterogeneous or echolucent, it has shown limited success in predicting plaque ruptures and stroke occurrences [26-28,30-32].
In a swine model of carotid thrombosis induced by arterial injury, Corti et al. [33] obtained MR images using black-blood T1-weighted and T2-weighted MRI to assess the age of thrombus by assessing different oxygenation states of erythrocytic hemoglobin in the thrombus and changes in intracellular/matrix content of proteins and RBC hydration over time. Black-blood MRI using double inversion recovery techniques can effectively null the signal of flowing blood, thereby delineating other stationary structures such as vascular walls and thrombi from the lumen [34,35]. During the preparation period, a non-selective first pulse inverts all the spins in the field, following which, a slice-selective second pulse of the magnetic field restores the magnetization of the spins within the slice of interest while leaving the spins outside inverted. Imaging begins when the blood containing inverted spins replaces the unaffected blood and the magnetization vectors of the flowing blood cross the null point, termed as the inversion time [35]. Therefore, without use of any contrast agents, the black-blood MRI technique allows the detection of both occlusive and wall-adherent thrombi and the differentiation between fresh and old thrombi. In the study by Corti et al. [33], acute thrombi appeared hyperintense on T2-weighted MR images at 6 hours; the signal intensity (SI) of the thrombus was 197±25% in comparison with that of adjacent muscles [33]. The thrombus SI increased to peak levels (246±51%) at 1 week and decreased to plateau (120±15%) at 6 weeks, when complete thrombus organization was confirmed histologically. The T1-weighted MR images showed a similar pattern with lower SI than that seen in T2-weighted MR images. Despite the ability of the black-blood MRI technique to detect arterial thrombosis and define the age of thrombi, contrast agents may be needed to improve image quality, precisely differentiate between the thrombus and the vessel wall, and allow for the detection of complicated high-risk plaques. Since most of the SI data were derived from complete occlusive thrombi, further investigation using small mural or mobile thrombi should be performed. Despite the limitations, this imaging technique may be a useful tool for studying thrombus age-related pathophysiology and drug therapy.
Johnstone et al. [36] induced atherosclerotic plaque disruption in the modified Constantinides model using Russell’s viper venom and histamine. MR images were acquired, and the imaging data were correlated with the histopathology data related to aortic wall thickness, thrombus size, thrombus length, and anatomical location. By combining in vivo MRI with the modified animal model of atherosclerosis and plaque disruption, the authors were able to identify the formation of new thrombi upon pharmacological triggering. However, only 6 out of the 9 animals were confirmed for intraluminal thrombus formation, possibly due to the low sensitivity of MRI without the use of any thrombus-seeking contrast agents. Thus, they developed a fibrin-binding gadolinium-labeled peptide EP-1873 and studied this imaging agent in the animal model of plaque rupture and thrombosis [37]. The new imaging probe enabled them to detect acute and subacute thrombosis by directly visualizing the thrombus, yielding a 100% success rate, as confirmed by histological correlation studies. In another study, this group employed diffusion-weighted MRI in order to distinguish the atherothrombus relative to the vessel. This imaging modality provided superior contrast due to restricted diffusion coefficient of the thrombus (1.0×10-3 mm2/s) compared to that of the tissue (1.5×10-3 mm2/s) [38]. The authors suggested that higher-resolution MRI would be required for better differentiation of lipids from the fibrous or small thrombotic components of the pre-trigger plaque.
Identification of high-risk plaques containing both hemorrhage and thrombus is beneficial for the prediction of acute ischemic stroke, which is often caused by mild degrees of stenosis. Moody et al. [39] utilized magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging (MRDTI) for detecting methemoglobin within intraplaque hemorrhage as a marker of complicated plaques. The MRDTI showed a high sensitivity (84%) and specificity (84%) in detecting thrombi in 63 patients with ischemic stroke. The advantage of this technique lies in its easy applicability on most available MRI setups without the need for additional hardware or software. Combining MRDTI with targeted probes, such as imaging agents targeting fibrin or activated platelets, will augment this technique and provide valuable insights into the pathophysiological processes characteristic of complicated plaques. Furthermore, dedicated surface coils for the imaging of the carotid bifurcation will considerably improve spatial resolution, and imaging will better reflect the true nature of the atheromatous lesion.
Weisstanner et al. [40] used susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) to visualize thrombi in patients with acute ischemic stroke. SWI displayed strong correlation of thrombus location with that predicted using time-of-flight MR angiography (MRA), first-pass gadolinium-enhanced MRA, and digital subtraction angiography and showed that thrombus length has no effect on the reperfusion success of endovascular therapy. These results suggest that SWI along with standard MRI may be more useful in thrombus detection. However, it is notable that SWI could overestimate maximal thrombus length because of different magnetic susceptibility of thrombi relative to the surrounding tissue. Although thrombus length does not affect the chances of successful reperfusion when using multimodal endovascular revascularization techniques, it was observed that high clot burden was significantly associated with the severity of clinical outcome at 3 months.
To detect active vulnerable plaques with higher sensitivity, Flacke et al. [30] developed lipid-encapsulated liquid perfluorocarbon nanoparticles (250 nm nominal diameter), a fibrin-targeted MR contrast agent, carrying high gadolinium-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA) payloads. This imaging probe could adhere to the clot surface and create a very thin gadolinium-rich layer that encases the surface of fibrin clots as small as 500 μm. Thus, it was suggested that this direct thrombus-imaging agent may allow for the detection of tiny intravascular thrombi within fissures of active vulnerable plaques. Thus, direct diagnosis of intimal fibrin deposition with targeted paramagnetic nanoparticles in a patient with functionally non-significant carotid stenosis may indicate early surgical or interventional therapy. Such imaging techniques enable early detection of impending thromboemboli and reliably determine the risk of ischemic stroke.
Overoye-Chan et al. [20] developed a different type of MRI contrast agent to detect fibrin in thrombi: EP-2104R that comprises an 11 amino acid peptide derivatized with 2 Gd-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-like moieties at both the C-termius and N-terminus of the peptide (4 Gd in total). To test the feasibility of EP-2104R, a phase II clinical study enrolled 52 subjects with confirmed thrombi in the venous system, heart, or arterial system. MRI using this novel agent visualized thrombi that are not readily visible in precontrast imaging, and showed additional enhancement of thrombi that are visible in precontrast imaging. However, due to lower blood background, thrombi were more clearly visible when imaged at 2 to 6 hours after intravenous injection of EP-2104R, than those imaged within 1 hour. The delayed improvement of target-to-background signal ratio may limit the clinical use of this contrast agent in the context of hyperacute ischemic stroke, where “time lost is brain lost.” Uppal et al. [21] performed direct “cerebral” thrombus imaging using MRI and EP-2104R in a small number of rats with embolic stroke (Figure 1). Imaging was performed very early (~20 min) after the placement of thrombus in the right internal carotid artery at the level of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Thus, further studies using larger sample sizes should be performed to determine the effective time window of imaging after thromboembolic stroke. It is notable that the Gd-DTPA did not interfere with the EP-2104R detection of the thrombus. This merits further investigation of high doses of Gd-DTPA, in order to verify that it can be used for the perfusion study after thrombus identification using EP-2104R.
To visualize activated platelets in carotid artery thrombi and monitor the thrombolytic effects in a mouse model of carotid thrombosis, Muhlen et al. [41] used MRI and microparticles of iron oxide (MPIO) conjugated with a single-chain antibody targeting ligand-induced binding sites (LIBS) on the platelet integrin GPIIb/IIIa. The authors found that LIBS is a highly specific target for thrombus imaging because GPIIb/IIIa is abundant and changes its conformation upon platelet activation. They also demonstrated MR visualization of activated platelets ex vivo on fresh symptomatic carotid atheromas removed from patients with stroke. However, compared to nanoparticles, these microparticles can facilitate infarct progression due to a higher probability of capillary plugging or increase the probability of non-specific imaging due to increased random sequestration by other clots or the reticuloendothelial system (including cells and tissues in the blood, spleen, liver, lungs, bone marrow, and lymph nodes). Despite these limitations, LIBS-MPIO-induced signals reflected the numbers of bound MPIOs and thrombus size, suggesting that this MR-based thrombus-imaging agent may have potential as a quantitative tool. Furthermore, a recent animal study [42] demonstrated that the LIBS-MPIO imaging agent allowed noninvasive characterization of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by visualizing platelet-driven inflammation and potential obstruction of the microcirculation. In addition, late gadolinium enhancement could be used subsequently to visualize myocardial necrosis, indicating that the imaging agent can serve as a dual-function probe.
More recently, Heidt et al. [43] showed delivery and specific binding of a contrast agent targeted against activated platelets for non-invasive detection of murine pulmonary thromboemboli, using MRI. This platelet-targeted thrombus-imaging agent may also allow for detection of cerebral thromboemboli.
The advantage of PET (vs. CT or MRI) [44] is its high sensitivity in identifying picomolar concentrations of target molecules in the human body. For target-specific delivery of radionuclides (e.g., 99mTC, 123I, and 18F), small peptides with <30 amino acid residues are preferred ligands because of their fast clearance from the bloodstream, allowing a high target-to-background ratio and good image quality. PET utilizes a radiolabeled molecular tracer and a PET scanner to observe in vivo radioactivity. The advantage of PET lies in its high sensitivity compared to that of MRI and CT. However, since PET is limited by the relatively low spatial resolution it offers, it must be combined with either MRI or CT for precise anatomical localization of the radioactive signal.
Neither clinical feasibility nor utility of PET in managing acute stroke in patients has been extensively studied [45]. In addition to radiation exposure, several important factors that should be considered include the relatively long interval between probe injection and PET imaging, 24/7 availability of PET, and the inability of patients with acute stroke maintaining a fixed posture during imaging. However, when combined with endovascular clot retrieval or penumbra imaging to extend the therapeutic window, PET-based thrombus imaging could potentially serve as a tool for acute stroke management. The time constraints would be less stringent for detecting residual thromboemboli to predict and prevent recurrent stroke in the subacute or chronic period.
Aziz et al. [46] demonstrated that arterial thrombosis was strongly correlated with an increased uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) seen on PET/CT after generating thrombi in the aortas of rabbits. Maximal standardized uptake value (SUV) was significantly higher in segments with thrombosis compared to those without thrombi: 113% increase (P=0.002). However, since vulnerable plaques that are prone to rupture and subsequent thrombosis can also take up high levels of FDG, more specific PET probes targeting thrombi may be required.
Hara et al. [47] used FDG-PET/CT and a neutrophil-targeting probe to detect deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the jugular vein of mice. They demonstrated that thrombus-related radioactivity correlated with the number of neutrophils in thrombi. The advantage of this technique is its capability of identifying neutrophil-dependent inflammation within the thrombus in DVT. However, it should be considered that inflammation of the vein wall could also contribute to the increase in the FDG signal.
To develop fibrin-targeted PET probes, Ciesienski et al. [48] conjugated fibrin-specific peptides to 64Cu-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (64Cu-DOTA). Although these probes showed dissociation constants (Kd) for the soluble fibrin fragment in nanomolar quantities, their metabolic instability made it impossible to produce a high signal relative to the blood background. To resolve this issue, the authors also advanced fibrin-binding PET probes by replacing DOTA with either 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1-glutaric acid-4,7-acetic acid (NODAGA) or the 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid (NOTA)-monoamide chelator, both of which yielded stable chelate complexes with the copper ions [49]. In assessments of PET imaging efficacy, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and metabolic stability of the probes in a rat model of carotid artery thrombosis, this method demonstrated a clear visualization of the thrombus (a 5-fold or higher thrombus-to-background ratio) and enhanced metabolic stability (>85% in blood at 4 hours after injection). More recently, they used PET/CT and whole-body PET/MRI to identify the location of arterial and venous thrombi utilizing 64Cu-labeled fibrin-binding probes (64Cu-FBP8) (Figure 2) [49,50]. For both arterial and venous thrombosis, younger clots took up 64Cu-FBP8 more readily than older ones, suggesting that PET imaging can be used to identify the age of the thrombus. High thrombus uptake, rapid systemic clearance, low off-target retention, and small size of the probe may allow for the detection of small thrombi using a clinical PET scanner; however, clinical validation studies still need to be performed in different settings.
CT is available in most emergency departments worldwide and is usually the first imaging modality for most time-critical decision-making in administering tPA. Since soft-tissue resolution in human CT is often insufficient to distinguish the thrombus from the surrounding blood pool, non-contrast CT does not usually allow a precise assessment of the extent and distribution of thromboemboli [7,10]. Clinicians often rely on the “dense artery” sign [51-53], which refers to the appearance of a cerebral artery on non-enhanced CT. However, this strategy has poor sensitivity. In a recent prospective study involving 117 patients with acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack and 65 age-matched controls [53], the hyperdense MCA sign was observed in only 15% of all ischemic strokes and 25% of all MCA strokes. Moreover, agreement between expert neuroradiologists on the presence of a hyperdense MCA sign was not high (Kappa=0.747). The low sensitivity and higher possibility of disagreement between non-experts raise doubts about the practical utility of the dense artery sign in making time-sensitive decisions regarding optimal recanalization strategies [53]. In another study involving 35 patients with clinically suspected stroke [54], susceptibility-weighted MRI was found to be superior (sensitivity/specificity: 85%/100%) to fluid-attenuation inversion-recovery MRI (61%/98%) and CT (52%/93%) in detecting cerebral thromboemboli.
To overcome the aforementioned limitations, Kim’s group [7] developed the first hyperacute direct thrombus imaging technique using CT and glycol-chitosan-coated gold nanoparticles (GC-AuNPs). Following intravenous injection of GC-AuNPs in mice (n=127), microCT imaging demonstrated a 100% success rate in the detection of 1-2 mm-sized carotid thrombi in a prompt (<5 min) and quantitative manner. In vivo AuNP-microCT imaging could be used to not only capture baseline thrombus burden but also serially monitor the therapeutic efficacy of tPA-mediated thrombolysis. When translated into stroke practice, this novel thrombus-imaging technique may allow clinicians to pursue personalized thrombolytic therapy by demonstrating thrombus burden and distribution in a prompt and quantitative manner. Due to the long circulating half-life of GC-AuNPs, the direct thrombus imaging allows long-term (up to 3 weeks) monitoring of thrombotic recurrences without additional AuNP administration, thereby facilitating the identification of recurrent or residual thrombi, and further guides the therapy to treat to completion. Furthermore, the authors successfully illustrated the dynamic nature of post-tPA thrombus evolution in vivo in near-real time (Figure 3), indicating that AuNP-microCT thrombus imaging probably serves as a new, simple, and robust tool in neurovascular studies.
Following the aforementioned study, Grover et al. [55] also employed microCT and gold nanoparticles in their study to detect venous thrombi in mice. They successfully demonstrated the utility of gold nanoparticles in CT-based direct thrombus imaging that allowed repeated assessments of venous thrombi in mice.
Recently, Kim’s group has reported, for the first time, the generation and characterization of a novel CT-based fibrin-targeted nanoparticle imaging agent (fib-GC-AuNPs) for direct imaging of cerebral thromboembolism (Figure 4) as well as in situ carotid thrombosis [10,56]. Fibrin-binding and thrombus-visualizing capacities of fib-GC-AuNPs were superior to those of GC-AuNPs, indicating that targeting nanoparticles with a fibrin-binding peptide strongly increases the amount of nanoparticles that localize to thrombi. Following intravenous injection of the targeted agent in a mouse model of embolic stroke, microCT imaging allowed for prompt detection and quantification of cerebral thromboemboli, and determining the success of tPA therapy. It was also demonstrated that residual thrombus burden at 24 hours was highly correlated with the final infarct size at 24 hours.
CT-based direct thrombus imaging is unlikely to add much time to the emergency situation in most patients with hyperacute stroke with a narrow treatment window in contrast with modalities such as MRI or nuclear imaging, where considerable time is necessary to obtain information and make decisions on personalized thrombolytic therapy [10]. Kim’s group suggested [10] that multi-energy CT could be a potentially useful tool in differentiating fib-GC-AuNP-related thrombus marking (for fibrin-rich clots) from the dense artery sign (for erythrocyte-rich clots) [52], based on the differences in their attenuation properties at different X-ray energies [57]. In addition, they proposed that AuNPs and flat-panel CT, which has relatively low contrast sensitivity, may be useful in tracking the evolution of thrombi and scattering of thromboemboli during intra-arterial recanalization therapy and guide the recanalization therapy in near-real time [10].
When translated into clinical practice, direct thrombus imaging is likely to improve the safety and efficacy of recanalization therapy by allowing for a personalized thrombolytic therapy by helping clinicians i) compare the risks and benefits of potential treatment options, ii) determine whether they should perform intravenous tPA-mediated thrombolysis, intraarterial urokinase-mediated thrombolysis, or endovascular clot retrieval, iii) optimize tPA dosage to match thrombus burden, and iv) select specific endovascular therapies or devices [7,10]. Conventional imaging modalities would be greatly augmented by employing cutting-edge direct thrombus-imaging techniques, ultimately resulting in a more accurate balance between achieving satisfactory tissue reperfusion and avoiding hemorrhagic complications in acute cerebral infarction [7,10]. In addition, direct thrombus imaging could enable assessment of the completeness of thrombolysis both locally and at thromboembolic sites, and detect residual thrombus elements and future thrombotic recurrences [7,10].
Thrombus imaging studies have most commonly used small-animal imaging equipment in rodent models of stroke (Table 1). However, dedicated time and effort will be required to address the translational gap between conventional CT/MRI/PET and micro-CT/MRI/PET as well as that between animals and humans.
The United States National Cancer Institute states that, “Most engineered nanoparticles are far less toxic than household cleaning products.” (http://nano.cancer.gov/learn/now/safety.asp). However, safety concerns about nanoparticles still exist [58], including biocompatibility, potential allergic reactions due to complement activation, and immune-system aberrations. Although speculative, it may be possible that thrombus-targeting agents could aggravate thrombosis itself. Taken together, these findings suggest that in vivo distribution and toxicity profiles and diagnostic efficacies of the nanoagents should be thoroughly investigated for successful translation of thrombus imaging into the clinical setting.
Currently, theranostics is a popular topic in nanomedicine and molecular imaging research. It is defined as an integration of therapeutic and imaging functionalities on a single platform that allows not only accurate diagnosis but also drug delivery and monitoring of the drug therapy through tracking of the theranostic agent itself [59]. This real-time information can be used to adjust or modify the treatment strategy, leading to customized treatment. Simultaneous visualization and treatment of underlying pathology would facilitate the assessment of safety and toxicity and real-time therapeutic efficacy, allowing precision medicine to produce better outcomes. Thrombus imaging agents could potentially serve as a theranostic platform [10], whereby thrombus-specific delivery of thrombolytic agents or anti-thrombotic agents can occur concomitantly with direct imaging of the thrombus.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jeong-Yeon Kim for preparing the figures and Su-Kyoung Lee for editing the manuscript.
Notes
Figure 1.
Coronal slice from 3D T1-weighted images at the level of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) origin. The EP-2104R-enhanced image (B) clearly identifies the thrombus (arrow) that was not visible on the image acquired before EP-2104R injection (A). Pictorial representation of the location of the thrombus within the cerebral arterial tree (C). BA indicates basilar artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; ICA, internal carotid artery; OA, olfactory artery; ACA, anterior cerebral artery. Figure and caption reprinted from Uppal et al. Stroke (2016) [21] with permission.
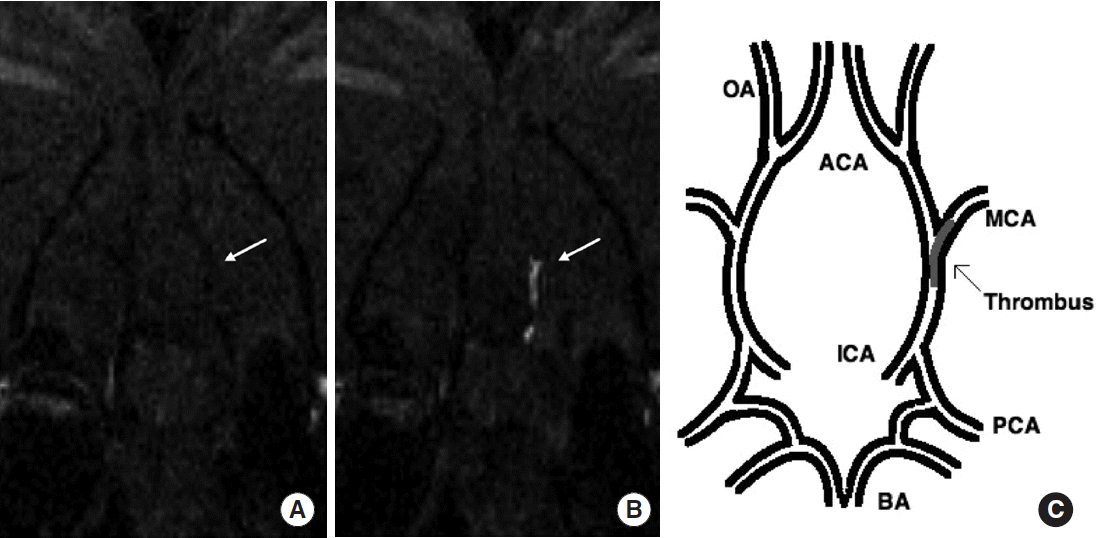
Figure 2.
Representative sagittal views of CT, PET, and fused PET/CT images reconstructed from data 30-90 minutes after injection of 64Cu-FBP8, a probe synthesized using a known fibrin-specific peptide conjugated to 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1-glutaric acid-4,7-acetic acid. A rat model of carotid arterial thrombosis was used. Thick arrow indicates thrombus; arrowhead, surgical area; and thin arrow, common carotid artery visualized by CT angiography. Figure and caption reprinted from Blasi et al. J Nucl Med (2014) [49] with permission.
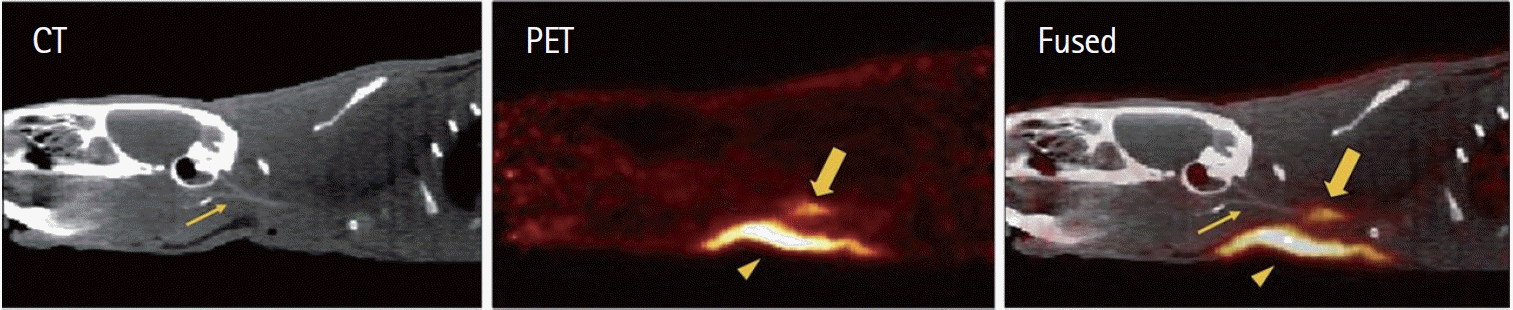
Figure 3.
Representative serial microCT images illustrating the dynamic nature of post-tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) thrombus evolution. In the lower-row animal, proximal thrombus growth (yellow arrows) is accompanied by distal thrombus resolution (red arrowhead) and embolization (blue arrows), followed by the distal migration of the entire thrombus body (white arrow). In the lower-row animal, proximal thrombus resolution (yellow arrows) is accompanied by distal thrombus growth (red arrowhead) and embolization (blue arrows). Scale bars=1 mm. I.V.=intravenous. Figure and caption reprinted from Kim et al. Ann Neurol (2013) [7] with permission.

Figure 4.
Schematic view of microCT-based direct thrombus imaging using fibrin-targeted glycol-chitosan-coated gold nanoparticles (fib-GC-AuNPs). Serial microCT thrombus images were acquired at baseline (5 minutes after intravenous injection of fib-GC-AuNPs and 1 hour after the embolic stroke), and at 3 and 24 hours after tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) treatment. Direct thrombus imaging permits prompt localization of cerebral thrombi in the circle of Willis. Treatment with tPA, which was initiated after the baseline imaging (total dose of 24 mg/kg tPA administered as a 60 μL bolus injection followed by 540 μL continuous infusion over 30 minutes), shows the dissolution of the thrombus at 3 and 24 hours (arrow-heads). This demonstrates that thrombus marking can allow therapeutic monitoring of thrombolysis. Figure and caption reprinted from Kim et al. Theranostics (2015) [10] after modification with permission.
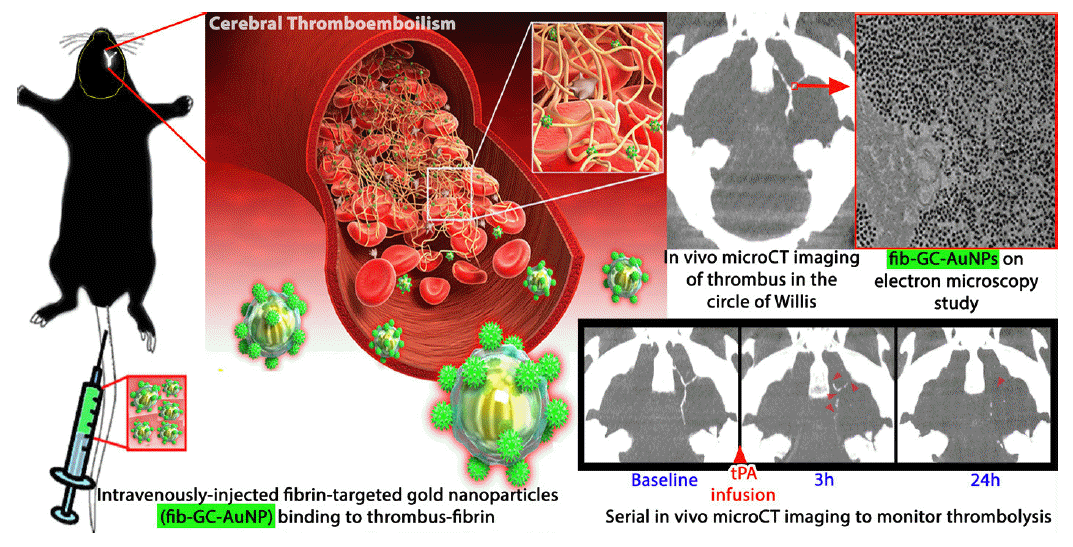
Table 1.
Summary of direct thrombus-imaging studies
| Group (year) | Model | Imaging modality | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flacke et al. [30] (2001) | Atherosclerosis in dogs | Gadolinium-diethylenetriaminepe tacetate-bis-oleate-nanoparticle magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | -Fibrin-targeted paramagnetic nanoparticles |
| -Sensitive detection of vulnerable plaques | |||
| Johnstone et al. [36] (2001) | Intraluminal thrombus in rabbits | Contiguous cross-sectional T2 weighted MRI | -Measurement of thrombus formation after pharmacological triggering |
| -Determination of presence, location, and size of thrombus | |||
| Corti et al. [33] (2002) | Arterial thrombus in pigs | Black-blood MRI | -Detection of arterial thrombosis |
| -Potential application in determining thrombus age | |||
| Moody et al. [39] (2003) | Patients with cerebral ischemia | 3D T1-weighted direct thrombus MRI | -Identifying complicated plaques |
| -Easy to apply on commercially available scanners without additional hardware or software | |||
| Botnar et al. [37] (2004) | Acute thrombosis after plaque rupture in rabbits | Fibrin-binding gadolinium-labeled peptide, EP-1873, MRI | -Fibrin-binding contrast agents |
| -in vivo MRI of thrombosis after plaque rupture | |||
| Sirol et al. [60] (2005) | Carotid artery thrombosis in rabbits | Fibrin-binding gadolinium-labeled peptide, EP-2104R, MRI | -Fibrin-targeted contrast agents |
| -in vivo detection of chronic or organized thrombus using EP-2014R | |||
| -Discrimination of occlusive arterial thrombi from non-occlusive ones | |||
| Viereck et al. [38] (2005) | Arterial thrombosis in rabbits | Diffusion-weighted MRI | -Noninvasive in vivo detection of atherothrombosis |
| -Diagnostic tool for plaque-associated white thrombi | |||
| -Improved contrast between the thrombus and the underlying plaque | |||
| Muhlen et al. [41] (2008) | Thrombosis in mice | Single-chain antibody conjugated iron oxide microparticles MRI | -Targeting activated platelets |
| -Monitoring of thrombotic treatment | |||
| -ex vivo MRI of human carotid plaques | |||
| Overoye-Chan et al. [20] (2008) | Thrombosis in humans | Fibrin-binding gadolinium-labeled peptide, EP-2104R, MRI | -Fibrin-targeted contrast agents |
| -Detection of thrombi not normally visible in precontrast imaging | |||
| Klink et al. [61] (2010) | Carotid thrombosis in mice | Gadolinium-based paramagnetic agent, P975, MRI | -Integrin αIIbβ3-targeted (activated platelet) paramagnetic contrast agent |
| -in vivo imaging of platelet-rich acute thrombi | |||
| Weisstanner et al. [40] (2014) | Patients with acute ischemic stroke | Time-of-flight MR angiography (MRA) | -Susceptibility-weighed imaging for visualization of thrombotic material |
| -96% of success rate for thrombus detection by susceptibility-weighted imaging | |||
| -Thrombus length may not have an impact on success of endovascular reperfusion therapy in middle cerebral artery occlusions | |||
| Wen et al. [62] (2015) | Carotid artery thrombosis in mice | Virus nanoparticle MRI | -Fibrin-binding virus particles |
| -Nanoparticle shape dependency for thrombus targeting | |||
| Gale et al. [63] (2015) | Arterial thrombosis in rats | Manganese-based-fibrin-binding probe MRI | -Stable Manganese complex as a Gadolinium alternative |
| -Fibrin-targeted and equivalent thrombus enhancement to EP-2014R | |||
| Heidt et al. [43] (2016) | Pulmonary embolism in mice | Single-chain antibody conjugated iron oxide microparticles and T2-weigthted MRI | -Activated platelet-targeted agent |
| -Detection of pulmonary thromboemboli | |||
| -Increasing sensitivity of MRI for pulmonary thromboemboli | |||
| Aziz et al. [46] (2008) | Arterial thrombosis in rabbits | Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (18FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT) angiography | -Detection of plaque inflammation and thrombosis |
| -Feasibility study in the atherosclerosis and thrombosis that may have clinical relevance | |||
| Patel et al. [64] (2011) | Arterial thrombosis in rabbits | 18F-FDG-PET | -Monitoring pharmacological effects of ezetimibe on plaque disruption and thrombosis |
| -Plaque rupture and thrombosis are associated with inflammatory response and cholesterol crystal formation | |||
| Ciesienski et al. [48] (2013) | Carotid artery thrombosis in rats | 64Cu-fibrin-binding-probe 8 (64Cu-FBP8), DOTA-labeled probes PET | -New fibrin targeting PET probes |
| -Effective detection of an arterial thrombus | |||
| Ay et al. [65] (2014) | Mural and occlusive thrombosis in rats | 64Cu-FBP7,CB-TE2A-labeled probes PET | -Thrombus detection and therapy monitoring with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) |
| -Detectable for both non-occlusive and occlusive thrombi | |||
| -Quantification of in vivo thrombolysis | |||
| Hara et al. [47] (2014) | Deep vein thrombosis in mice and humans | FDG-PET/CT | -Enabling the assessment of thrombus age and inflammation |
| -Detection of neutrophil-rich thrombus | |||
| Blasi et al. [49] (2014) | Thrombosis in rats | 64Cu-FBP8, NOTA-labeled probes PET | -Enhanced fibrin targeting PET probes |
| -Improved metabolic stability compared to DOTA derivative | |||
| -High thrombus-to-background ratio for imaging of thrombosis | |||
| Blasi et al. [50] (2015) | Multi-site thrombosis in rats | 64Cu-FBP8 PET/CT | -Whole-body thrombus detection |
| -Noninvasive evaluation of fibrin content in clots | |||
| -Finding different fibrin contents in arterial and venous clots | |||
| Kim et al. [7] (2013) | Carotid arterial thrombosis in mice | Gold nanoparticle microCT | -Direct thrombus imaging with gold nanoparticles |
| -Monitoring the therapeutic efficacy of thrombolysis in large sample numbers (n=118) | |||
| -Repeating CT imaging after up to 3 weeks without additional gold nanoparticles | |||
| Kim et al. [10] (2015) | Embolic ischemic stroke and carotid thrombosis in mice | Fibrin-targeted gold nanoparticle microCT | -Superior specificity of fibrin-targeted gold nanoparticles to thrombi compared to non-targeted gold nanoparticles |
| -Prompt detection and quantification of cerebral thrombi in vivo | |||
| -Reliability of thrombi imaging proficiency from huge sample numbers (n=107) | |||
| Grover et al. [55] (2015) | Venous thrombosis in mice | Gold nanoparticle microCT | -Longitudinal assessment of venous thrombus |
| -Extravasation of gold nanoparticles | |||
| -Reduced thrombus volume 7 days after induction |
References
1. Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016;133:e38-360.


2. Kirmani JF, Alkawi A, Panezai S, Gizzi M. Advances in thrombolytics for treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2012;79:S119-125.


3. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rtPA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581-1587.


4. Adibhatla RM, Hatcher JF. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of stroke: therapeutic strategies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2008;7:243-253.



5. Gravanis I, Tsirka SE. Tissue-type plasminogen activator as a therapeutic target in stroke. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2008;12:159-170.



6. Guerrero WR, Grotta JC. Defining intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator failure. Stroke 2013;44:819-821.


7. Kim DE, Kim JY, Sun IC, Schellingerhout D, Lee SK, Ahn CH, et al. Hyperacute direct thrombus imaging using computed tomography and gold nanoparticles. Ann Neurol 2013;73:617-625.


8. Anderson CS, Robinson T, Lindley RI, Arima H, Lavados PM, Lee TH, et al. Low-Dose versus Standard-Dose Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke. N Engl J Med 2016;374:2313-2323.


9. Jaberi A, Lum C, Stefanski P, Thornhill R, Iancu D, Petrcich W, et al. Computed tomography angiography intraluminal filling defect is predictive of internal carotid artery free-floating thrombus. Neuroradiology 2014;56:15-23.


10. Kim JY, Ryu JH, Schellingerhout D, Sun IC, Lee SK, Jeon S, et al. Direct Imaging of Cerebral Thromboemboli Using Computed Tomography and Fibrin-targeted Gold Nanoparticles. Theranostics 2015;5:1098-1114.



11. Lee DK, Nahrendorf M, Schellingerhout D, Kim DE. Will molecular optical imaging have clinically important roles in stroke management, and how? J Clin Neurol 2010;6:10-18.



12. Kim DE, Kim JY, Nahrendorf M, Lee SK, Ryu JH, Kim K, et al. Direct thrombus imaging as a means to control the variability of mouse embolic infarct models: the role of optical molecular imaging. Stroke 2011;42:3566-3573.


13. Kramer MC, Rittersma SZ, de Winter RJ, Ladich ER, Fowler DR, Liang YH, et al. Relationship of thrombus healing to underlying plaque morphology in sudden coronary death. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:122-132.


14. Young L, Ockelford P, Milne D, Rolfe-Vyson V, McKelvie S, Harper P. Post-treatment residual thrombus increases the risk of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and mortality. J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:1919-1924.


16. Ahn SG, Choi HH, Lee JH, Lee JW, Youn YJ, Yoo SY, et al. The impact of initial and residual thrombus burden on the no-reflow phenomenon in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis 2015;26:245-253.


17. Chueh JY, Kuhn AL, Puri AS, Wilson SD, Wakhloo AK, Gounis MJ. Reduction in distal emboli with proximal flow control during mechanical thrombectomy: a quantitative in vitro study. Stroke 2013;44:1396-1401.


18. Gobin YP, Starkman S, Duckwiler GR, Grobelny T, Kidwell CS, Jahan R, et al. MERCI 1: a phase 1 study of Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia. Stroke 2004;35:2848-2854.


19. Applegate RJ. Optimal therapy for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the role of residual thrombus. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1874-1876.


20. Overoye-Chan K, Koerner S, Looby RJ, Kolodziej AF, Zech SG, Deng Q, et al. EP-2104R: a fibrin-specific gadolinium-Based MRI contrast agent for detection of thrombus. J Am Chem Soc 2008;130:6025-6039.


21. Uppal R, Ay I, Dai G, Kim YR, Sorensen AG, Caravan P. Molecular MRI of intracranial thrombus in a rat ischemic stroke model. Stroke 2010;41:1271-1277.



22. Walter J, Debra AH, Asad S, Jeanine MW, Mamdouh B. An overview of hemostasis and thrombosis. Textbook of Interventional Cardiovascular Pharmacology: Chapter 1 An overview of hemostasis and thrombosis. CRC Press 2007;1:29.
23. Burke AP, Farb A, Malcom GT, Liang YH, Smialek J, Virmani R. Coronary risk factors and plaque morphology in men with coronary disease who died suddenly. N Engl J Med 1997;336:1276-1282.


24. Crouse JR, Craven TE, Hagaman AP, Bond MG. Association of coronary disease with segment-specific intimal-medial thickening of the extracranial carotid artery. Circulation 1995;92:1141-1147.


25. Virmani R, Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Farb A. Vulnerable plaque: the pathology of unstable coronary lesions. J Interv Cardiol 2002;15:439-446.


26. JM UK-I, Young V, Gillard JH. Carotid-artery imaging in the diagnosis and management of patients at risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:569-580.


27. Nighoghossian N, Derex L, Douek P. The vulnerable carotid artery plaque: current imaging methods and new perspectives. Stroke 2005;36:2764-2772.


28. Yuan C, Kerwin WS, Ferguson MS, Polissar N, Zhang S, Cai J, et al. Contrast-enhanced high resolution MRI for atherosclerotic carotid artery tissue characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002;15:62-67.


29. Glagov S, Weisenberg E, Zarins CK, Stankunavicius R, Kolettis GJ. Compensatory enlargement of human atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med 1987;316:1371-1375.


30. Flacke S, Fischer S, Scott MJ, Fuhrhop RJ, Allen JS, McLean M, et al. Novel MRI contrast agent for molecular imaging of fibrin: implications for detecting vulnerable plaques. Circulation 2001;104:1280-1285.


31. Lindner JR, Song J, Xu F, Klibanov AL, Singbartl K, Ley K, et al. Noninvasive ultrasound imaging of inflammation using microbubbles targeted to activated leukocytes. Circulation 2000;102:2745-2750.


32. Weinberger J, Azhar S, Danisi F, Hayes R, Goldman M. A new noninvasive technique for imaging atherosclerotic plaque in the aortic arch of stroke patients by transcutaneous real-time B-mode ultrasonography: an initial report. Stroke 1998;29:673-676.


33. Corti R, Osende JI, Fayad ZA, Fallon JT, Fuster V, Mizsei G, et al. In vivo noninvasive detection and age definition of arterial thrombus by MRI. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:1366-1373.


35. Song HK, Wright AC, Wolf RL, Wehrli FW. Multislice double inversion pulse sequence for efficient black-blood MRI. Magn Reson Med 2002;47:616-620.


36. Johnstone MT, Botnar RM, Perez AS, Stewart R, Quist WC, Hamilton JA, et al. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of experimental thrombosis in a rabbit model. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001;21:1556-1560.



37. Botnar RM, Perez AS, Witte S, Wiethoff AJ, Laredo J, Hamilton J, et al. In vivo molecular imaging of acute and subacute thrombosis using a fibrin-binding magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. Circulation 2004;109:2023-2029.



38. Viereck J, Ruberg FL, Qiao Y, Perez AS, Detwiller K, Johnstone M, et al. MRI of atherothrombosis associated with plaque rupture. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005;25:240-245.


39. Moody AR, Murphy RE, Morgan PS, Martel AL, Delay GS, Allder S, et al. Characterization of complicated carotid plaque with magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging in patients with cerebral ischemia. Circulation 2003;107:3047-3052.


40. Weisstanner C, Gratz PP, Schroth G, Verma RK, Kochl A, Jung S, et al. Thrombus imaging in acute stroke: correlation of thrombus length on susceptibility-weighted imaging with endovascular reperfusion success. Eur Radiol 2014;24:1735-1741.




41. von zur Muhlen C, von Elverfeldt D, Moeller JA, Choudhury RP, Paul D, Hagemeyer CE, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent targeted toward activated platelets allows in vivo detection of thrombosis and monitoring of thrombolysis. Circulation 2008;118:258-267.


42. von Elverfeldt D, Maier A, Duerschmied D, Braig M, Witsch T, Wang X, et al. Dual-contrast molecular imaging allows noninvasive characterization of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury after coronary vessel occlusion in mice by magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 2014;130:676-687.


43. Heidt T, Ehrismann S, Hövener JB, Neudorfer I, Hilgendorf I, Reisert M, et al. Molecular Imaging of Activated Platelets Allows the Detection of Pulmonary Embolism with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Sci Rep 2016;6:25044.




44. Kim DE. Principles and Methods of Molecular Imaging in Stroke. In : Caplan LR BJ, Leary MC, Lo EH, Thomas AJ, Yenari M, Zhang JH, editors. Primer on cerebrovascular diseases 2nd ed. San Diego, California, U.S.A.: Elsevier/Academic Press; in press.
45. Bunevicius A, Yuan H, Lin W. The potential roles of 18F-FDG-PET in management of acute stroke patients. Biomed Res Int 2013;2013:634598.




46. Aziz K, Berger K, Claycombe K, Huang R, Patel R, Abela GS. Noninvasive detection and localization of vulnerable plaque and arterial thrombosis with computed tomography angiography/positron emission tomography. Circulation 2008;117:2061-2070.


47. Hara T, Truelove J, Tawakol A, Wojtkiewicz GR, Hucker WJ, MacNabb MH, et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography enables the detection of recurrent same-site deep vein thrombosis by illuminating recently formed, neutrophil-rich thrombus. Circulation 2014;130:1044-1052.



48. Ciesienski KL, Yang Y, Ay I, Chonde DB, Loving GS, Rietz TA, et al. Fibrin-targeted PET probes for the detection of thrombi. Mol Pharm 2013;10:1100-1110.



49. Blasi F, Oliveira BL, Rietz TA, Rotile NJ, Day H, Looby RJ, et al. Effect of Chelate Type and Radioisotope on the Imaging Efficacy of 4 Fibrin-Specific PET Probes. J Nucl Med 2014;55:1157-1163.



50. Blasi F, Oliveira BL, Rietz TA, Rotile NJ, Naha PC, Cormode DP, et al. Multisite Thrombus Imaging and Fibrin Content Estimation With a Single Whole-Body PET Scan in Rats. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2015;35:2114-2121.



51. Jha B, Kothari M. Pearls & oy-sters: hyperdense or pseudohyperdense MCA sign: a Damocles sword? Neurology 2009;72:e116-117.


52. Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Yong WH, Starkman S, Tsang MP, Moya AL, et al. CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke 2011;42:1237-1243.



53. Aouad P, Hughes A, Valecha N, Gawarikar Y, Ahmad K, O’Neil R, et al. Prevalence, Comorbid Associations and Prognostic Value of the Hyperdense Middle Cerebral Artery Sign. ISRN Stroke 2013;2013:6.


54. Mamlouk MD, Tsai FY, Drachman D, Stradling D, Hasso AN. Cerebral thromboembolism: value of susceptibility-weighted imaging in the initial diagnosis of acute infarction. Neuroradiol J 2012;25:45-56.


55. Grover SP, Saha P, Jenkins J, Mukkavilli A, Lyons OT, Patel AS, et al. Quantification of experimental venous thrombus resolution by longitudinal nanogold-enhanced micro-computed tomography. Thromb Res 2015;136:1285-1290.



56. Kim DE, Kim JY, Lee SK, Ryu JH, Kwon IC, Ahn CH, et al. Combined near-infrared fluorescent imaging and micro-computed tomography for directly visualizing cerebral thromboemboli. J Vis Exp (in press).



57. Anderson NG, Butler AP, Scott NJ, Cook NJ, Butzer JS, Schleich N, et al. Spectroscopic (multi-energy) CT distinguishes iodine and barium contrast material in MICE. Eur Radiol 2010;20:2126-2134.


59. Xie J, Lee S, Chen X. Nanoparticle-based theranostic agents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2010;62:1064-1079.



60. Sirol M, Fuster V, Badimon JJ, Fallon JT, Moreno PR, Toussaint JF, et al. Chronic thrombus detection with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and a fibrin-targeted contrast agent. Circulation 2005;112:1594-1600.


61. Klink A, Lancelot E, Ballet S, Vucic E, Fabre JE, Gonzalez W, et al. Magnetic resonance molecular imaging of thrombosis in an arachidonic acid mouse model using an activated platelet targeted probe. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2010;30:403-410.



62. Wen AM, Wang Y, Jiang K, Hsu GC, Gao H, Lee KL, et al. Shaping bio-inspired nanotechnologies to target thrombosis for dual optical-magnetic resonance imaging. J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med 2015;3:6037-6045.



63. Gale EM, Atanasova IP, Blasi F, Ay I, Caravan P. A Manganese Alternative to Gadolinium for MRI Contrast. J Am Chem Soc 2015;137:15548-15557.



64. Patel R, Janoudi A, Vedre A, Aziz K, Tamhane U, Rubinstein J, et al. Plaque rupture and thrombosis are reduced by lowering cholesterol levels and crystallization with ezetimibe and are correlated with fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011;31:2007-2014.