 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 19(3); 2017 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background and Purpose
Many studies have evaluated the association between weather and stroke, with variable conclusions. Herein we determined the relationships between daily meteorological parameters and acute stroke incidence in South Korea.
Methods
Patients with acute stroke (2,894) were identified by standard sampling of a nationwide insurance claims database from January to December 2011. We used multiple Poisson regression analyses of stroke incidence and meteorological parameters (mean temperature, diurnal temperature change, temperature differences over the preceding 24 hours, atmospheric pressure, humidity, wind speed, and physiologically equivalent temperature) to calculate the relative risk of stroke incidence associated with meteorological parameters.
Results
There were no seasonal variations in the incidences of ischemic (2,176) or hemorrhagic (718) stroke. Temperature change during the day was positively correlated with ischemic stroke in men (relative risk [RR] 1.027; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.006-1.05) and older patients (Ōēź65 years) (RR 1.031, 95% CI 1.011-1.052). Temperature differences over the preceding 24 hours had a negative correlation with all strokes (RR 0.968, 95% CI 0.941-0.996), especially among older women. Diurnal variation of atmospheric pressure was also significantly associated with the incidence of ischemic stroke (age<65 years, RR 1.051, 95% CI 1.011-1.092; ageŌēź65 years, RR 0.966, 95% CI 0.936-0.997).
There is increasing concern regarding environmental factors such as climate change due to their health effects, especially on cerebrovascular diseases [1]. Daily meteorological changes have been reported to be associated with various stroke subtypes, although the results have been controversial [2-4]. Furthermore, previous studies have mostly focused on the relationship between mean temperature and stroke incidence [5-7]. Diurnal temperature change is an indicator related to global climate change, which is also related to cardiovascular disease-related mortality [8-10]. In addition, atmospheric pressure affects heart rate variability and eventually cardiovascular events [11]. Humidity and wind speed are also suggested to be related to vascular events, as indicated by the index of physiologically equivalent temperature (PET) [12]. However, these meteorological variables have not been thoroughly investigated for their contribution to stroke occurrence until now.
In Korea, the government has investigated these associations and developed a warning system for citizens to properly prepare for possible threats [13]. For example, the Korean Meteorological Administration has developed a stroke risk index using the National Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) database in 2004 as part of the ŌĆØdevelopment of the weather watch/warning system for health eventsŌĆØ project [13]. This predictive model was developed on the basis of daily stroke incidence data and meteorological variables over a period of eight years (1996-2003). However, stroke incidence was extracted from a hospital admission database [13]. As a result, the time intervals between stroke onset and daily meteorological factors could not be speculated. Furthermore, the inclusion of patients without stroke in cases where stroke was not a primary diagnosis renders the results difficult to interpret. Considering that about two-thirds of patients arrive at the emergency room within 6 hours after symptom onset [14], it may be more reasonable to investigate a link between daily meteorological variables and acute stroke incidence using the emergency admission database.
South Korea has four distinctive seasons and a relatively wide temporal variation in climate. Using these characteristics, we aimed to investigate the associations between daily meteorological variables and acute stroke occurrence using a nationwide insurance claims database.
We extracted eligible patients based on HIRA claims from January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2011. Our institution made an agreement with the Meteorological Administration for the development of a health forecast system in September of 2010. We merged this database of daily meteorological variables with the national health insurance claims database, which included a nationwide daily disease incidence database. Eligibility criteria were as follows: admission via the emergency department; diagnosis with standard disease codes for cerebral infarction, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, or other non-traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage (International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision I63, I60, I61, and I62, respectively) as the final primary diagnosis at the time of hospital discharge; minimum age of 18 years. The Institutional Review Board approved this research protocol with a waiver of consent due to minimal risks to the participants.
A nationwide sample of patients from the HIRA database was randomly selected from all patients based on a demographically stratified extraction method with a high extraction ratio of inpatient claims. The extraction method was demographically stratified with five-year age intervals, and the extraction ratios were 13% for inpatients and 1% for outpatients. This resulted in total samples of 700,000 inpatient and 500,000 outpatient claims. The enrollment flowchart is presented in Figure 1.
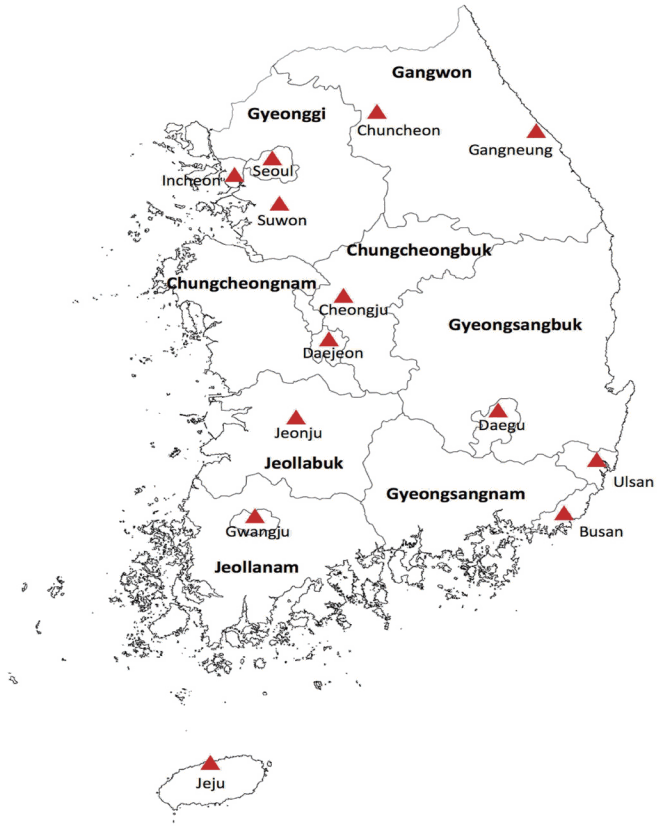
We merged the daily acute stroke incidence database from HIRA with the daily meteorological data obtained from the Meteorological Administration of South Korea. Meteorological variables, which were extracted from the climate observation regions of 13 major cities located at latitudes ranging from 33┬░ to 37┬░N (Figure 2). We calculated mean values for all meteorological variables before merging the database with the nationwide stroke incidence data due to the narrow climate range in South Korea and the small numbers of patients within each region.
The meteorological variables included daily measurements of temperature (mean, maximum, and minimum), diurnal temperature range, temperature change over the preceding 24 hours, diurnal variation Ōēź10┬░C (categorical), PET, atmospheric pressure (sea level, maximum, minimum, and diurnal variation), humidity (mean, maximum, and minimum), and wind speed (mean and maximum). The temperature change over the preceding 24 hours, diurnal variation Ōēź10┬░C (categorical), and PET were calculated using the above-mentioned variables, and PET was calculated using the following equation [15]:
The temperature change over the preceding 24 hours was a negative value when the mean temperature of the corresponding day was lower than that of the previous day. Diurnal variation was dichotomized as Ōēź10┬░C and <10┬░C [16].
Simple correlation analyses were conducted to evaluate the associations between meteorological variables and stroke incidence according to age group (<65 years vs. Ōēź65 years), sex, and stroke subtypes (ischemic stroke vs. hemorrhagic stroke) (SAS syntax, PROC CORR). We selected meteorological variables with statistical significances of P<0.20 in the simple correlation analyses between meteorological variables and stroke incidence for further multiple regression analysis. We evaluated multicollinearity among the meteorological variables able to affect acute stroke incidence prior to multiple regression analysis. We then selected the final explanatory variables based on the simple correlation analyses and the evaluation of multicollinearity. Because stroke incidence had a Poisson distribution, we used multiple Poisson regression to study stroke incidence associated with meaningful meteorological variables while adjusting for sex and age group according to stroke subtypes (SAS syntax, PROC GENMOD). Relative risks (RRs) were calculated to explain the risk of acute stroke incidence according to the change in each meteorological variable. In order to estimate monthly stroke incidence, we divided the number of acute stroke cases in the corresponding month by the total number of subjects at risk of stroke in the HIRA database, i.e., total number of subjects aged 18 years or older (1,112,831 subjects), and multiplied by 100,000 to calculate the incidence per 100,000 in our population. We present the monthly stroke incidence by stroke subtype compared to values for the month with the highest incidence (Chi-squared test). Seasonal stroke incidence was also investigated, and the seasons were classified as spring (March, April, and May), summer (June, July, and August), autumn (September, October, and November), and winter (December, January, and February). We used SAS 9.4 software (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) for statistical analyses, and the statistical significance level was set at P<0.05.
Among the 58,534,774 total insurance claims for emergency cases in HIRA, we selected 2,006,052 claims from patients diagnosed with the standard disease codes I60-I63 (Figure 1). Among these, 1,990,611 claims were from patients older than 18 years of age. A total of 605,224 of these claims were related to patients who were admitted to the hospital through the emergency department. Considering duplicate data from the same patients, 2,894 subjects were selected for the final analyses. The baseline characteristics of the enrolled subjects are described in Table 1. Ischemic stroke accounted for three-quarters of all stroke cases. Patients with ischemic stroke were older than those with hemorrhagic stroke (69.28┬▒12.55 vs. 61.31┬▒15.24, P<0.01). Ischemic stroke was prevalent among patients aged Ōēź65 years, while hemorrhagic stroke was prevalent among those aged <65 years. Sex differences were not evident in either hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke.
The monthly incidence of acute stroke is summarized in Table 2. Monthly stroke incidence was compared to that for December, as it was the month with the highest incidence. The incidences of ischemic stroke in February and November were significantly lower than that in December. We did not observe any seasonal variations in the incidence of acute stroke.
The average annual temperatures of the study period were 12.4┬░C (mean temperature), -9.8┬░C (mean minimum temperature, in January), and 29.2┬░C (mean maximum temperature, in August). The following variables were incorporated into the final model based on the results of the simple correlation analyses and evaluation of multicollinearity: diurnal temperature changes, diurnal variation of atmospheric pressure, PET, temperature differences over the previous day, and diurnal temperature change Ōēź10┬░C. Humidity and wind speed did not have any significant associations with stroke incidence in the simple correlation analyses. Table 3 shows the relative risk associated with each meteorological variable for stroke incidence according to age, sex, and stroke subtype, as determined by Poisson regression models.
Diurnal temperature changes and temperature differences over the preceding 24 hours had significant associations with the incidences of ischemic stroke and any stroke. Diurnal temperature change had a positive correlation in men. Specifically, a 1┬░C change in temperature conferred a 2.4% higher risk for acute stroke. Similarly, in those older than 65 years of age, a 1┬░C change in temperature was associated with a 2.7% higher risk of acute ischemic stroke (RR 1.027, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.008-1.047). In contrast, the temperature change over the preceding 24 hours had a negative correlation with the incidence of any stroke (RR 0.968, 95% CI 0.941-0.996). These associations were observed especially in women and the elderly older than 65 years of age. Ischemic stroke also had a similar association with temperature change over the preceding 24 hours.
Diurnal variation of atmospheric pressure was significantly associated with the incidence of ischemic stroke, and these associations were in opposite directions in the different to age groups (age<65 years, RR 1.051, 95% CI 1.011-1.092; ageŌēź65 years, RR 0.966, 95% CI 0.936-0.997).
There were no significant correlations between hemorrhagic stroke and meteorological variables. PET and temperature changes Ōēź10┬░C did not have any significant associations with the risk for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke in any of the sex or age groups.
In our study, diurnal temperature change, temperature differences over the preceding 24 hours, and diurnal variation of atmospheric pressure were associated with daily stroke incidence. Hemorrhagic stroke did not have any significant associations with meteorological factors. There was no clear seasonal variation in our study.
The association between diurnal temperature changes and stroke has not been thoroughly investigated until now. A previous study, which was conducted at a single center with 303 patients younger than 60 years, did not reveal a significant relationship between diurnal temperature changes and stroke occurrence regardless of whether continuous measures or categorical variables were used across 5┬░C changes [17]. Another study in Hong Kong showed that an increase of 1┬░C in diurnal temperature was associated with a 1.7% increase in cardiovascular mortality [18]. In a recent meta-analysis, it was suggested that few studies had investigated an association between daily temperature range and stroke incidence [7]. Similarly, there has been little research on the correlation between fluctuations in atmospheric pressure and stroke occurrence [19]. Thus, our results fill an important gap in current knowledge. We investigated various meteorological parameters, including diurnal changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure, for their associations with acute stroke. These factors had seldom been investigated before. Consequently, their importance was stressed in a recent meta-analysis [7].
The exact mechanism for the associations between diurnal changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure and stroke are still unknown. However, these associations can be estimated based on studies of other diseases, such as myocardial infarction and respiratory infection [20,21]. Sudden temperature changes can cause hemodynamic changes and change cardiovascular workload in elderly individuals who have a decreased ability to sweat and poor ability to maintain in vivo homeostasis [20]. This triggers a series of pathological processes [18]. Furthermore, it can be assumed that individuals with low income levels are more likely to be exposed to temperature variability due to poor accessibility to appropriate temperature-controlled facilities [22]. In addition, sudden changes in temperature may alter immune function and release of inflammatory mediators and lead to respiratory infection [23]. These infections are reported to be related to the occurrence of acute stroke [24,25].
It has been suggested that changes in atmospheric pressure may lead to plaque ruptures [19]. It is not yet established whether atmospheric pressure can affect other stroke mechanisms, such as embolism formation. These environmental stresses may strain the cerebral vascular system and affect stroke mortality [8].
Our results regarding diurnal temperature changes and temperature changes over the preceding 24 hours seem to be contradictory, as the former had a positive correlation with stroke incidence while the latter had a negative association. Diurnal temperature changes are measured as absolute values and have clear implications. However, temperature changes over the preceding 24 hours can have both positive and negative values, and their interpretation may be more complex. When this measure has a negative value, its interpretation is consistent with that of diurnal temperature changes. To illustrate these associations, we computed the relative risk of acute stroke for temperature changes over the preceding 24 hours of -2┬░C vs. -1┬░C. Since the temperature changes over the preceding 24 hours were negative values, the temperature had dropped compared to the previous day. A temperature change over the preceding 24 hours of -1┬░C indicates a decrement of 1┬░C, but less than -2┬░C. We found that a 1┬░C decrement in temperature over the preceding 24 hours leads to a decrease in the relative risk of acute stroke of 3.2%. However, if the result has a positive value, the correlation is in the opposite direction. The risk of stroke was lower when the mean temperature of the corresponding day was higher than that of the previous day. This result seems to be contrary to the above-mentioned relationship between diurnal temperature changes and stroke risk. Temperature change over the preceding 24 hours is a measure used to compare the mean values of two consecutive days, and has a wider time range than the diurnal temperature change. In other words, we may consider that the body has a longer time to adapt to the temperature change and to avoid its adverse effects when compared to diurnal temperature changes. However, these explanations have not been proven and should be verified in subsequent studies.
Many studies are dichotomized and divide patients into age groups at 65 years of age [9,26,27]. These studies showed that the elderly had more deleterious cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease-related responses to cold exposure than younger subjects [9,27]. Previous studies have shown that elderly, female, and less-educated subjects were more vulnerable to the mortality associated with diurnal temperature changes [10,22]. Some studies have suggested that slower reactions to the temperature changes make these groups more vulnerable to adverse biologic effects [7]. Some research suggests a possible role for estrogen in this vulnerability. Estrogen might lead to the vasoconstriction of intracerebral arteries via stimulation of the adrenergic alpha 2C-receptor [28,29]. Higher thresholds for sweating and poor regulation of body temperature are additional possible explanations for the vulnerability of the elderly [30].
In our study, there was no seasonal variation in acute stroke incidence for either ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes. Similarly, in a large community-based study of first-ever lifetime stroke with about 105,000 subjects, there was no significant seasonal variation over 4 years [31]. There might be various explanations for this observation, including improved social safety systems used by disadvantaged groups to cope with hot and cold seasons, climate changes, and differences in study settings, such as altitude.
Similar studies on the seasonal and monthly variations of stroke incidence have been conducted in Korea [5]. For example, a single hospital-based study in a restricted area of Seoul assessed the seasonal and monthly variations of stroke incidence over a 10-year study period. Our study is distinctive from the above study, as we focused on patients who were admitted via emergency departments so as to be conservative regarding the diagnosis of acute stroke [21,32]. As a result, seasonal variation was not evident in our study, which had a more conservative diagnosis and used a nationwide database.
In our study, we used national health insurance claims data from HIRA. The HIRA-National Patients Sample in South Korea is different from the National Inpatient Sample in the United States of America or the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. The sampling method of the HIRA database is patient-based and is similar to the National Health Insurance Research Database, although the demographically stratified sampling of HIRA in South Korea is different from the random sampling of the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. The National Inpatient Sample in the USA is hospital-based and is influenced by the characteristics and location of each hospital. A strong point of the HIRA-National Patients Sample claims database is the efficiency of data usage considering the ratio of inpatients and outpatients and their variances. However, this database does not incorporate nonpayment items and is relatively lacking in detailed data that may be used to adjust for various confounding factors.
Our study included patients with acute stroke who were admitted via the emergency department to distinguish them from patients without stroke. This conservative method is in line with those of previous studies [21,26]. According to a recent statistical report, about 60% of patients with acute stroke arrive at the emergency room within 6 hours after symptom onset in Korea [14]. Based on these statistics, we focused on analyzing the associations between daily meteorological factors and more immediate stroke incidence using the emergency admissions database.
Several limitations of our study should be considered. First, since we used the HIRA database, we were unable to access data regarding all vascular risk factors of individual subjects due to technical problems and reliability issues with the extraction of these variables from a national health insurance claims database. Further investigations should be carried out to determine how vascular risk factors mediate changes in the effects of daily meteorological factors and emergency stroke admission. In addition, there might be other confounding factors, such as viral infection and aggravation of underlying diseases in winter, air pollution, and indoor circumstances and activities. In fact, a previous study indicates that poverty, inequality, and deprivation might be effect modifiers of high winter mortality [33]. Institutionalization in nursing homes might also affect the associations between meteorological factors and stroke occurrence. Second, we averaged all meteorological variables across the nation. The total land area of South Korea is approximately 100,032 km2 and is less than the areas of most of the states in the USA. Thus, we averaged all meteorological variables and stroke occurrence data across the nation. However, for this reason, more detailed associations could not be investigated in this analysis. Third, we did not consider the time lag between meteorological factors and stroke occurrence. We aimed to investigate the relatively immediate effects of daily meteorological factors on the occurrence of stroke, and evaluated emergency room records against meteorological factors from the same day. Fourth, our nation consists of mostly a single ethnicity, so our results should be interpreted with caution before generalization. Lastly, we conducted our analysis using a one-year representative database. It is thus not appropriate to show extrapolate the observed trends to other time periods.
In conclusion, our study reveals correlations between daily meteorological variables and acute stroke incidence using a national healthcare claims data. Diurnal temperature changes, temperature changes over the preceding 24 hours, and diurnal variation of atmospheric pressure were important meteorological factors associated with stroke occurrence. These associations were more prominent in patients aged over 65 years. Our results emphasize the necessity of the development and application of more precise weather watch/warning systems for health events to benefit vulnerable elderly subjects in coping with sudden environmental changes associated with recent climate change patterns. Further investigation of the pathophysiological link between diurnal variations of temperature and atmospheric pressure and stroke occurrence is also required.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant of 2014 Myung-In academic award from Korean Neurological Association.
Figure┬Ā1.
Flow chart describing study subject selection. HIRA, Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service; ER, emergency room.

Table┬Ā1.
Baseline characteristics of study subjects
Table┬Ā2.
Monthly incidence of acute stroke
| Acute stroke (n) | Per 100,000 persons | P* | Hemorrhagic stroke (n) | Per 100,000 persons | P* | Ischemic stroke (n) | Per 100,000 persons | P* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly incidence of acute stroke | |||||||||
| ŌĆāJanuary | 225 | 20.2 | 0.11 | 61 | 5.5 | 0.86 | 164 | 14.7 | 0.08 |
| ŌĆāFebruary | 205 | 18.4 | 0.01 | 47 | 4.2 | 0.13 | 158 | 14.2 | 0.04 |
| ŌĆāMarch | 223 | 20.0 | 0.09 | 43 | 3.9 | 0.051 | 180 | 16.2 | 0.38 |
| ŌĆāApril | 240 | 21.6 | 0.37 | 57 | 5.1 | 0.58 | 183 | 16.4 | 0.47 |
| ŌĆāMay | 239 | 21.5 | 0.35 | 59 | 5.3 | 0.72 | 180 | 16.2 | 0.38 |
| ŌĆāJune | 222 | 19.9 | 0.08 | 61 | 5.5 | 0.86 | 161 | 14.5 | 0.06 |
| ŌĆāJuly | 242 | 21.7 | 0.42 | 57 | 5.1 | 0.58 | 185 | 16.6 | 0.54 |
| ŌĆāAugust | 242 | 21.7 | 0.42 | 61 | 5.5 | 0.86 | 181 | 16.3 | 0.41 |
| ŌĆāSeptember | 229 | 20.6 | 0.16 | 58 | 5.2 | 0.65 | 171 | 15.4 | 0.18 |
| ŌĆāOctober | 227 | 20.4 | 0.13 | 55 | 4.9 | 0.46 | 172 | 15.5 | 0.19 |
| ŌĆāNovember | 214 | 19.2 | 0.03 | 57 | 5.1 | 0.58 | 157 | 14.1 | 0.03 |
| ŌĆāDecember | 260 | 23.4 | Ref | 63 | 5.7 | Ref | 197 | 17.7 | Ref |
| Seasonal incidence of acute stroke | |||||||||
| ŌĆāSpring | 702 | 63.1 | 0.75 | 159 | 14.3 | 0.51 | 543 | 48.8 | 0.46 |
| ŌĆāSummer | 706 | 63.3 | 0.67 | 179 | 16.1 | 0.67 | 527 | 47.4 | 0.80 |
| ŌĆāAutumn | 670 | 60.2 | 0.59 | 170 | 15.2 | 0.96 | 500 | 45.0 | 0.55 |
| ŌĆāWinter | 690 | 62.0 | Ref | 171 | 15.4 | Ref | 519 | 46.6 | Ref |
Table┬Ā3.
Relative risks for acute stroke according to age and sex
|
Meteorological variables |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diurnal temperature change (╦ÜC) (95% CI) | Diurnal variation of atmospheric pressure (hPa) (95% CI) | PET (╦ÜC) (95% CI) | Temperature Change over preceding 24 h (╦ÜC) (95% CI) | Diurnal temperature change Ōēź10╦ÜC (95% CI) | |||
| AS | 1.017 (0.991-1.044) | 0.984 (0.960-1.009) | 1.001 (0.996-1.006) | 0.968* (0.941-0.996) | 1.017 (0.991-1.044) | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 1.024* (1.004-1.045) | 0.990 (0.960-1.021) | 1.002 (0.995-1.008) | 0.972 (0.939-1.007) | -ŌĆĀ | ||
| Female | 1.022 (0.990-1.054) | 0.983 (0.954-1.012) | 1.000 (0.994-1.006) | 0.956* (0.924-0.990) | 1.022 (0.990-1.054) | ||
| Age (years) | |||||||
| <65 | 0.995 (0.960-1.031) | 1.003 (0.971-1.036) | 1.003 (0.996-1.011) | 0.996 (0.958-1.035) | 0.995 (0.960-1.031) | ||
| Ōēź65 | 1.027* (1.008-1.047) | 0.973 (0.944-1.002) | 0.997 (0.991-1.003) | 0.953* (0.921-0.985) | - | ||
| HS | 0.994 (0.951-1.038) | 0.988 (0.950-1.028) | 1.002 (0.994-1.011) | 0.982 (0.936-1.030) | 0.994 (0.951-1.038) | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 1.012 (0.953-1.075) | 0.986 (0.935-1.039) | 0.999 (0.987-1.011) | 0.968 (0.909-1.031) | 1.012 (0.953-1.075) | ||
| Female | 1.003 (0.941-1.069) | 0.991 (0.935-1.051) | 1.005 (0.993-1.018) | 1.011 (0.939-1.089) | 1.003 (0.941-1.069) | ||
| Age (years) | |||||||
| <65 | 1.000 (0.943-1.061) | 0.998 (0.947-1.052) | 1.001 (0.989-1.013) | 0.996 (0.934-1.063) | 1.000 (0.943-1.061) | ||
| Ōēź65 | 0.982 (0.917-1.052) | 0.985 (0.929-1.045) | 1.001 (0.988-1.013) | 0.9837 (0.916-1.056) | 0.982 (0.917-1.052) | ||
| IS | 1.026 (0.997-1.056) | 0.978 (0.952-1.005) | 1.000 (0.995-1.006) | 0.960* (0.931-0.990) | 1.026 (0.997-1.056) | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 1.027* (1.006-1.050) | 0.987 (0.955-1.021) | 1.003 (0.996-1.010) | 0.971 (0.936-1.009) | - | ||
| Female | 1.016 (0.980-1.053) | 0.978 (0.945-1.011) | 0.999 (0.992-1.006) | 0.944* (0.907-0.981) | 1.016 (0.980-1.053) | ||
| Age (years) | |||||||
| <65 | 1.002 (0.958-1.048) | 1.051* (1.011-1.092) | 1.000 (0.991-1.009) | 0.987 (0.743-1.312) | - | ||
| Ōēź65 | 1.031* (1.011-1.052) | 0.966* (0.936-0.997) | 0.999 (0.992-1.005) | 0.949* (0.916-0.983) | - | ||
References
1. Shah AS, Lee KK, McAllister DA, Hunter A, Nair H, Whiteley W, et al. Short term exposure to air pollution and stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2015;350:h1295.



2. Ogata T, Kimura K, Minematsu K, Kazui S, Yamaguchi T; Japan Multicenter Stroke InvestigatorsŌĆÖ Collaboration. Variation in ischemic stroke frequency in Japan by season and by other variables. J Neurol Sci 2004;225:85-89.


3. Wang Y, Levi CR, Attia JR, DŌĆÖEste CA, Spratt N, Fisher J. Seasonal variation in stroke in the Hunter Region, Australia: a 5-year hospital-based study, 1995-2000. Stroke 2003;34:1144-1150.


4. Oberg AL, Ferguson JA, McIntyre LM, Horner RD. Incidence of stroke and season of the year: evidence of an association. Am J Epidemiol 2000;152:558-564.



5. Han MH, Yi HJ, Kim YS, Kim YS. Effect of seasonal and monthly variation in weather and air pollution factors on stroke incidence in Seoul, Korea. Stroke 2015;46:927-935.


6. Dawson J, Weir C, Wright F, Bryden C, Aslanyan S, Lees K, et al. Associations between meteorological variables and acute stroke hospital admissions in the west of Scotland. Acta Neurol Scand 2008;117:85-89.


7. Lian H, Ruan Y, Liang R, Liu X, Fan Z. Short-term effect of ambient temperature and the risk of stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2015;12:9068-9088.



8. Chen G, Zhang Y, Song G, Jiang L, Zhao N, Chen B, et al. Is diurnal temperature range a risk factor for acute stroke death? Int J Cardiol 2007;116:408-409.


9. Tam WW, Wong TW, Chair SY, Wong AH. Diurnal temperature range and daily cardiovascular mortalities among the elderly in Hong Kong. Arch Environ Occup Health 2009;64:202-206.


10. Yang J, Liu HZ, Ou CQ, Lin GZ, Zhou Q, Shen GC, et al. Global climate change: impact of diurnal temperature range on mortality in Guangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 2013;175:131-136.


11. Delyukov A, Gorgo Y, Corn├®lissen G, Otsuka K, Halberg F. Natural environmental associations in a 50-day human electrocardiogram. Int J Biometeorol 2001;45:90-99.


12. Ferrari J, Shiue I, Seyfang L, Matzarakis A, Lang W; Austrian Stroke Registry Collaborators. Weather as physiologically equivalent was not associated with ischemic stroke onsets in Vienna, 2004-2010. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2015;22:8756-8762.


13. Kim J, Ha JS, Jun S, Park TS, Kim H. The weather watch/warning system for stroke and asthma in South Korea. Int J Environ Health Res 2008;18:117-127.


14. Hong KS, Bang OY, Kim JS, Heo JH, Yu KH, Bae HJ, et al. Stroke statistics in Korea: part II stroke awareness and acute stroke care, a report from the Korean Stroke Society and Clinical Research Center for stroke. J Stroke 2013;15:67-77.



15. H├Čppe P. The physiological equivalent temperature - a universal index for the biometeorological assessment of the thermal environment. Int J Biometeorol 1999;43:71-75.


16. Shaposhnikov D, Revich B, Gurfinkel Y, Naumova E. The influence of meteorological and geomagnetic factors on acute myocardial infarction and brain stroke in Moscow, Russia. Int J Biometeorol 2014;58:799-808.


17. Kyobutungi C, Grau A, Stieglbauer G, Becher H. Absolute temperature, temperature changes and stroke risk: a case-crossover study. Eur J Epidemiol 2005;20:693-698.


18. Xu Z, Huang C, Turner LR, Su H, Qiao Z, Tong S. Is diurnal temperature range a risk factor for childhood diarrhea? PLoS One 2013;8:e64713.



19. Houck PD, Lethen JE, Riggs MW, Gantt DS, Dehmer GJ. Relation of atmospheric pressure changes and the occurrences of acute myocardial infarction and stroke. Am J Cardiol 2005;96:45-51.


20. Cao J, Cheng Y, Zhao N, Song W, Jiang C, Chen R, et al. Diurnal temperature range is a risk factor for coronary heart disease death. J Epidemiol 2009;19:328-332.



21. Ge WZ, Xu F, Zhao ZH, Zhao JZ, Kan HD. Association between diurnal temperature range and respiratory tract infections. Biomed Environ Sci 2013;26:222-225.

22. Lim YH, Park AK, Kim H. Modifiers of diurnal temperature range and mortality association in six Korean cities. Int J Biometeorol 2012;56:33-42.


24. Grau AJ, Buggle F, Heindl S, Steichen-Wiehn C, Banerjee T, Maiwald M, et al. Recent infection as a risk factor for cerebrovascular ischemia. Stroke 1995;26:373-379.


25. Grau AJ, Buggle F, Becher H, Zimmermann E, Spiel M, Fent T, et al. Recent bacterial and viral infection is a risk factor for cerebrovascular ischemia: clinical and biochemical studies. Neurology 1998;50:196-203.


26. Wang XY, Barnett AG, Hu W, Tong S. Temperature variation and emergency hospital admissions for stroke in Brisbane, Australia, 1996-2005. Int J Biometeorol 2009;53:535-541.



27. Analitis A, Katsouyanni K, Biggeri A, Baccini M, Forsberg B, Bisanti L, et al. Effects of cold weather on mortality: results from 15 European cities within the PHEWE project. Am J Epidemiol 2008;168:1397-1408.



28. Sato F, Matsushita S, Hyodo K, Akishima S, Imazuru T, Tokunaga C, et al. Sex difference in peripheral arterial response to cold exposure. Circ J 2008;72:1367-1372.


29. Eid AH, Maiti K, Mitra S, Chotani MA, Flavahan S, Bailey SR, et al. Estrogen increases smooth muscle expression of alpha2C-adrenoceptors and cold-induced constriction of cutaneous arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007;293:H1955-H1961.


31. Rothwell PM, Wroe SJ, Slattery J, Warlow CP. Is stroke incidence related to season or temperature? The Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. Lancet 1996;347:934-936.