 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 21(1); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background and Purpose
Although arbitrary blood pressure (BP) thresholds exist for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients eligible for intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), current international recommendations lack clarity on the impact of mean pre- and post-IVT BP levels on clinical outcomes.
Methods
Eligible studies involving IVT-treated AIS patients were identified that reported the association of mean systolic BP (SBP) or diastolic BP levels before and after IVT with the following outcomes: 3-month favorable functional outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] scores of 0-1) and 3-month functional independence (mRS scores of 0-2), 3-month mortality and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). Unadjusted analyses of standardized mean differences and adjusted analyses of studies reporting odds ratios (ORadj) per 10 mm Hg BP increment were performed using random-effects models.
Results
We identified 26 studies comprising 56,513 patients. Higher pre- (P=0.02) and posttreatment (P=0.006) SBP levels were observed in patients with sICH. Patients with 3-month functional independence had lower post-treatment (P<0.001) SBP whereas trended towards lower pre-treatment (P=0.06) SBP. In adjusted analyses, elevated pre- (ORadj, 1.08; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.16) and post-treatment (ORadj, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.25) SBP levels were associated with increased likelihood of sICH. Increasing pre- (ORadj, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.84 to 0.98) and post-treatment (ORadj, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.57 to 0.87) SBP values were also related to lower odds of 3-month functional independence.
Intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) is the only approved systemic reperfusion therapy for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients [1], and confers a number needed to treat of eight to improve functional outcome in one additional AIS [2]. The beneficial effect of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) may be hampered in AIS patients with elevated acute blood pressure (BP) levels [3]. Current American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA) guidelines recommend strict, though arbitrary, thresholds of systolic BP (SBP) >185 mm Hg and diastolic BP (DBP) >110 mm Hg before tPA-bolus, as well as during and within 24 hours after alteplase infusion (SBP >180 mm Hg and DBP >105 mm Hg) [4]. Observational data indicate that BP protocol violations increase the risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) [5,6], while elevated acute BP levels may reduce the odds of tPA-induced recanalization [7] and the likelihood of functional independence [8]. On the other hand, it may be argued that IVT may be delayed or even denied in AIS patients with extremely elevated BP levels due to these stringent BP thresholds [3]. In addition, aggressive BP reduction during the first hours of acute cerebral ischemia may reduce viable penumbral tissue and result in expansion of the infarction and further neurological deterioration [9,10]. Finally, in the absence of randomized data, clear consensus is lacking for the optimal BP control before, during and after tPA infusion in AIS patients treated with IVT. In view of the former considerations, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis that sought to evaluate the impact of elevated acute BP levels before and after systemic thrombolysis on different clinical outcomes in AIS patients.
Authors declare that all supporting data are available within the article and its online supplementary files. We adopted the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for systematic reviews and metaanalyses [11]. The present manuscript also adheres to the AHA Journals’ implementation of the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) guidelines [12]. The study design (systematic review and meta-analysis) was exempt for approval from the Institutional Review Board of our institution (Universities of Tennessee & West Virginia-Charleston Division).
Eligible studies that reported association of mean BP levels and clinical outcomes in AIS patients treated with IVT were identified by systematically searching in Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid Embase, and Scopus databases. The combination of search strings used to query all the databases included: “blood pressure,” “systolic,” “diastolic,” “stroke,” and “cerebral ischemia”. The complete search algorithm used in MEDLINE is available in the online supplement. We restricted our search to articles in English language, and our search spanned from database inception to February 24, 2018. Additional manual search of conference abstracts and bibliographies of articles meeting study criteria for a comprehensive literature search was conducted.
We identified studies that investigated the association of acute BP levels with clinical outcomes in AIS patients treated with IVT. We documented mean SBP and DBP levels reported as mean±SD during pre- and post-IVT intervals. For studies that did not report mean BP levels before tPA bolus, admission BP levels were used for descriptive analyses. During the postthrombolysis interval, we recorded mean BP levels documented within 2 to 4 hours following tPA infusion. If this data was unavailable, mean BP levels within 24 to 72 hours of IVT administration were used. Additional data on BP variability (BPV) including successive variation (SV) was collected if available from the included studies. In case of missing data, the authors of relevant studies were contacted and previously unpublished data was occasionally provided according to their discretion. We excluded studies that reported (1) outcomes not reported as per our inclusion criteria such as parenchymal hematoma or asymptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, (2) treatment with intra-arterial thrombolysis, mechanical thrombectomy, or systemic thrombolysis using agents other than alteplase, (3) descriptive data for BP levels reported as median values, (4) studies reporting mean arterial pressure levels instead of SBP or DBP levels, and (5) case reports.
We evaluated the following clinical outcomes: 3-month favorable functional outcome (defined as modified Rankin Scale [mRS] scores 0-1), 3-month functional independence (defined as mRS-scores of 0-2), 3-month mortality, sICH according to the definitions of included studies (Supplementary Table 1) and tPA-induced recanalization (in AIS patients with proximal intracranial occlusions) according to the definitions of included studies. Two authors (K.M. and A.F.) independently reviewed all the retrieved articles. In case of disagreements regarding the literature search results, the senior author (G.T.) was consulted to formulate a mutual consensus. The following information was extracted: name of study, first author and year of publication, mean age, sex distribution, total number of study participants, and clinical outcomes.
We used the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale to explore sources of bias amongst the included observational studies as previously described [13]. This scale uses multiple-choice questions to address the areas of selection, comparability, and exposure/outcome assessment. High quality ratings are identified with a star and studies can earn a maximum of nine star-points. A maximum of one star can be awarded for each item within the selection and exposure/outcome categories and maximum of two stars for the comparability category. The quality control and bias identification were performed independently by two reviewers (K.M. and A.F.), and disagreements if any, were resolved by a third tie-breaking evaluator (G.T.).
In both unadjusted and adjusted for potential confounders analyses both pre-treatment and post-treatment SBP/DBP values were handled as continuous variables, while the outcomes of interest were handled as dichotomous variables. Differences in mean pre-treatment and post-treatment BP values according to the outcomes of interest were reported in the form of standardized mean differences (SMDs) in all unadjusted analyses. We also conducted adjusted (for potential confounders) analyses evaluating the association of pre- and post-IVT BP levels with different clinical outcomes. The adjusted odds ratios (ORsadj) of these associations are all presented per 10 mm Hg increments in SBP or DBP levels.
SMD estimates were calculated as the mean differences divided by the corresponding pooled standard deviations, to expresses the size of the intervention effect in each study relative to the variability observed in that study [14]. In all analyses SMDs and ORs of individual studies were pooled using the random-effects model (DerSimonian Laird) [15]. We used inverse variance method to calculate SMD for continuous variables. SMD were interpreted using a general rule of thumb reported by Cohen [16], in which an SMD of 0.2 represents a small effect, an SMD of 0.5 represents a medium effect, and an SMD of 0.8 or larger represents a large effect. All available ORadj on the association of SBP and DBP increments with the respective outcomes of interest were rescaled to 10 mm Hg BP increments by raising the corresponding ORadj to the appropriate power [17], in studies not providing ORadj for the 10 mm Hg scale. After the overall analyses using the DerSimonian Laird method we performed additional sensitivity analyses for all outcomes of interest using the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method [18]. We also performed meta-regression analyses, with the use of the random-effects model, to explore heterogeneity and further evaluate the potential association between the unadjusted outcome provided by the majority of included studies and the dichotomous and normally distributed patients’ baseline characteristics.
As per the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [19], we assessed for heterogeneity using Cochran Q and I2 statistics. For the qualitative interpretation of heterogeneity, I2 >50% and I2 >75% indicated substantial and considerable heterogeneity, respectively. Publication bias across individual studies was graphically evaluated using a funnel plot [19], while funnel plot asymmetry was assessed using the Egger’s linear regression test with P<0.10 significance level. For all other outcomes of interest we performed equivalent z test for each pooled estimate, and a two-tailed P levels <0.05 was considered statistically significant. In case of funnel plot asymmetry we performed relevant adjustment for potential publication bias using the Duval-Tweedie “trim and fill” approach [20].
All statistical analyses were carried out with Cochrane Collaboration’s Review Manager Software Package (RevMan 5.3), OpenMetaAnalyst21 and the Comprehensive Meta-analysis version 2 software (Biostat, Englewood, NJ, USA; https://www.meta-analysis.com).
Systematic search of all the databases yielded 769 articles. After removing the duplicates, the titles and abstracts from the remaining 669 studies were screened and 33 potentially eligible studies for the meta-analysis were retained. After retrieving the full-text version of the aforementioned 33 studies, seven studies were excluded due to lack of clinical outcome reporting, articles in language other than English language or use of thrombolysis other than alteplase (Supplementary Table 2). After careful evaluation and without disagreements amongst the two reviewers, 26 studies [6-8,22-44] were included that met the study protocol’s inclusion criteria. The detailed flow chart of the current meta-analysis is presented in Supplementary Figure 1.
The included 26 studies comprising 56,513 patients are summarized in Table 1. Three studies were post hoc analysis of randomized-controlled clinical trials including 1,443 AIS patients, while we also evaluated 23 observational studies (eight prospective and 15 retrospective) with 55,070 AIS patients. The baseline characteristics of the included patients are presented in Supplementary Table 3. Three authors of included studies responded to our request to provide previously unpublished data [7,22,34]. Eight studies reported their adjusted analyses using 10-mm Hg increments in SBP or DBP [6,24,26,30,32,37,39,44]; three studies used 1-mm Hg increments [7,34,35], whereas the remaining studies failed to report the exact BP increments in their adjusted analyses (Supplementary Table 4). Five studies were conducted in China, three in Finland, two in Japan, one each in Germany, Norway, Portugal, Italy, Spain, United States, whereas the remaining were multicenter, international studies.
We assessed the risk of bias amongst the included studies using Newcastle-Ottawa scale (Supplementary Table 5). The risk of selection and comparability bias was considered low in all the studies. Outcome bias was counted as moderate as majority of the studies did not report the data on patients lost to follow-up or outcome assessment. The overall score of Newcastle-Ottawa scale was 214/234 (91.4%), which is considered to represent an overall high quality.
We inspected funnel plot symmetry and Egger’s statistical test for outcomes involving ≥10 studies [19]. On inspection of funnel plots, no evidence of asymmetry was observed in studies reporting pre-treatment BP parameters, either unadjusted for 3-month functional independence (Supplementary Figure 2), or adjusted 3-month functional independence (Supplementary Figure 3). Similarly, we did not observe publication bias among studies reporting pre-treatment BP parameters, either unadjusted for 3-month functional independence (Egger’s test P=0.70), or adjusted for 3-month favorable functional outcome (P=0.11) and 3-month functional independence (P=0.35). However, both graphical inspection and the Egger’s test (P=0.030) uncovered the asymmetry of the funnel plot of studies reporting adjusted associations of pre-treatment SBP with 3-month favorable functional outcome (Supplementary Figure 4).
Tables 2 and 3 present an overview on the overall unadjusted and adjusted analyses investigating the association of BP levels with various clinical outcomes.
Lower post-treatment SBP levels were observed in patients with 3-month favorable functional outcome (Supplementary Figure 5A), while the two groups did not differ in terms of DBP levels (Supplementary Figure 5B). Pre-treatment SBP (Supplementary Figure 6A) and DBP (Supplementary Figure 6B) did not differ between patients with and without 3-month favorable functional outcome. Patients with 3-month functional independence demonstrated a lower trend towards pre-IVT SBP levels (Supplementary Figure 7A), whereas had a significantly lower SBP levels after alteplase infusion (Supplementary Figure 7B). No difference in mean pre-treatment (Supplementary Figure 8A) and post-treatment (Supplementary Figure 8B) DBP levels was noted in patients with and without 3-month functional independence.
Higher pre-treatment (Supplementary Figure 9A) and posttreatment SBP levels (Supplementary Figure 9B) were observed in patients with sICH. No difference was documented in both pre-treatment (Supplementary Figure 10A) and post-treatment (Supplementary Figure 10B) DBP levels in patients with and without sICH. No difference in mean pre-treatment SBP (Supplementary Figure 11A) and DBP levels were noted in patients who were dead or alive at 3 months (Supplementary Figure 11B). No data was available to compare post-treatment BP levels and mortality.
Lower mean pre-treatment SBP levels were recorded in AIS patients with proximal intracranial occlusion who achieved tPA-induced recanalization (Supplementary Figure 12A), whereas no difference was observed for pre-treatment DBP levels (Supplementary Figure 12B). No data was available to evaluate the association of post-treatment BP levels with arterial recanalization.
We conducted additional analyses to assess the available associations of BPV quantified by SV in BP levels with various clinical outcomes. Elevated post-treatment SV-SBP levels were observed in patients with sICH (two studies: SMD, 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.35 to 1.30; P=0.0007; P for Cochran Q statistic=0.26; I2=20%) (Supplementary Figure 13). No additional data was available to evaluate the difference in mean pre- and post-treatment SV-BP levels with other clinical outcomes.
After adjusting for potential confounders, we evaluated the associations of mean BP levels before and after tPA infusion with various outcomes.
Increasing mean pre-treatment SBP levels were independently associated with reduced odds of 3-month favorable functional outcome (ORadj, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.87 to 0.95) (Figure 1A) and 3-month functional independence (ORadj, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.84 to 0.98) (Figure 1B). Due to the emerging funnel plot asymmetry for the outcome of 3-month favorable functional outcome we performed additional analysis to account for the possibility of publication bias and after imputing two missing studies with the trim and fill method (ORadj, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.84 to 1.03) (Supplementary Figure 14). Also, higher pre-treatment SBP levels independently increased the likelihood of sICH (ORadj, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.16) (Figure 1C). No associations were noted between mean pre-treatment SBP levels and 3-month mortality (P=0.14) (Figure 1D) and arterial recanalization (P=0.28) (Supplementary Figure 15). Similarly, no associations were observed between mean pre-treatment DBP levels and 3-month favorable functional outcome (P=0.95) (Supplementary Figure 16), 3-month functional independence (P=0.23) (Supplementary Figure 17), sICH (P=0.95) (Supplementary Figure 18), 3-month mortality (P=0.28) (Supplementary Figure 19), and arterial recanalization (P=0.70) (Supplementary Figure 20).
Higher mean post-treatment SBP levels were independently associated with reduced odds of 3-month favorable functional outcome (ORadj, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.78 to 0.88) (Figure 2A) and 3-month functional independence (ORadj, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.57 to 0.87) (Figure 2B). Increasing mean post-treatment SBP were independently related to higher likelihood of sICH (ORadj, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.25) (Figure 2C). No association was noted between mean post-treatment SBP levels and 3-month mortality (P=0.07) (Figure 2D). Similarly, no associations were observed between mean post-treatment DBP levels and 3-month favorable functional outcome (P=0.68) (Supplementary Figure 21), 3-month functional independence (P=0.21) (Supplementary Figure 22), sICH (P=0.38) (Supplementary Figure 23), and 3-month mortality (P=0.57) (Supplementary Figure 24).
Additionally, higher mean post-treatment SV-SBP levels were independently associated with reduced odds of 3-month favorable functional outcome (ORadj, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.27 to 0.91) (Supplementary Figure 25) and increased likelihood of 3-month mortality (ORadj, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.25 to 2.77) (Supplementary Figure 26). Increasing mean post-treatment SV-SBP levels tended to be associated with increased risk of sICH (P=0.06) (Supplementary Figure 27). Similarly, higher mean post-treatment SV-DBP levels were independently related to higher odds of 3-month mortality (P=0.003) (Supplementary Figure 28) and sICH (P=0.004) (Supplementary Figure 29). Finally, no association was detected between SV-DBP and favorable functional outcome (P=0.39) (Supplementary Figure 30).
In the sensitivity analyses using the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method we found no significant disparities with the DerSimonian Laird method for the vast majority of associations, except for the unadjusted associations of post-treatment SBP with sICH and 3-month functional independence, which were found to be marginally non-significant after introducing the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method (Supplementary Tables 6 and 7).
In the meta-regression analyses only the prevalence of diabetes was found to be inversely related to the likelihood of 3-month functional independence (coefficient, -0.013; 95% CI, -0.024 to -0.003; P=0.014) (Supplementary Table 8).
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association between acute BP levels and clinical outcomes of AIS patients treated with IVT. Among 56,513 tPA-treated AIS patients, increasing mean BP levels before and after tPA infusion reduced the likelihood of 3-month favorable functional outcome as well as 3-month functional independence. This association persisted in our subgroup and adjusted analyses. Although associations between increasing BP values and higher odds of functional dependence and sICH risk were documented in unadjusted and adjusted for potential confounders analyses (Tables 2 and 3), they were succinctly greater for functional outcomes, possibly reflecting that the association of elevated BP with worse functional outcome is not solely explained by the increase in sICH risk. The association of increasing pretreatment BP levels with lower odds of recanalization in large vessel occlusion patients treated with IVT and endovascular reperfusion therapies may represent another potential mechanism that may account for the relationship of increasing BP levels with worse functional outcomes in AIS patients treated with systemic thrombolysis [7,45]. This hypothesis is also supported by the findings of the present meta-analysis, since AIS patients with tPA-induced successful recanalization had lower pre-treatment SBP levels compared to patients with persisting occlusion. The inverse relationship between increased pretreatment SBP levels and vessel patency might be attributed to the potential association of elevated pretreatment SBP with both increased baseline thrombus burden and impaired endogenous capacity for fibrinolysis [7]. No studies investigated the relationship of post-treatment BP levels with arterial recanalization and we were unable to assess this association in the present meta-analysis. Additionally, increasing BPV after tPA infusion appeared to be related to higher likelihood of sICH, mortality and poor post-stroke recovery.
Our findings are in line with various individual and pooled analyses of European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS) [43], ECASS 2 [44], and Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-International Stroke Thrombolysis Register (SITS-ISTR) [22] trials documenting poor outcomes in AIS patients with elevated preand post-IVT SBP levels. Notably, both linear [22] and U-shaped [22,46] associations have been reported between post-tPA SBP levels and sICH as well as 3-month mortality respectively.
Optimization of BP during AIS requires determination of various hemodynamic factors including presence of ischemic penumbra, large vessel occlusion, collateral and recanalization status, and underlying etiopathogenic mechanisms [47]. Approximately three-fourths of AIS patients present with elevated SBP and/or DBP levels [48]. The underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood; however, early activation of sympathetic adrenomedullary pathway and altered cerebral autoregulation within ischemic penumbra are plausible explanations [49]. Wider BP fluctuations in IVT-treated patients can exacerbate reperfusion injury of blood-brain barrier and lead to hemorrhage and cerebral edema complications. Additionally, ischemic penumbra surrounding the large infarct core is more susceptible to changes in systemic BP and reperfusion injury [50]. Due to impaired cerebral autoregulation during AIS, systemically elevated BP levels and increased BPV are associated with compromised cerebral perfusion, that likely predispose to poor functional outcomes in AIS patients treated with IVT [34,35]. The positive association that we documented between increasing BPV after tPA infusion with higher odds of mortality, poor functional outcomes and sICH lends support to the former considerations.
Our findings are in line with the recent AHA/ASA guidelines for BP control in AIS patients treated with IVT [4]. However, an optimal BP level that renders a negligible risk of sICH while avoiding the impairment of cerebral perfusion remains unknown (Class I; Level of Evidence B). The recently presented randomized-controlled clinical trials [51,52] attempting to evaluate the impact of BP reduction on early outcomes of AIS patients were not specifically designed to address the role of very early (within a few hours), rapid and intensive BP lowering, in AIS patients treated with tPA. The second arm of ENhanced Control of Hypertension ANd Thrombolysis strokE stuDy (ENCHANTED) trial may provide more definitive data on whether early intensive BP lowering is superior to standard guideline-recommended BP management for the clinical outcome of death or disability at 90 days in AIS patients treated with IVT [53].
Certain limitations of the present report need to be acknowledged. First, substantial heterogeneity was documented in our adjusted analyses since only few studies reported associations on the increments of BP levels adjusted for different confounding variables. Additionally, variability was noted in the use of adjudicated definitions for sICH amongst the included studies. This likely renders a major source of bias that needs to be weighed while carefully interpreting the results of our metaanalysis. Moreover, it should be noted that adjusted analyses for the outcomes of interest were not available in a substantial proportion of included studies (Supplementary Table 4). Second, it should be acknowledged that despite the vast number of different analyses that were conducted we performed no correction for multiple comparisons. This decision was made a priori during the preparation of our manuscript protocol and after taking into account that the associations that were tested were both discrete and pre-specified. Nevertheless, it should be noted that many of the correlations were highly significant (P<0.001) and reproducible in both adjusted and unadjusted analyses (Tables 2 and 3). Thus statistical significance would have been achieved even after correcting for multiple comparisons and using a stricter threshold for independent associations on multivariable logistic regression models (e.g., P<0.005). Third, our study did not evaluate separately the association of BP variables with outcomes according to stroke subtype, infarct size, location or vascular status of the corresponding arteries and perfusion status of the corresponding vascular territories. It might be postulated that significant disparities could be present on the association of pre-treatment BP with outcomes between patients with hypoperfusion due to major cerebral artery occlusion and patients with small vessel disease. Therefore, the reported associations and effect estimates by 10 mm Hg BP increments should be interpreted with caution as they represent an oversimplification of a more complex situation not accounting for many other parameters, including the vascular and perfusion status. Fourth, not all the studies reported mean BP levels during pre- or post-IVT time intervals. Accordingly, wherever mean BP levels were unavailable, we recorded admission BP levels, and selected BP levels following IVT that were closer to the termination of alteplase infusion. This decision was made a priori during our meta-analysis protocol to avoid the possibility of reporting bias [54]. Fifth, there are different indices of BPV, but we only assessed SV using limited available data from the scarce studies that assessed the relationship of BPV (quantified by SV) with clinical outcomes in AIS patients treated with IVT. Sixth, it should be acknowledged that in the present meta-analysis we were unable to test the hypothesis of a U-shaped relationship between BP parameters and clinical outcomes of AIS patients treated with IVT, despite occasional reports supporting that both acute low and high BP levels may adversely affect outcomes in the settings of AIS [16,26]. Last and most important, our analyses were based on observational studies or post hoc analyses from randomized controlled trials that were not designed to evaluate the association of different BP levels with outcomes in a randomized fashion. Thus, apart from inherent biases related to the design of the included studies, various disparities in the monitoring BP levels (methodology and frequency of serial BP measurements) and the antihypertensive medications used to treat excessive BP levels may have also contributed to the documented heterogeneity across included studies.
Our systematic review and meta-analysis indicated that elevated BP levels before and after tPA infusion are associated with reduced likelihood of good functional outcomes and increased odds of sICH. These associations persisted even after adjustment for potential confounders, while substantial heterogeneity was documented in the majority of the reported associations. Given that the association of higher BP levels with worse clinical outcomes that we detected in the current meta-analysis cannot yield direct evidence of causality with certainty, future randomized clinical trials are required to provide definitive data regarding the potential association of BP control with improved clinical outcomes of AIS patients treated with IVT and to identify the optimal BP range in this high-risk for sICH population.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2018.02369.
Supplementary Table 1.
Definitions of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage utilized by included studies
Supplementary Table 3.
Baseline characteristics of acute ischemic stroke patients across included studies
Supplementary Table 4.
Studies with adjusted analyses based on 1 mm Hg or 10 mm Hg BP increments
Supplementary Table 5.
Quality assessment of included studies with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale
Supplementary Table 6.
Sensitivity analyses on the primary and secondary analyses of pre-treatment BP impact on various outcomes
Supplementary Table 7.
Sensitivity analyses on the primary and secondary analyses of post-treatment BP impact on various outcomes
Supplementary Table 8.
Meta-regression analyses on the association of baseline characteristics with the likelihood of functional independence at 3 months
Supplementary Figure 1.
Flow-chart diagram presenting the selection of eligible studies.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Funnel plot of the included studies evaluating the unadjusted associations of pre-treatment blood pressure variables with functional independence. SE, standard error; SMD, standardized mean difference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
Supplementary Figure 3.
Funnel plot of the included studies evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment blood pressure variables with functional independence. SE, standard error; OR, odds ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
Supplementary Figure 4.
Funnel plot of the included studies evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment blood pressure variables with favorable functional outcome. SE, standard error; OR, odds ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
Supplementary Figure 5.
Forest plots evaluating the associations of post-treatment (A) systolic blood pressure levels and (B) diastolic blood pressure levels with favorable functional outcome. mRS, modified Rankin Scale; SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 6.
Forest plots evaluating the association of pre-treatment (A) systolic blood pressure levels and (B) diastolic blood pressure levels with favorable functional outcome. mRS, modified Rankin Scale; SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 7.
Forest plots evaluating the association of (A) pre-treatment and (B) post-treatment systolic blood pressure levels with functional independence. mRS, modified Rankin Scale; SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 8.
Forest plots evaluating the association of (A) pre-treatment and (B) post-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels with functional independence. mRS, modified Rankin Scale; SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 9.
Forest plot evaluating the associations of (A) pre-treatment and (B) post-treatment systolic blood pressure levels with symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 10.
Forest Plots evaluating the association of (A) pre-treatment and (B) post-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels with symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 11.
Forest plots evaluating the association of pre-treatment (A) systolic blood pressure levels and (B) diastolic blood pressure levels with mortality. SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 12.
Forest plots evaluating the association of pre-treatment (A) systolic blood pressure levels and (B) diastolic blood pressure levels with recanalization. SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 13.
Forest plot evaluating the association of post-treatment successive variation of systolic blood pressure levels and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SMD, standardized mean difference; SD, standard deviation; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 14.
Funnel plot of the included (blue circles) and imputed (red circles) by the Duval and Tweedie’s trim and fill method studies evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment blood pressure variables with favorable functional outcome.
Supplementary Figure 15.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment systolic blood pressure levels and recanalization. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 16.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and favorable functional outcome. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
Supplementary Figure 17.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and functional independence. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
Supplementary Figure 18.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 19.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and mortality. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 20.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of pre-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and recanalization. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 21.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of post-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and favorable functional outcome. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
Supplementary Figure 22.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of post-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and functional independence. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
Supplementary Figure 23.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of post-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 24.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted association of post-treatment diastolic blood pressure levels and mortality. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 25.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted associations of post-treatment successive variation of systolic blood pressure levels and favorable functional outcome. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
Supplementary Figure 26.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted associations of post-treatment successive variation of systolic blood pressure levels and mortality. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 27.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted associations of post-treatment successive variation of systolic blood pressure levels and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 28.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted associations of post-treatment successive variation of diastolic blood pressure levels and mortality. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 29.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted associations of post-treatment successive variation of diastolic blood pressure levels and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH). SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval.
Supplementary Figure 30.
Forest plot evaluating the adjusted associations of post-treatment successive variation of diastolic blood pressure levels and favorable functional outcome. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; sICH, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.
Figure 1.
Forest plot presenting the adjusted for potential confounders associations of pre-treatment systolic blood pressure levels with (A) favorable functional outcome, (B) functional independence, (C) symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), and (D) mortality. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
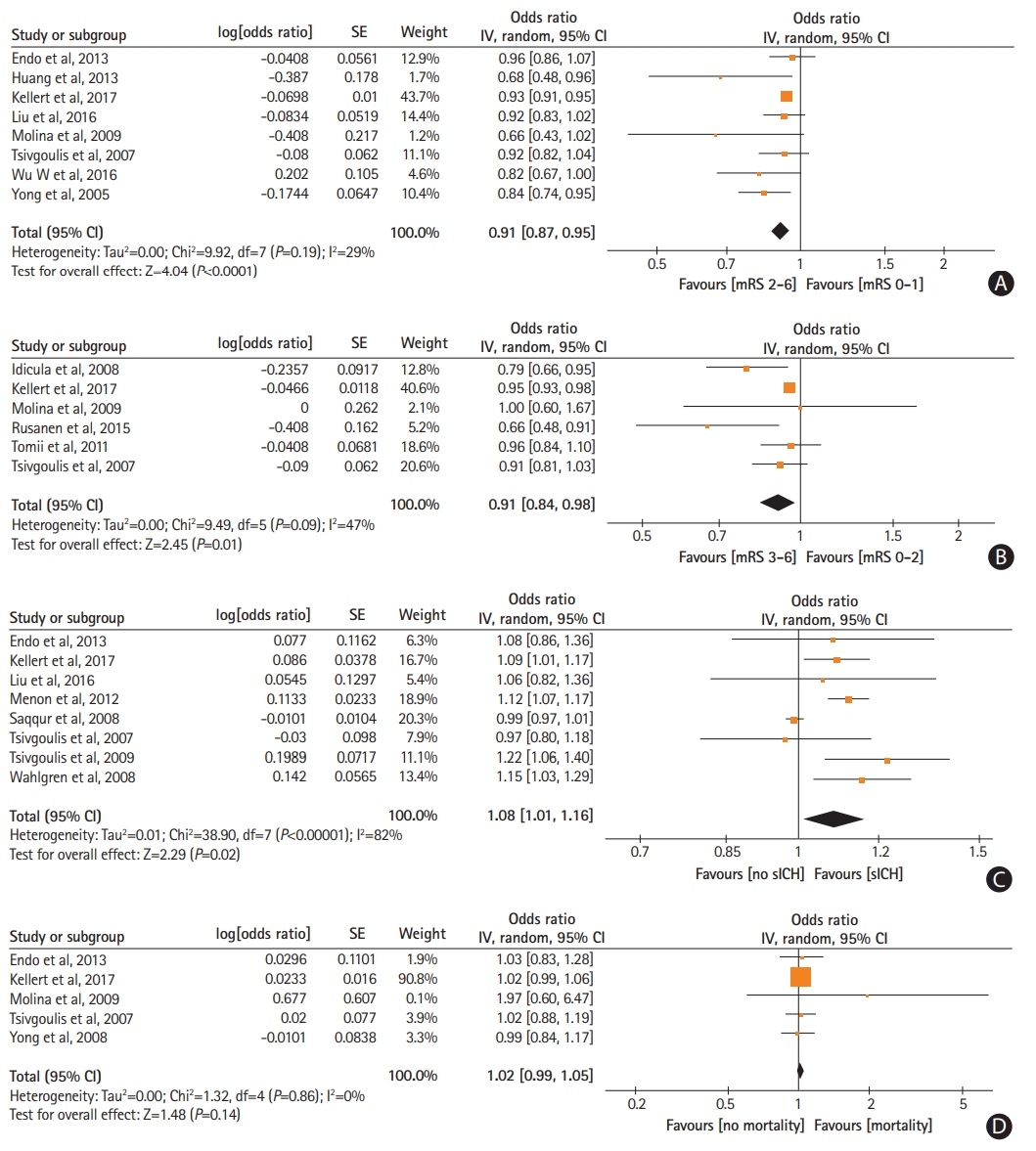
Figure 2.
Forest plot presenting the adjusted for potential confounders associations of post-treatment systolic blood pressure levels with (A) favorable functional outcome, (B) functional independence, (C) symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), and (D) mortality. SE, standard error; IV, intravenous; CI, confidence interval; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
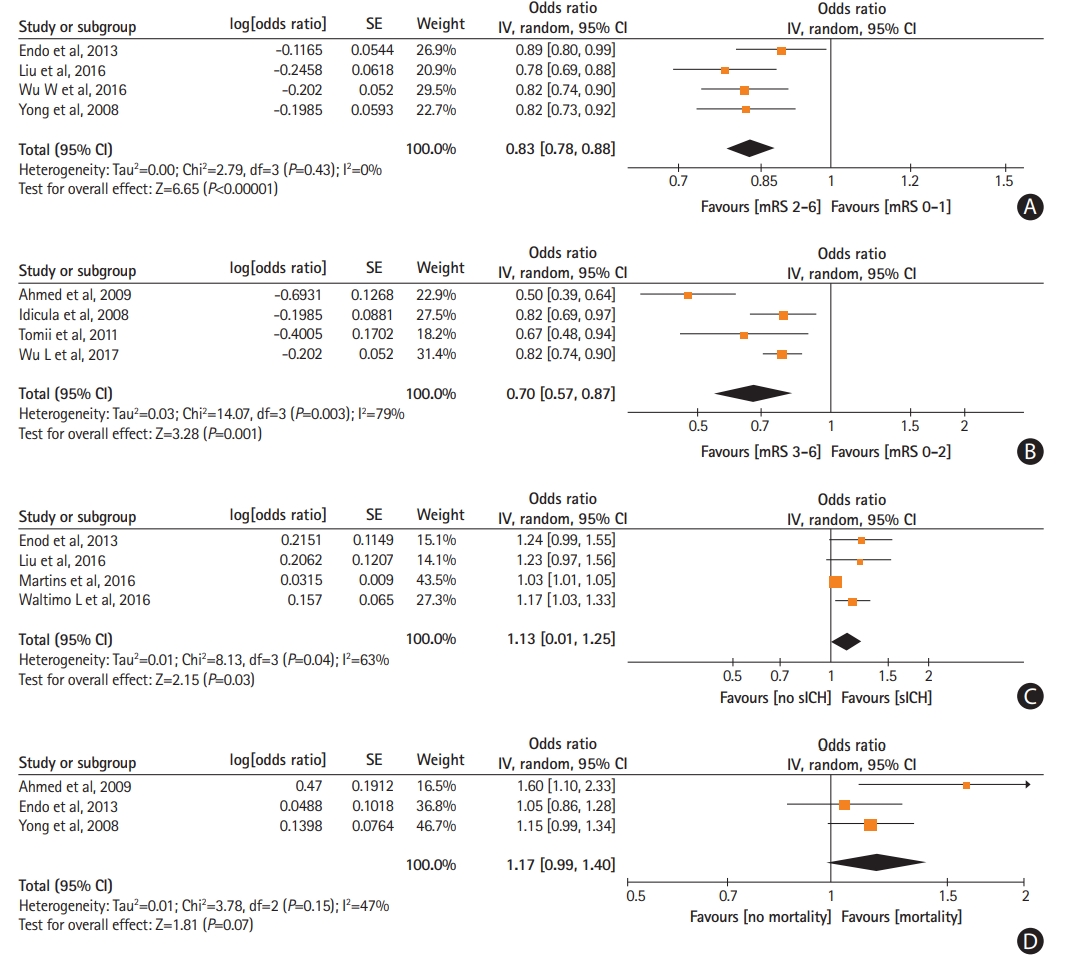
Table 1.
Study design and characteristics of included studies in our meta-analysis
| Study | Country | Study design, registry | No. of patients | BP monitoring | sICH definitions used | Adjusted variables | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed et al. (2009) [22] | Multinational | Retrospective, SITS-ISTR (2002-2007) | 11,080 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | SITS-MOST | Age, sex, weight, OTT, baseline NIHSS, glucose, and imaging, vascular risk factors, anti-HTN and antiplatelet medication, functional independence | 2, 4* |
| Delgado-Mederos et al. (2008) [24] | Spain | Prospective | 80 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | - | Baseline NIHSS, vascular risk factors, occlusion site, anti-HTN treatment | 2, 5† |
| Endo et al. (2013) [24] | Japan | Retrospective, SAMURAI rt-PA | 527 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | ECASS 2 | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, OTT, vascular risk factors, anti-HTN treatment prior to IVT, ASPECTS | 1, 3, 4* |
| Huang et al. (2013) [25] | China | Retrospective | 101 | Admission: IVT | ECASS 2 | Baseline NIHSS and serum glucose, DM, leukoaraiosis | 1† |
| 1* | |||||||
| Idicula et al. (2008) [26] | Norway | Prospective | 127 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | - | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, vascular risk factors | 2* |
| Kellert et al. (2012) [27] | Germany | Retrospective | 427 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | ECASS 2 | - | 3† |
| Kellert et al. (2017) [28] | Multinational | Prospective, SITS-ISTR (2002-2013) | 16,434 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | ECASS 2 SITS-MOST | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, vascular risk factors, SBP | 1, 2, 3, 4* |
| Lindsberg et al. (2003) [29] | Finland | Retrospective | 75 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | - | - | 2† |
| 2* | |||||||
| Liu et al. (2016) [30] | China | Retrospective | 461 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | ECASS 2 | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, OTT, glucose, vascular risk factors | 3† |
| 1, 3* | |||||||
| Martins et al. (2016) [31] | Portugal | Retrospective | 674 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | NINDS | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, Endovascular therapy, vascular risk factors, SBP | 3* |
| Menon et al. (2012) [32] | Multinational | Prospective | 10,242 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | NINDS | Age, sex, race, baseline NIHSS, SBP, glucose | 3* |
| Molina et al. (2004) [33] | Multinational | Prospective, CLOTBUST | 177 | Admission: IVT | ECASS 2 | - | 2† |
| 2* | |||||||
| Molina et al. (2009) [34] | Multinational | RCT, TUCSON | 35 | Admission: 36 hr after IVT | SITS-MOST | Age, sex, OTT, baseline NIHSS | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5† |
| 1, 2, 4* | |||||||
| Rusanen et al. (2015) [35] | Finland | Retrospective | 104 | Admission: IVT | - | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, OTT, vascular risk factors, occlusion site | 2* |
| Saqqur et al. (2008) [36] | Multinational | Retrospective | 349 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | ECASS 3 | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, glucose, SBP, OTT | 3† |
| 3* | |||||||
| Tomii et al. (2011) [37] | Japan | Prospective | 125 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | - | Age, baseline NIHSS, vascular risk factors, eGFR | 2* |
| Toni et al. (2012) [38] | Italy | Retrospective, SITS-ISTR (2002-2010) | 3,246 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | SITS-MOST | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, glucose, BP, OTT, vascular risk factors, functional independence | 2, 3* |
| Tsivgoulis et al. (2007) [7] | Multinational | Retrospective, CLOTBUST | 351 | Admission: 2 hr after IVT | ECASS 3 | Age, sex, OTT, baseline NIHSS and serum glucose | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5† |
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5* | |||||||
| Tsivgoulis et al. (2009) [6] | USA | Retrospective | 510 | Admission: IVT | ECASS 3 | Age, sex, OTT, baseline NIHSS, vascular risk factors and medications | 3† |
| 3* | |||||||
| Wahlgren et al. (2008) [8] | Multinational | Prospective, SITS-MOST (2002-2006) | 6,483 | Admission: IVT | SITS-MOST | Age, sex, weight, ASPECTS, baseline NIHSS and glucose, vascular risk factors and medications, SBP, functional independence | 2, 3, 4* |
| Waltimo et al. (2016) [39] | Finland | Retrospective | 1,868 | Admission: 48 hr after IVT | ECASS 2, NINDS, SITS-MOST | Age, SBP, baseline NIHSS, glucose and ASPECTS | 3* |
| Wu et al. (2017) [40] | China | Retrospective | 420 | Admission: IVT | - | Age, sex, BMI, baseline NIHSS, OTT, SBP, vascular risk factors | 2† |
| 2* | |||||||
| Wu et al. (2016) [41] | China | Prospective, TIMS-CHINA | 1,128 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | NINDS | Age, sex, baseline NIHSS, ASPECTS, OTT, aspirin use | 1, 2, 3* |
| Yan et al. (2015) [42] | China | Retrospective | 161 | Admission: 2 hr after IVT | ECASS 2 | Vascular risk factors | 5† |
| Yong et al. (2005) [43] | Multinational | Post hoc RCT, ECASS | 615 | Admission: 72 hr after IVT | - | Age, sex, weight, baseline SSS, OTT, aspirin use, ASPECTS, vascular risk factors | 1† |
| Yong et al. (2008) [44] | Multinational | Post hoc RCT, ECASS 2 | 793 | Admission: 24 hr after IVT | - | Age, sex, baseline SSS, OTT, aspirin use, ASPECTS, vascular risk factors | 1, 4* |
(1) Favorable functional outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0-1), (2) functional independence (mRS 0-2), (3) sICH, (4) mortality, (5) recanalization.
BP, blood pressure; sICH, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage; SITS-ISTR, Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-International Stroke Thrombolysis Register; IVT, intravenous thrombolysis; SITS-MOST, Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study; OTT, onset-to-treatment; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; HTN, hypertension; SAMURAI rt-PA, Stroke Acute Management with Urgent Risk-factor Assessment and Improvement recombinant tissue plasminogen activator; ECASS, European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study; ASPECTS, Alberta stroke program early CT score; DM, diabetes mellitus; SBP, systolic blood pressure; NINDS, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; CLOTBUST, Combined Lysis of Thrombus in Brain ischemia using transcranial Ultrasound and Systemic tPA; RCT, randomized controlled trial; TUCSON, transcranial ultrasound in clinical sonothrombolysis; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; BMI, body mass index; TIMS-CHINA, thrombolysis implementation and monitor of acute ischemic stroke in China; SSS, Scandinavian Stroke Scale.
Table 2.
Overview of primary and secondary analyses of pre-treatment BP impact on various outcomes
| Clinical outcome | BP level |
Unadjusted analyses |
Adjusted analyses* |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studies | SMD (95% CI) | P | Heterogeneity | Studies | OR (95% CI) | P | Heterogeneity | ||
| FFO | SBP | 5 | -0.18 (-0.40 to 0.04) | 0.120 | I2=76%, P for Cochran Q=0.002 | 8 | 0.91 (0.87 to 0.95) | <0.001 | I2=29%, P for Cochran Q=0.19 |
| DBP | 4 | -0.01 (-0.11 to 0.10) | 0.900 | I2=17%, P for Cochran Q=0.30 | 2 | 1.00 (0.89 to 1.14) | 0.950 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.75 | |
| FI | SBP | 7 | -0.17 (-0.34 to 0.01) | 0.060 | I2=61%, P for Cochran Q=0.02 | 6 | 0.91 (0.84 to 0.98) | 0.010 | I2=47%, P for Cochran Q=0.09 |
| DBP | 6 | 0.11 (-0.10 to 0.33) | 0.300 | I2=49%, P for Cochran Q=0.08 | 3 | 1.36 (0.82 to 2.26) | 0.230 | I2=64%, P for Cochran Q=0.06 | |
| sICH | SBP | 6 | 0.24 (0.04 to 0.43) | 0.020 | I2=37%, P for Cochran Q=0.16 | 8 | 1.08 (1.01 to 1.16) | 0.020 | I2=82%, P for Cochran Q <0.001 |
| DBP | 4 | 0.11 (-0.03 to 0.24) | 0.120 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.83 | 1 | 0.99 (0.73 to 1.34) | 0.950 | - | |
| Mortality | SBP | 3 | 0.17 (-0.09 to 0.44) | 0.200 | I2=60%, P for Cochran Q=0.08 | 5 | 1.02 (0.99 to 1.05) | 0.140 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.86 |
| DBP | 2 | -0.00 (-0.06 to 0.06) | 0.990 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.83 | 2 | 0.86 (0.66 to 1.13) | 0.280 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.79 | |
| Recanalization | SBP | 3 | -0.21 (-0.41 to -0.01) | 0.040 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.94 | 2 | 0.47 (0.12 to 1.83) | 0.280 | I2=73%, P for Cochran Q =0.05 |
| DBP | 2 | -0.30 (-0.67 to 0.06) | 0.110 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.82 | 1 | 0.90 (0.54 to 1.52) | 0.700 | - | |
BP, blood pressure; SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; FFO, favorable functional outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0-1); SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FI, functional independence (mRS 0-2); sICH, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.
Table 3.
Overview of primary and secondary analyses of post-treatment BP impact on various outcomes
| Clinical outcome | BP level |
Unadjusted analyses |
Adjusted analyses* |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Studies | SMD (95% CI) | P | Heterogeneity | Studies | OR (95% CI) | P | Heterogeneity | ||
| FFO | SBP | 2 | -0.19 (-0.26 to -0.13) | <0.001 | I2=9%, P for Cochran Q= 0.29 | 4 | 0.83 (0.78 to 0.88) | <0.001 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.43 |
| DBP | 2 | -0.01 (-0.07 to 0.05) | 0.780 | I2=8%, P for Cochran Q=0.30 | 1 | 0.97 (0.84 to 1.12) | 0.680 | - | |
| FI | SBP | 4 | -0.19 (-0.23 to -0.15) | <0.001 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.64 | 4 | 0.70 (0.57 to 0.87) | 0.001 | I2=79%, P for Cochran Q<0.01 |
| DBP | 3 | 0.00 (-0.04 to 0.04) | 1.000 | I2=0%, P for Cochran Q=0.70 | 1 | 0.86 (0.68 to 1.09) | 0.210 | - | |
| sICH | SBP | 3 | 0.50 (0.14 to 0.86) | 0.006 | I2=33%, P for Cochran Q=0.23 | 4 | 1.13 (1.01 to 1.25) | 0.030 | I2=63%, P for Cochran Q=0.04 |
| DBP | 3 | 0.20 (-0.31 to 0.71) | 0.450 | I2=57%, P for Cochran Q=0.10 | 2 | 1.07 (0.92 to 1.26) | 0.380 | I2=36%, P for Cochran Q=0.21 | |
| Mortality | SBP | - | - | - | - | 3 | 1.17 (0.99 to 1.40) | 0.070 | I2=47%, P for Cochran Q=0.15 |
| DBP | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.09 (0.81 to 1.47) | 0.570 | - | |
BP, blood pressure; SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; FFO, favorable functional outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0-1); SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FI, functional independence (mRS 0-2); sICH, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.
References
1. Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Dávalos A, Guidetti D, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1317-1329.


2. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581-1587.


3. Tsivgoulis G, Kotsis V, Giannopoulos S. Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke: effective blood pressure control matters. Int J Stroke 2011;6:125-127.


4. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018;49:e46-e110.


5. Lopez-Yunez AM, Bruno A, Williams LS, Yilmaz E, Zurrú C, Biller J. Protocol violations in community-based rTPA stroke treatment are associated with symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2001;32:12-16.


6. Tsivgoulis G, Frey JL, Flaster M, Sharma VK, Lao AY, Hoover SL, et al. Pre-tissue plasminogen activator blood pressure levels and risk of symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2009;40:3631-3634.


7. Tsivgoulis G, Saqqur M, Sharma VK, Lao AY, Hill MD, Alexandrov AV, et al. Association of pretreatment blood pressure with tissue plasminogen activator-induced arterial recanalization in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007;38:961-966.


8. Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Eriksson N, Aichner F, Bluhmki E, Dávalos A, et al. Multivariable analysis of outcome predictors and adjustment of main outcome results to baseline data profile in randomized controlled trials: Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-MOnitoring STudy (SITS-MOST). Stroke 2008;39:3316-3322.


9. Oliveira-Filho J, Silva SC, Trabuco CC, Pedreira BB, Sousa EU, Bacellar A. Detrimental effect of blood pressure reduction in the first 24 hours of acute stroke onset. Neurology 2003;61:1047-51.


10. Castillo J, Leira R, García MM, Serena J, Blanco M, Dávalos A. Blood pressure decrease during the acute phase of ischemic stroke is associated with brain injury and poor stroke outcome. Stroke 2004;35:520-526.


11. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol 2009;62:e1-e34.


12. AHA/ASA Journals. Transparency and openness promotion (TOP) guidelines for authors publishing in an American Heart Association Journal http://www.ahajournals.org/content/TOP-guidelines. Accessed November 28, 2018.
13. Katsanos AH, Parissis J, Frogoudaki A, Vrettou AR, Ikonomidis I, Paraskevaidis I, et al. Heart failure and the risk of ischemic stroke recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci 2016;362:182-187.


14. Deeks JJ, Higgins JPG, Altman DG. 9.2.3.2 The standardized mean difference. In: Higgins JPG, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.1.0 ed. Oxford, UK: Cochrane Collaboration; 2011.
16. Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988.
18. IntHout J, Ioannidis JP, Borm GF. The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014;14:25.




19. Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002.


20. Duval S, Tweedie R. A nonparametric “trim and fill” method of accounting for publication bias in meta-analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 2000;95:89-98.

21. Wallace BC, Dahabreh IJ, Trikalinos TA, Lau J, Trow P, Schmid CH. Closing the gap between methodologists and end-users: R as a computational back-end. J Stat Softw 2012;49:1-15.

22. Ahmed N, Wahlgren N, Brainin M, Castillo J, Ford GA, Kaste M, et al. Relationship of blood pressure, antihypertensive therapy, and outcome in ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis: retrospective analysis from Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-International Stroke Thrombolysis Register (SITS-ISTR). Stroke 2009;40:2442-2449.


23. Delgado-Mederos R, Ribo M, Rovira A, Rubiera M, Munuera J, Santamarina E, et al. Prognostic significance of blood pressure variability after thrombolysis in acute stroke. Neurology 2008;71:552-558.


24. Endo K, Kario K, Koga M, Nakagawara J, Shiokawa Y, Yamagami H, et al. Impact of early blood pressure variability on stroke outcomes after thrombolysis: the SAMURAI rt-PA Registry. Stroke 2013;44:816-818.


25. Huang YH, Zhuo ST, Chen YF, Li MM, Lin YY, Yang ML, et al. Factors influencing clinical outcomes of acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013;126:4685-4690.


26. Idicula TT, Waje-Andreassen U, Brogger J, Naess H, Lundstadsveen MT, Thomassen L. The effect of physiologic derangement in patients with stroke treated with thrombolysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2008;17:141-146.


27. Kellert L, Sykora M, Gumbinger C, Herrmann O, Ringleb PA. Blood pressure variability after intravenous thrombolysis in acute stroke does not predict intracerebral hemorrhage but poor outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis 2012;33:135-140.


28. Kellert L, Hametner C, Ahmed N, Rauch G, MacLeod MJ, Perini F, et al. Reciprocal interaction of 24-hour blood pressure variability and systolic blood pressure on outcome in stroke thrombolysis. Stroke 2017;48:1827-1834.


29. Lindsberg PJ, Soinne L, Roine RO, Salonen O, Tatlisumak T, Kallela M, et al. Community-based thrombolytic therapy of acute ischemic stroke in Helsinki. Stroke 2003;34:1443-1449.


30. Liu K, Yan S, Zhang S, Guo Y, Lou M. Systolic blood pressure variability is associated with severe hemorrhagic transformation in the early stage after thrombolysis. Transl Stroke Res 2016;7:186-191.



31. Martins AI, Sargento-Freitas J, Silva F, Jesus-Ribeiro J, Correia I, Gomes JP, et al. Recanalization modulates association between blood pressure and functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2016;47:1571-1576.


32. Menon BK, Saver JL, Prabhakaran S, Reeves M, Liang L, Olson DM, et al. Risk score for intracranial hemorrhage in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator. Stroke 2012;43:2293-2299.


33. Molina CA, Alexandrov AV, Demchuk AM, Saqqur M, Uchino K, Alvarez-Sabín J, et al. Improving the predictive accuracy of recanalization on stroke outcome in patients treated with tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 2004;35:151-156.


34. Molina CA, Barreto AD, Tsivgoulis G, Sierzenski P, Malkoff MD, Rubiera M, et al. Transcranial ultrasound in clinical sonothrombolysis (TUCSON) trial. Ann Neurol 2009;66:28-38.


35. Rusanen H, Saarinen JT, Sillanpää N. The association of blood pressure and collateral circulation in hyperacute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Cerebrovasc Dis 2015;39:130-137.


36. Saqqur M, Tsivgoulis G, Molina CA, Demchuk AM, Siddiqui M, Alvarez-Sabín J, et al. Symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage and recanalization after IV rt-PA: a multicenter study. Neurology 2008;71:1304-1312.


37. Tomii Y, Toyoda K, Nakashima T, Nezu T, Koga M, Yokota C, et al. Effects of hyperacute blood pressure and heart rate on stroke outcomes after intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. J Hypertens 2011;29:1980-1987.


38. Toni D, Ahmed N, Anzini A, Lorenzano S, Brozman M, Kaste M, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis in young stroke patients: results from the SITS-ISTR. Neurology 2012;78:880-887.


39. Waltimo T, Haapaniemi E, Surakka IL, Melkas S, Sairanen T, Sibolt G, et al. Post-thrombolytic blood pressure and symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Eur J Neurol 2016;23:1757-1762.


40. Wu L, Huang X, Wu D, Zhao W, Wu C, Che R, et al. Relationship between post-thrombolysis blood pressure and outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients undergoing thrombolysis therapy. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2017;26:2279-2286.


41. Wu W, Huo X, Zhao X, Liao X, Wang C, Pan Y, et al. Relationship between blood pressure and outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients administered lytic medication in the TIMS-China Study. PLoS One 2016;11:e0144260.



42. Yan S, Liu K, Cao J, Liebeskind DS, Lou M. “Sudden drop” in blood pressure is associated with recanalization after thrombolysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e1132.



43. Yong M, Diener HC, Kaste M, Mau J. Characteristics of blood pressure profiles as predictors of long-term outcome after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2005;36:2619-2625.


44. Yong M, Kaste M. Association of characteristics of blood pressure profiles and stroke outcomes in the ECASS-II trial. Stroke 2008;39:366-372.


45. Nogueira RG, Liebeskind DS, Sung G, Duckwiler G, Smith WS; MERCI, et al. Predictors of good clinical outcomes, mortality, and successful revascularization in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing thrombectomy: pooled analysis of the Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) and Multi MERCI Trials. Stroke 2009;40:3777-3783.


46. Vemmos KN, Tsivgoulis G, Spengos K, Zakopoulos N, Synetos A, Kotsis V, et al. Association between 24-h blood pressure monitoring variables and brain oedema in patients with hyperacute stroke. J Hypertens 2003;21:2167-2173.


47. Ntaios G, Lambrou D, Michel P. Blood pressure changes in acute ischemic stroke and outcome with respect to stroke etiology. Neurology 2012;79:1440-1448.


48. Leonardi-Bee J, Bath PM, Phillips SJ, Sandercock PA; IST Collaborative Group. Blood pressure and clinical outcomes in the International Stroke Trial. Stroke 2002;33:1315-1320.


49. Chamorro A, Amaro S, Vargas M, Obach V, Cervera A, Gómez-Choco M, et al. Catecholamines, infection, and death in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci 2007;252:29-35.


50. Mistry EA, Mistry AM, Nakawah MO, Khattar NK, Fortuny EM, Cruz AS, et al. Systolic blood pressure within 24 hours after thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke correlates with outcome. J Am Heart Assoc 2017;6:e006167.



51. Sandset EC, Bath PM, Boysen G, Jatuzis D, Kõrv J, Lüders S, et al. The angiotensin-receptor blocker candesartan for treatment of acute stroke (SCAST): a randomised, placebocontrolled, double-blind trial. Lancet 2011;377:741-750.


52. ENOS Trial Investigators. Efficacy of nitric oxide, with or without continuing antihypertensive treatment, for management of high blood pressure in acute stroke (ENOS): a partial-factorial randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015;385:617-628.



53. Huang Y, Sharma VK, Robinson T, Lindley RI, Chen X, Kim JS, et al. Rationale, design, and progress of the ENhanced Control of Hypertension ANd Thrombolysis strokE stuDy (ENCHANTED) trial: an international multicenter 2×2 quasi-factorial randomized controlled trial of low- vs. standard-dose rt-PA and early intensive vs. guideline-recommended blood pressure lowering in patients with acute ischaemic stroke eligible for thrombolysis treatment. Int J Stroke 2015;10:778-788.


- TOOLS
-
-
 PDF Links
PDF Links
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link XML Download
XML Download-
 Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI
-
 Download Citation
Download Citation
 Supplement1
Supplement1 Supplement2
Supplement2 Supplement3
Supplement3 Supplement4
Supplement4 Supplement5
Supplement5 Supplement6
Supplement6 Supplement7
Supplement7 Supplement8
Supplement8 Supplement9
Supplement9 Supplement10
Supplement10 Supplement11
Supplement11 Supplement12
Supplement12 Supplement13
Supplement13 Supplement14
Supplement14 Supplement15
Supplement15 Supplement16
Supplement16 Supplement17
Supplement17 Supplement18
Supplement18 Supplement19
Supplement19 Supplement20
Supplement20 Supplement21
Supplement21 Supplement22
Supplement22 Supplement23
Supplement23 Supplement24
Supplement24 Supplement25
Supplement25 Supplement26
Supplement26 Supplement27
Supplement27 Supplement28
Supplement28 Supplement29
Supplement29 Supplement30
Supplement30 Supplement31
Supplement31 Supplement32
Supplement32 Supplement33
Supplement33 Supplement34
Supplement34 Supplement35
Supplement35 Supplement36
Supplement36 Supplement37
Supplement37 Supplement38
Supplement38 Supplement39
Supplement39 Print
Print
-