 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 22(2); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia (IADE), also known as dilatative arteriopathy of the brain vessels, refers to an increase in the length and diameter of at least one intracranial artery, and accounts for approximately 12% of all patients with stroke. However, the association of IADE with stroke is usually unclear. Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is characterized by pathological changes in the small vessels. Clinically, patients with CSVD can be asymptomatic or present with stroke or cognitive decline. In the past 20 years, a series of studies have strongly promoted an understanding of the association between IADE and CSVD from clinical and pathological perspectives. It has been proposed that IADE and CSVD may be attributed to abnormal vascular remodeling driven by an abnormal matrix metalloproteinase/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase pathway. Also, IAD-Erelated hemodynamic changes may result in initiation or progression of CSVD. Additionally, genetic factors are implicated in the pathogenesis of IADE and CSVD. Patients with Fabry’s disease and late-onset Pompe’s disease are prone to developing concomitant IADE and CSVD, and patients with collagen IV alpha 1 or 2 gene (COL4A1/COL4A2) and forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) variants present with IADE and CSVD. Race, strain, familial status, and vascular risk factors may be involved in the pathogenesis of IADE and CSVD. As well, experiments in mice have pointed to genetic strain as a predisposing factor for IADE and CSVD. However, there have been few direct genetic studies aimed towards determining the association between IADE and CSVD. In the future, more clinical and basic research studies are needed to elucidate the causal relationship between IADE and CSVD and the related molecular and genetic mechanisms.
Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia (IADE), refers to an increase in the length and diameter of at least one intracranial artery, and it accounts for approximately 12% of all patients with stroke [1]. Affected intracranial arteries are dilated, elongated, and sometimes tortuous. IADE in the posterior circulation is more common than its counterpart in the anterior circulation. IADE occurring in the basilar artery (BA), also known as BA dolichoectasia, accounts for 80% of all cases. IADE with involvement of both the BA and the vertebral artery is named vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD) [2,3].
The pathophysiology of IADE is largely unknown, but it can be viewed as a common final pathway of an arterial wall response or damage in the tunica media due to various mechanisms, such as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) dysfunction or muscle cell or elastic fibre injury [1]. Patients with dolichoectasia may present with brain infarction, transient ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage, compression of a cranial nerve, and the brainstem or third ventricle with hydrocephalus [1-3]. A systematic review of 375 patients with VBD identified the 5 year risk of brain infarction (17.6%), brainstem compression (10.3%), transient ischemic attack (TIA; 10.1%), hemorrhagic stroke (4.7%), and subarachnoid hemorrhage (2.3%) [4]. The diagnostic criteria for IADE have not been established, but an imaging diagnosis has been widely accepted. Smoker et al. [5] recommended a cutoff of 4.5 mm diameter at the level of mid pons to define BA ectasia based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [5]. Passero and Rossi [6] have suggested diameter cutoffs for the internal carotid (≥7 mm), middle cerebral artery (≥4 mm), and vertebral artery (≥4 mm) to indicate ectasia. Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a common disease in elderly patients. Radiological characteristics of CSVD include small subcortical infarcts, lacunes, white matter hyperintensities (WMHs), enlarged perivascular spaces, microbleeds, and brain atrophy [7]. Clinically, patients with CSVD can be asymptomatic or present with stroke or cognitive decline.
CSVD is characterized by pathological changes in the small vessels. The main target of CSVD is the endothelium. Considering the structural and functional correlation between large arteries and small vessels, CSVD may be associated with physiological alterations in large arteries. These alterations include the two types of vascular aging, which are atherosclerosis and increase of vascular tortuosity [8,9]. In a large cohort of elderly community participants, carotid atherosclerosis was associated with a higher prevalence of CSVD [8]. Another report implied that some markers of carotid structure and function could be used to triage patients at high risk of CSVD, such as carotid plaque and increasing carotid lumen diameter, Young’s elastic modulus, and higher circumferential wall stress [9]. The underlying molecular mechanisms behind the impairment of endothelial function in systemic vessels and the damage in the vascular wall of large and small arteries may provide new insight into the correlation between CSVD and cerebral large vessel atherosclerosis disease [10]. Ince et al. [11] demonstrated that patients with IADE are more likely to develop stroke with a clinical and radiographic pattern of lacunar infarction (LI) when they display an increase in vascular tortuosity and CSVD. Recently, some researchers have proposed a common physiopathology for IADE and CSVD, such as dysfunction of the extracellular matrix (ECM), disrupted proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells, and mutual hemodynamic alteration [1-3,12]. IADE and CSVD are usually investigated separately [4,6,13], although increasing evidence has indicated that they are associated and should be studied together [9,14]. However, the mechanisms underlying the correlation between IADE and CSVD remain unknown. In this review, we summarize the current concepts and views regarding the association between IADE and CSVD as well as the underlying mechanisms.
Large arteries and small vessels are structurally continuous and subject to hemodynamic effects. From a pathophysiological perspective, the function of large arteries as an elastic reservoir can reduce the direct pressure load on distal small vessels. Therefore, theoretically, the pathological changes of large and small vessels should be parallel [15]. In a large cohort of elderly community participants, the carotid plaque was associated with a higher prevalence of LIs, increased WMH volume, and larger carotid lumen diameter, which predicted an increased prevalence of LIs, whereas functional markers of carotid stiffness were associated with increased WMH burden [8]. These associations were attenuated but maintained after adjustment for vascular risk factors. The authors proposed that CSVD was not associated with the intimamedia thickness of the common carotid artery [8]. These findings indicate that structural and functional characteristics of carotid arteries may serve as a predictive factor for risk of CSVD, although more studies are still needed. However, emerging evidence has revealed that the severity of CSVD is not parallel to the degree of large artery stenosis. For example, some severe CSVD cases with several vascular risk factors were discovered with normal large artery structures on magnetic resonance artery (MRA) or computed tomographic angiography. Therefore, an understanding of the correlation between large vessel changes and CSVD as well as the underlying mechanisms will be of great significance for the prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular disease [16]. The non-parallelism in cerebral large- and small-vessel changes suggests that the assessment of pathological changes in the artery wall should not be limited to atherosclerosis, but should also include functional features such as vascular elasticity and compliance [17]. The hemodynamic characteristics of IADE are consistent with the changes in arterial elasticity and compliance [13]. Therefore, some researchers have proposed that IADE and CSVD may represent two distinct entities with unique physiopathologic patterns.
As early as 1998, Ince et al. [11] from the Mayo clinic reported that patients with dolichoectasia diagnosed by cranial computed tomography scans were more likely to have LI than those without dolichoectasia (42% vs. 17%). Then Pico et al. [18] conducted a series of studies on the relationship between IADE and CSVD. In 2003, they found that the distribution of cerebral infarction subtypes was different between stroke patients with and without IADE. More specifically, they noted that lacunar stroke was more frequent in patients with IADE, and the association between IADE and lacunar stroke remained significant after adjustment for age, sex, hypertension, and previous myocardial infarction [18]. This case-control study provided further evidence to support the correlation between IADE and CSVD. In 2005, the authors evaluated the MRI profiles of 510 patients with cerebral infarction in which the diagnosis was classified into multilacunar infarction, leukoaraiosis, dilated perivascular spaces, and IADE. When compared with stroke patients without IADE, stroke patients with IADE had significantly more frequent multilacunar infarction, severe leukoaraiosis, and severe perivascular spaces. Elderly age and familial history of stroke were independent risk factors for dilated perivascular spaces. The authors also noted that IADE in stroke patients was independently associated with parenchymal manifestations of CSVD, suggesting that these entities may have a common biological basis [19]. In 2007, Pico et al. [20] investigated the entire arterial system from the heart to the intracranial small arteries in 381 consecutive autopsies from patients with stroke. They found that patients with IADE had a >2-fold increase in prevalence of BA plaques and ulcerated plaques in the aortic arch, and CSVD was more frequent in patients with IADE than those without IADE. These findings validate the theory that IADE and CSVD may share common pathophysiological processes, which is a milestone (Figure 1). In 2013, Park et al. [21] conducted a prospective stroke registry study and recruited a consecutive series of 182 patients hospitalized due to ischemic stroke or TIA. The authors found that VBD in patients with ischemic stroke or TIA was independently associated with cerebral microbleeds (CMBs), especially in the posterior circulation territory. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to reveal the relationship between CMBs and VBD in stroke patients. Our clinical study also found that patients with VBD were prone to having WMH and CMBs, and that CMBs were more common in the area supplied by the posterior circulation (Figure 2) (unpublished data). The appearance of CMBs in VBD is an intriguing phenomenon and the exact mechanisms needs further study. As is well known, elderly age is a risk factor for CSVD. In 2017, Thijs et al. [22] analyzed data from the Stroke in Young Fabry Patients (SIFAP1) study, a large prospective, hospital-based screening study for Fabry disease in young (<55 years) TIA/stroke patients. They found that dolichoectasia was more common in patients with small infarctions in the brainstem and white matter. Microbleeds, higher grades of WMH, and CSVD were more often present in patients with dolichoectasia. Dolichoectasia was associated with imaging markers of CSVD and brainstem localization of acute and old infarcts in younger patients with TIA and ischemic stroke. These findings support the correlation between IADE and CSVD in young patients, further suggesting that this correlation may be affected by not only age but also other underlying factors.
Although the above mentioned studies, which are based on independent cohorts, have demonstrated the association between VBD and CSVD, some researchers have also found inconsistent results in larger populations. In 2017, Del Brutto et al. [23] assessed the prevalence of VBD and CSVD using MRI and MRA in elderly adults (≥60 years) living in rural Ecuador. The authors found that VBD was associated with both WMH and CMBs; additionally, associations with imaging markers of CSVD differed according to whether the subject had dolichoectasia. In 2018, researchers investigated the risk factors of IADE and intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS) and their relationship with neuroimaging markers of CSVD in a population-based study. They found that ICAS was associated with lacunas, increased WMH volume and brain atrophy, whereas IADE was mainly associated with dilated perivascular spaces in basal ganglia and, to a lesser extent, associated with lacunas and microbleeds [24]. IADE and ICAS had different associations with various imaging phenotypes of CSVD, suggesting different physiopathological mechanisms. In the same year, another research team analyzed the imaging data from the Clopidogrel in High-risk patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events (CHANCE) trial [25]. They presented that small artery occlusion was more prevalent in patients with dolichoectasia compared with those without dolichoectasia. These two studies had differences in types of CSVD and VBD, which may yield potential biases. Similarly, we also speculated that the association between VBD and CSVD might have heterogeneity among different races.
In 2019, Fierini et al. [14] investigated the clinical and demographic characteristics of patients with IADE and described the coexistence of CSVD and systemic arteriopathy. The authors found a variable grade of global cortical atrophy and systemic arterial ectasia in most IADE patients. The involvement of brain-supplying arteries is presumably a part of systemic arteriopathy in patients with IADE, including not only large arteries but also small vessels. This, highlights the necessity of assessing the whole arterial system in clinical practice. Moreover, the neuropsychological examinations revealed a multidomain cognitive impairment in most IADE patients. Their findings indicated that CSVD is frequent in patients with IADE, but most of the IADE patients may have different degrees of cognitive decline. The definitive correlation between IADE and cognitive dysfunction is unknown and requires further study.
In the past 20 years, a series of independent cohort to population-based studies have strongly promoted the association between VBD and CSVD from the clinical and pathological perspectives and included different ages and races. Over time, increasing evidence has revealed that VBD is associated with imaging markers of different CSVD subtypes, which may be variable in different age groups (Table 1). In addition, the prevalence of BA or intracranial dolichoectasia is varied in different studies and different populations, suggesting the incidence of dolichoectasia may differ across races. However, to date, no strong evidence supporting a difference in prevalence has been found along racial or ethnic lines. From our review of the correlated literature and three major studies in Asia, we found no significant differences in the incidence of IADE or VBD and the association between CSVD when the Asian studies were compared to studies from western countries. Furthermore, the intrinsic pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the association between IADE and CSVD remain unclear.
There are some presumed interrelationships between the two entities, such as hemodynamic alteration, MMP, and genetic factors.
The primary relationship between IADE and CSVD is lacunar infarct, in particular at pons, which strongly supports the theory that IADE results in CSVD. IADE can cause brain infarction, but this may also be a coincidental finding. Potential mechanisms of brain infarction in patients with IADE include major distortion and obstruction of perforating arteries arising from the dolichoectatic BA, in situ thrombosis, and emboli from the dolichoectatic artery [1,2]. Intraluminal thrombus can be a complication of an atherosclerotic plaque or be present without any underlying atherosclerotic lesion. Slow blood flow and morphological changes to the ectatic artery can lead to intraluminal thrombus formation [26]. The relative frequency of these risk factors is unknown, but an atherosclerotic plaque was reported in ten (43%) of 23 patients with basilar dolichoectasia in an autopsy study [27]. In a case-control study, the arterial territory of the cerebral infarction was supplied by a dolichoectatic artery in 70% of cases [18]. Of 35 Korean patients, BA dolichoectasia was noted in 11 (31%) patients with paramedian pontine infarction without vertebrobasilar stenosis [28].
Hemodynamics may play an important role in dolichoectasia [29]. Formation of a cerebral aneurysm initiates in response to excessive hemodynamic stress from vascular bifurcation to the intracranial arterial wall. The hemodynamic stress may lead to endothelial dysfunction, infiltration of inflammatory cells, phenotypic modulation and degeneration of smooth muscles, remodeling of ECM, and subsequent cell death and vessel wall degeneration. During the process, hemodynamic alterations, an inflammatory reaction by activated macrophages, and vascular smooth muscle cell death are presumably essential for the development of a brain aneurysm [30]. Among patients with unilateral vertebral artery hypoplasia, a trend of both arterial dilatation over the other dominant vertebral artery and elongation to the BA has been observed [31], suggesting that the dominant vertebral artery by hemodynamic alteration may be a risk factor for VBD. Tanaka et al. [32] reported a significant association between BA diameter and the pulsatility index of the carotid artery, which represents the vascular resistance. Also, increased vascular resistance, atherosclerosis, and increased flow volume may play a role in BA dilation.
Hemodynamic factors can also play a crucial role in the process of CSVD. Large artery stiffening, carotid and intracranial arterial pulsatility, and hemodynamic markers of arteries have all recently been shown to be associated with CSVD [33]. The measures of cerebral and extracerebral vasodilator responses correlated with the radiologic burden of symptomatic patients with CSVD [34]. Vessel wall changes owing to hemodynamic factors may in fact be responsible for the rupture of the vessel. This may present as hemorrhagic CSVD or structural restriction of the vessel lumen (or its functional dysregulation), which can lead to a state of chronic hypoperfusion that is responsible for incomplete infarct or acute focal necrosis (lacunar infarct) [35].
IADE and CSVD may have a common pathogenesis via hemodynamic changes that contribute to endothelial injuries. Increased arterial stiffness and vascular resistance may underlie both BA dilation and CSVD [32]. Pulsatile hemodynamics relate to brain small perivascular spaces, and the association is the strongest among individuals with dilated brain arteries [36]. The small arteries and large arteries may affect each other with exaggerated arterial damage. As a possible hemodynamic result,the presence of microvascular structural alterations are near upon interrelationships with structural or mechanical changes of large conductance arteries [37]. Endothelial function impaired in systemic vessels has also been associated with lacunar stroke, and it is a good hemodynamic marker linked large arteries to small arteries that investigated by means of flow-mediated dilatation in the brachial artery [38]. A study showed that aortic arch pulse wave velocity was significantly associated with lacunar brain infarcts. Brachial artery flow mediated dilation was associated with Fazekas grade 2 or 3 periventricular WMHs [39]. These outcomes purported the possible association of aortic compliance and brachial endothelial function with CSVD. The vascular endothelium, located at the interface of blood and tissue, is essential for vascular homeostasis. It is capable of sensing changes in the hemodynamic forces and blood borne factors and responds by releasing various types of substances involved in the different pathways controlling endothelial function. Endothelial dysfunction may have an important role in the association between IADE and CSVD, although much molecular details still need to be clarified [40].
It is unclear whether IADE are primary changes preceding CSVD or secondary changes caused by impairment of upstream small vessels [41]. An easily accepted point of view is that IADE are primary changes preceding CSVD. However, another perspective is that CSVD occurs initially at reduced peripheral vascular beds that increase the pressure on larger cerebral vessels, leading to their enlargement [42]. Regardless of the mechanism, dilative arteriopathy may be a surrogate marker for CSVD.
MMPs may be potential biomarkers linking IADE and CSVD, although existing evidence is still limited to cross-sectional studies [1-3]. This hypothesis may be based on the fact that both IADE and small-vessel arteriopathy affect the media of the artery [1-3]. MMPs are a family of proteases that act on the ECM as the ratelimiting step for connective tissue remodeling [43]. During the formation and structural maintenance of vessels, MMPs (i.e., MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9) with elastase and collagenase activity are molecular contributors to aneurysm formation as well as instability of atherosclerotic plaques [44]. The MMP-3/5A allele, which is associated with increased proteolytic activity, is found in a higher frequency in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms and coronary aneurysms [45]. Pico et al. [46] reported similarly that the MMP-3/5A genotype is associated with IADE, indicating a role for MMPs in the development of cerebral dilative arteriopathy. Conversely, abnormal upregulation of MMPs at the cellular level promotes cytotoxicity and central nervous system inflammation by degrading basal lamina proteins, which leads to disruption of the blood-brain barrier and breakdown of myelin [47]. Increased MMP activities are involved in the pathogenesis of several central nervous system diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and acute stroke [48]. Among patients with CSVD, pathological studies have shown that diffuse inflammatory responses are associated with high levels of MMP-3-positive macrophages in damaged white matter as well as clustering of cells expressing MMP-2 and MMP-3 around the small penetrating vessels [20]. Therefore, we speculate that IADE and CSVD may have common triggers that activate a cascade of events that lead to an abnormal proteolytic balance. Furthermore, MMPs may represent potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of these cerebrovascular diseases.
Zhang et al. [49] evaluated correlations between MMP-2 and MMP-9 single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk of CSVD. Comparison analyses between CSVD patients and controls revealed a significant correlation between CSVD and hypertension, as well as a prevalence of hypertension in ischemic leukoaraiosis. Further genotype analysis showed that the frequency of the MMP-2-1306 CC genotype was higher in patients with ischemic leukoaraiosis than in the controls. Additionally, logistic regression analysis with adjustment for age, sex, and vascular risk factors showed that the MMP-2-1306 T/C polymorphism was an independent predictor for ischemic leukoaraiosis. Recently, our research team preliminarily tested the hypothesis that the imbalance between MMPs and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) may play a potential role in bridging VBD with LI and WMH. We studied 212 patients with vertigo who underwent multimodal MRI tests for VBD, LI, and WMH identification. Our results showed that the serum level of MMP-9 and the ratio of MMP-9/TIMP-1 levels were both significantly higher in vertigo patients with VBD and BA elongation compared to those with normal arterial size [50]. Our findings suggest MMP-9 and TIMP-1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of VBD and WMH, which may help with the diagnosis and treatment of these cerebrovascular diseases in the future.
The ECM is important for maintaining the structure and function of the tunica media component, and arteriopathy may be caused by injuries in the arterial wall. Therefore, we hypothesize that IADE and CSVD may be attributed to abnormal vascular remodeling that is driven by an abnormal MMP/TIMP pathway in response to common vascular risk factors and underlying genetic alterations, and that IADE-related hemodynamic changes may result in initiation or progression of CSVD. However, the definitive causal link between IADE and CSVD is still unknown (Figure 3).
Currently, it is thought that genetic factors are involved in the pathogenesis of IADE and CSVD. In the literature, the cooccurrence of VBD and single-gene inherited diseases has been reported, such as elastofibroblastic dysplasia type IV [51], neurofibroma type 1 [52], Fabry’s disease [53], Marfan’s syndrome [54], Pompe’s disease [55], autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease [56], and vascular tortuosity syndrome [57]. CSVD represents a heterogeneous group of disorders leading to stroke and cognitive impairment. While most CSVD appear sporadic and related to elderly age and hypertension, several early-onset monogenic forms have also been reported [58]. Genetic studies of sporadic CSVD have demonstrated a high degree of heritability, particularly among patients with young-onset stroke. Common genetic variants in monogenic diseases may contribute to pathological progress in several CSVD subtypes, revealing distinct genetic mechanisms in different subtypes of CSVD [59]. A genome-wide association study found that epidermal growth factor containing fibulin extracellular matrix protein 1 (EFEMP1), tripartite motif 65 (TRIM65), neuralized E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (NEURL1), and programmed cell death 11 (PDCD11) gene polymorphisms were related to the severity of WMH in CSVD [60]. However, there have been few direct genetic studies on the association between VBD and CSVD [61].
Patients with Fabry’s disease are prone to developing concurrent VBD and CSVD [62]. Fabry’s disease is characterized by intracellular lipid deposition (i.e., lysosomal glycosphingolipid deposition). The deposited lipid is mainly seen as vacuoles in endothelial and smooth muscle cells. In small vessels, this deposition can lead to luminal stenosis, whereas in medium-sized arteries it weakens the arterial wall leading to tortuosity and dilatation. On MRI, Fabry’s disease manifests as white matter lesions and the pulvinar sign (increased pulvinar signal intensity on T1-weighted imaging) [53]. A previous study also reported a higher prevalence of IADE in patients with late-onset Pompe’s disease [55]. It is worth noting that CMBs without leukoaraiosis have been reported in a 68-year-old patient with Pompe’s disease and IADE [56].
Mutations in the collagen IV alpha 1 or 2 gene (COL4A1/2) may damage the ECM, which may be the common pathological basis of VBD and CSVD. This genetic hypothesis strongly supports the association between VBD and CSVD (Figure 4) [63]. In a previous case report, a patient with severe VBD had complete gene duplication confirmed by quantitative multiplex polymerase chain reaction of short fluorescent fragment analysis and microsatellites spanning the COL4A1/COL4A2 locus [64]. The authors suspected that the mutations might also be associated with CSVD because of the presence of LIs, microbleeds, and leukoencephalopathy [64,65]. To date, most reported COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations are missense variants. A dominant-negative mechanism or haploinsufficiency may explain the mutation-related pathogenesis [66].
Recently, a new genetic alteration has been found to link IADE with CSVD. Two sibling pediatric patients, who were born with a 6p25.3 deletion, presented with carotid dolichoectasia and VBD [67]. MRI of both children showed asymptomatic elongation and dilation of the vertebrobasilar system and “kissing” carotid arteries; meanwhile, axial T2-weighted MRI demonstrated enlarged perivascular spaces in the two patients. Microarray analysis identified a 1.5-Mb deletion of 6p25.3 covering 15 genes including forkhead box C1 (FOXC1), which has been implicated in defects in vascular morphogenesis [67].
Although the clinical manifestations of VBD are well known, the role of genetic factors in its pathogenesis remains unclear. Previous evidence reporting the occurrence of VBD in these two siblings has highlighted the potential role of genetic factors in the development of VBD [68]. Dolichoectatic arteries have a thin arterial wall, with prominent degeneration of the internal elastic lamina and thinning of the media. Genetic alterations may lead to a predisposition to defects in arterial wall ECM components such as collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, and laminin, thus making these vessels susceptible to dilatation. The co-occurrence of IADE with abdominal aortic aneurysm and coronary artery ectasias has been reported, indicating that there may be a generalized (genetic) rather than a local (atherosclerosis) cause for the abnormal arterial dilatation [69]. In Caucasians, VBD is independently associated with LI, suggesting that racial factors may be involved in the association between VBD and CSVD [70]. In an experimental study, elastase was injected into the cisterna magna of C57BL/6J and 129/SvEv (SV129) mice. Successful VBD induction was noted in 67% of the C57BL/6J strain versus 0% of the SV129 strain. In the C57BL/6J mice, the researchers demonstrated arterial wall dilation and elongation characterized by internal elastic lamina disruption, muscular layer discontinuity, inflammatory cell infiltration, and high MMP expression in the media. C57BL/6J mice had a greater susceptibility to VBD induction than SV129 mice [71]. These findings are important for identifying pivotal elements relevant to the development of VBD. In the future, linkage analysis of different strains may provide new insight into the genetic determinants of VBD susceptibility.
Based on the above evidence, we hypothesize that genetic factors contribute to the association between VBD and CSVD (Figure 5).
Over the past 20 years, researchers have given more attention to the relationship between IADE and CSVD. Previous studies have shown that there is a correlation between IADE and imaging markers of different CSVD subtypes, and existing evidence supports that the correlation between IADE and CSVD may display heterogeneity among different age groups and different populations. However, the mechanisms underlying the association between IADE and CSVD remain unclear, but they may be related to hemodynamic factors, an abnormal MMP pathway, and genetic alterations. In the future, more clinical and basic research studies are needed to elucidate the causal relationship between IADE and CSVD and the related molecular mechanisms. It will be very interesting to compare genetic differences with IADE and CSVD between Asian and western countries because CSVD is more common in Asians, and there is some indication through existing evidence that ethnic differences may play a role.
Figure 1.
A 66-year-old hypertensive male smoker who succumbed to a substantial right putaminal and ventricular hemorrhage. (A) Basilar, vertebral, and internal carotid arteries were dolichoectatic with enlarged diameters and thin walls and were free of any atherosclerotic lesions. (B) There were multiple, small, deep infarcts and dilatation of perivascular spaces on the celloidin-fixed section (Loyez staining for myelin). (C) Microscopic examination of the brain showed cerebral small vessel disease with lipohyalinosis (×40). (D) Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed hyalinosclerosis (×40). Adapted from Pico et al. [20], with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
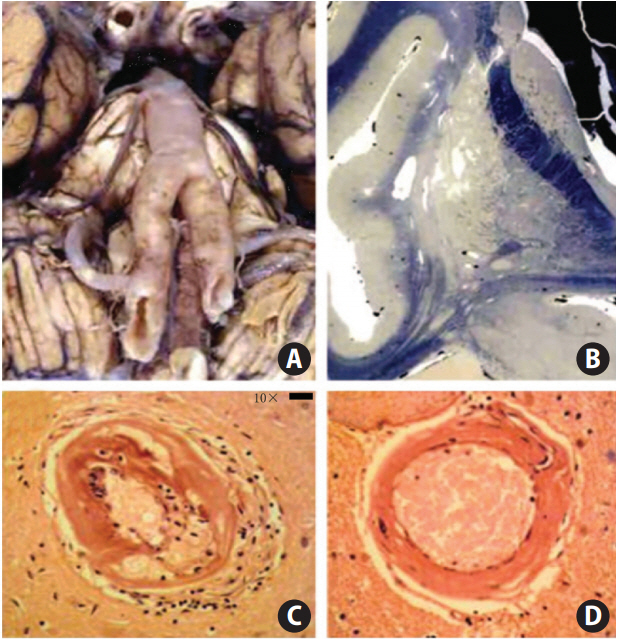
Figure 2.
Our representative case of a 71-year-old hypertensive woman presenting with vertigo and nausea. (A, B) Magnetic resonance angiography showed right vertebral artery dysplasia and basilar artery prolongation and tortuosity; T2-weighted (C) and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (D) imaging showed hyperintensity in bilateral periventricular white matter, corresponding to Fazekas Grade 3. (E, F, G) Susceptibility weighted imaging showed microbleeds in the pons, cerebellum, and thalamus. Red arrows showed microbleeds.

Figure 3.
Overview of pathological mechanisms underlying the association between intracranial arterial dolichoectasia (IADE) and cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). IADE and CSVD can be viewed as a common final pathway of arterial wall response or damage from various mechanisms. Hypothetical interaction between vascular aging, hemodynamic factors, predisposing genotype and imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) that might impair the tunica media, extracellular matrix, smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. CSVD and IADE could be found at the same time or IADE and CSVD are mutually affected by hemodynamic changes that result in initiation and progression of the two entities.
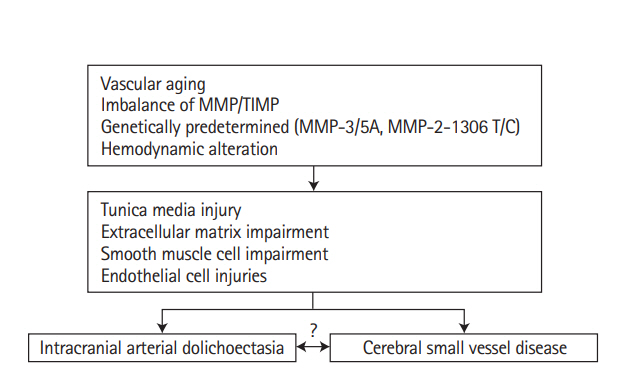
Figure 4.
Female patients from the age of 44 to 61 years old with cerebral small vessel disease harbored abnormalities in the collagen IV alpha 1 or 2 gene (COL4A1/COL4A2) locus. (Aa, Ab) These shows white matter lesions in a 44-year-old patient; (Ac-Ai) these shows acute subcortical infarction, cerebral microbleeds, white matter lesions and vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia in a 56-year-old patient; (Aj) it shows a small infarct under the right cortex in a 59-year-old patient; (Ak, Al) these shows the progression of white matter lesions in a 61-year-old patient. (B, C, D, E) Gene detection revealed abnormalities at the COL4A1/COL4A2 locus. Adapted from Renard et al. [63], with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figure 5.
Overview of genetic mechanisms underlying vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD) and cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). Fabry’s disease and late-onset Pompe disease are prone to a combination of intracranial arterial dolichoectasia (IADE) with CSVD. In addition, there was presentation of VBD with CSVD in cases of the collagen IV alpha 1 or 2 gene (COL4A1/COL4A2) mutations and forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) deletion in carrier siblings, indicating that there is a genetic association of IADE with CSVD. Racial factors, such as being Caucasian, may be involved in the association of VBD with IADE. Co-occurrence of diseases, mice strain and siblings with genetic variants increased susceptibility to IADE, pointing to the genetic nature of IADE. A genome-wide association study found that epidermal growth factor containing fibulin extracellular matrix protein 1 (EFEMP1), tripartite motif 65 (TRIM65), neuralized E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (NEURL1), and programmed cell death 11 (PDCD11) gene polymorphisms were related to the WMH level of CSVD image markers. The above evidence supports the theory that genetic factors might contribute to the co-occurrence of VBD with CSVD. WMH, white matter hyperintensity.

Table 1.
Existing studies investigating the correlation between IADE and CSVD
| Study | Population | Mean age of included patients | No. of patients | Ethnicity | Diagnostic method | Study design | Location of doli-choectasia | Marker of CSVD | Major findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ince et al. (1998) [11] | Stroke patients | 75 yr | 387 | Resident of Rochester | CT or MRI | Retrospective research | Both anterior and posterior circulation | Lacunar infarction | Lacunar infarction was more common among patients with dolichoectasia (42% vs. 17%). |
| Pico et al. (2003) [18] | Stroke patients | 18-85 yr old | 510 | Caucasian | MRI | Case-control study | Both anterior and posterior circulation | Lacunar infarction | Lacunar infarction was more frequent in patients with IADE (36% vs. 19%). |
| Pico et al. (2005) [19] | Stroke patients | 18-85 yr old | 510 | Caucasian | MRi | Case-control study | Both anterior and posterior circulation | Multilacunar infarction, leukoaraiosis, dilatation of perivascular spaces | Patients with IADE had higher incidences of multilacunar infarctions, severe leukoaraiosis, and severe perivascular spaces than patients without IADE. |
| Pico et aI. (2007) [20] | Stroke patients | 78 yr | 381 | Caucasian | Autopsies | Case-control study | Both anterior and posterior circulation | Lacunar infarction, multilacunes, dilatation of perivascular spaces | CSVD was more frequent in patients with IADE than those without IADE. The adjusted odds ratio was 3.85. |
| Park et al. (2013) [21] | Stroke patients/TIA | 68 yr old with VBD, and 65 yr old without VBD | 182 | Asian | MRI and GRE-MRI | Retrospective study | VBD | CMB, WMH | VBD was independently associated with CMBs, especially in the posterior circulation territory. |
| Thijs et al. (2017) [22] | TIA/stroke patients | 48 yr old with IADE, and 46 yr old without IADE | 3,850 | 15 European countries | MRI, GRE-T2* | Prospective, hospital-based, study | Both anterior and posterior circulation | Lacunar infarctions, WMH, CMB | Dolichoectasia was associated with imaging markers of CSVD and brain stem localization of acute and old infarcts in younger patients with TIA and ischemic stroke. |
| Del Brutto et al. (2017) [23] | Community-dwelling older adults living in rural Ecuador | 70 yr old | 346 | Ecuadorian native/Mestizo ethnic | MRI, GRE-MRI | Registered study | Basilar artery dolichoectasia | CMB, WMH, lacunar infarcts, enlarged perivascular spaces | Basilar artery diameter was associated with the severity of WMH. Dolichosis was associated with deep CMBs. Dolichoectasia was associated with both WMH and CMBs. |
| Zhai et al. (2018) [24] | An ongoing community-based cohort study in China | 57 yr old | 1,237 | Asian | MRI, SWI | Cross-sectional analysis of Shunyi cohort study | Both anterior and posterior circulation | CMB, WMH, lacunar infarcts, enlarged perivascular spaces, brain atrophy | Basilar arterial dolichoectasia was mainly associated with dilated perivascular spaces in basal ganglia and, to a lesser extent, associated with lacunes and microbleeds. |
| Zhang et al. (2018) [25] | TIA and minor stroke patients | 63 yr old | 1,089 | Asian | MRI | Registered study (CHANCE trial) | Basilar artery dolichoectasia | Small artery occlusion | Small artery occlusion was more prevalent in patients with dolichoectasia compared with those without dolichoectasia. |
| Fierini et al. (2019) [14] | Chronic cerebrovascular diseases | 68 yr old with IADE, and 70 yr old without IADE | 251 | Italian | MRI, GRE, and CTA | Cross-sectional analysis | Both anterior and posterior circulation | CMB, WMH, lacunar infarcts, enlarged perivascular spaces, brain atrophy | There was a high prevalence of CSVD in patients with IADE. Cognitive decline was frequent in these patients. |
IADE, intracranial arterial dolichoectasia; CSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; TIA, transient ischemic attack; VBD, vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia; GRE-MRI: gradient-echo magnetic resonance imaging; CMB, cerebral microbleed; WMH, white matter hyperintensity; T2*-weighted magnetic resonance imaging; SWI, susceptibility weighted imaging; CHANCE, Clopidogrel in High-risk patients with Acute Nondis-abling Cerebrovascular Events; CTA, computed tomographic angiography.
References
1. Pico F, Labreuche J, Amarenco P. Pathophysiology, presentation, prognosis, and management of intracranial arterial dolichoectasia. Lancet Neurol 2015;14:833-845.


2. Del Brutto VJ, Ortiz JG, Biller J. Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia. Front Neurol 2017;8:344.



3. Gutierrez J, Sacco RL, Wright CB. Dolichoectasia: an evolving arterial disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2011;7:41-50.



4. Wolters FJ, Rinkel GJ, Vergouwen MD. Clinical course and treatment of vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia: a systematic review of the literature. Neurol Res 2013;35:131-137.


5. Smoker WR, Price MJ, Keyes WD, Corbett JJ, Gentry LR. High-resolution computed tomography of the basilar artery: 1. Normal size and position. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1986;7:55-60.


7. Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:822-838.



8. Kim TH, Choi JW, Roh HG, Moon WJ, Moon SG, Chun YI, et al. Atherosclerotic arterial wall change of non-stenotic intracracranial arteries on high-resolution MRI at 3.0T: correlation with cerebrovascular risk factors and white matter hyperintensity. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2014;126:1-6.


9. Brisset M, Boutouyrie P, Pico F, Zhu Y, Zureik M, Schilling S, et al. Large-vessel correlates of cerebral small-vessel disease. Neurology 2013;80:662-669.



10. Zhu H, Li Z, Lv J, Zhao R. Effects of cerebral small vessel disease on the outcome of patients with ischemic stroke caused by large artery atherosclerosis. Neurol Res 2018;40:381-390.


11. Ince B, Petty GW, Brown RD Jr, Chu CP, Sicks JD, Whisnant JP. Dolichoectasia of the intracranial arteries in patients with first ischemic stroke: a population-based study. Neurology 1998;50:1694-1698.


12. Gutierrez J. Dolichoectasia and the risk of stroke and vascular disease: a critical appraisal. Curr Cardiol Rep 2014;16:525.



13. Lau KK, Pego P, Mazzucco S, Li L, Howard DP, Küker W, et al. Age and sex-specific associations of carotid pulsatility with small vessel disease burden in transient ischemic attack and ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 2018;13:832-839.



14. Fierini F, Poggesi A, Salvadori E, Acquafresca M, Fainardi E, Moretti M, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease and systemic arteriopathy in intracranial arterial dolichoectasia patients. Acta Neurol Scand 2019;139:150-157.


15. Schulz UG, Grüter BE, Briley D, Rothwell PM. Leukoaraiosis and increased cerebral susceptibility to ischemia: lack of confounding by carotid disease. J Am Heart Assoc 2013;2:e000261.



16. Lu T, Liang J, Wei N, Pan L, Yang H, Weng B, et al. Extracranial artery stenosis is associated with total MRI burden of cerebral small vessel disease in ischemic stroke patients of suspected small or large artery origins. Front Neurol 2019;10:243.



17. Xu WH. Large artery: an important target for cerebral small vessel diseases. Ann Transl Med 2014;2:78.


18. Pico F, Labreuche J, Touboul PJ, Amarenco P; GENIC Investigators. Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia and its relation with atherosclerosis and stroke subtype. Neurology 2003;61:1736-1742.


19. Pico F, Labreuche J, Touboul PJ, Leys D, Amarenco P. Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia and small-vessel disease in stroke patients. Ann Neurol 2005;57:472-479.


20. Pico F, Labreuche J, Seilhean D, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ, Amarenco P. Association of small-vessel disease with dilatative arteriopathy of the brain: neuropathologic evidence. Stroke 2007;38:1197-1202.


21. Park JM, Koo JS, Kim BK, Kwon O, Lee JJ, Kang K, et al. Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia as a risk factor for cerebral microbleeds. Eur J Neurol 2013;20:824-830.


22. Thijs V, Grittner U, Fazekas F, McCabe DJH, Giese AK, Kessler C, et al. Dolichoectasia and small vessel disease in young patients with transient ischemic attack and stroke. Stroke 2017;48:2361-2367.


23. Del Brutto OH, Mera RM, Del Brutto VJ, Costa AF, Zambrano M, Brorson J. Basilar artery dolichoectasia: prevalence and correlates with markers of cerebral small vessel disease in community-dwelling older adults. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2017;26:2909-2914.


24. Zhai FF, Yan S, Li ML, Han F, Wang Q, Zhou LX, et al. Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia and stenosis: risk factors and relation to cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2018;49:1135-1140.


25. Zhang X, Jing J, Zhao X, Liu L, Meng X, Wang A, et al. Prognosis of dolichoectasia in non-cardioembolic transient ischemic attack and minor stroke. Neurol Res 2018;40:452-458.


26. Lou M, Caplan LR. Vertebrobasilar dilatative arteriopathy (dolichoectasia). Ann N Y Acad Sci 2010;1184:121-133.


27. Nijensohn DE, Saez RJ, Reagan TJ. Clinical significance of basilar artery aneurysms. Neurology 1974;24:301-305.


28. Kwon HM, Kim JH, Lim JS, Park JH, Lee SH, Lee YS. Basilar artery dolichoectasia is associated with paramedian pontine infarction. Cerebrovasc Dis 2009;27:114-118.


29. Sho E, Sho M, Singh TM, Nanjo H, Komatsu M, Xu C, et al. Arterial enlargement in response to high flow requires early expression of matrix metalloproteinases to degrade extracellular matrix. Exp Mol Pathol 2002;73:142-153.


30. Aoki T. Inflammation mediates the pathogenesis of cerebral aneurysm and becomes therapeutic target. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2015;2:86-92.

31. Hong JM, Chung CS, Bang OY, Yong SW, Joo IS, Huh K. Vertebral artery dominance contributes to basilar artery curvature and peri-vertebrobasilar junctional infarcts. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009;80:1087-1092.


32. Tanaka M, Sakaguchi M, Miwa K, Okazaki S, Furukado S, Yagita Y, et al. Basilar artery diameter is an independent predictor of incident cardiovascular events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2013;33:2240-2244.


33. Webb AJ, Simoni M, Mazzucco S, Kuker W, Schulz U, Rothwell PM. Increased cerebral arterial pulsatility in patients with leukoaraiosis: arterial stiffness enhances transmission of aortic pulsatility. Stroke 2012;43:2631-2636.


34. Staszewski J, Skrobowska E, Piusińska-Macoch R, Brodacki B, Stępień A. Cerebral and extracerebral vasoreactivity in patients with different clinical manifestations of cerebral small-vessel disease: data from the significance of hemodynamic and hemostatic factors in the course of different manifestations of cerebral small-vessel disease study. J Ultrasound Med 2019;38:975-987.


35. Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:689-701.


36. Gutierrez J, DiTullio M, Cheung YKK, Alperin N, Bagci A, Sacco RL, et al. Brain arterial dilatation modifies the association between extracranial pulsatile hemodynamics and brain perivascular spaces: the Northern Manhattan Study. Hypertens Res 2019;42:1019-1028.




37. Rizzoni D, Agabiti-Rosei C, Agabiti-Rosei E. Hemodynamic consequences of changes in microvascular structure. Am J Hypertens 2017;30:939-946.



38. Pretnar-Oblak J, Sabovic M, Pogacnik T, Sebestjen M, Zaletel M. Flow-mediated dilatation and intima-media thickness in patients with lacunar infarctions. Acta Neurol Scand 2006;113:273-277.


39. Shan Y, Lin J, Xu P, Zeng M, Lin H, Yan H. Association of aortic compliance and brachial endothelial function with cerebral small vessel disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: assessment with high-resolution MRI. Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:1609317.




40. Poggesi A, Pasi M, Pescini F, Pantoni L, Inzitari D. Circulating biologic markers of endothelial dysfunction in cerebral small vessel disease: a review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016;36:72-94.



41. Ichikawa H, Takahashi N, Mukai M, Katoh H, Akizawa T, Kawamura M. Intracranial dilative arteriopathy is associated with chronic kidney disease and small vessel diseases in the elderly. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2009;18:435-442.


42. Ichikawa H, Mukai M, Katoh H, Hieda S, Murakami H, Kawamura M. Cerebral microbleeds and dilative remodeling of the basilar artery: a magnetic resonance imaging study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2011;20:429-435.


43. Van Doren SR. Matrix metalloproteinase interactions with collagen and elastin. Matrix Biol 2015;44-46:224-231.


44. Rabkin SW. The role matrix metalloproteinases in the production of aortic aneurysm. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2017;147:239-265.


45. Adovasio R, Calvagna C, Sgorlon G, Zamolo F, Mearelli F, Biolo G, et al. Growth rate of small abdominal aortic aneurysms and genetic polymorphisms of matrix metalloproteases-1, -3, and -9. Int J Angiol 2016;25:93-98.



46. Pico F, Jacob MP, Labreuche J, Soufir N, Touboul PJ, Benessiano J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 and intracranial arterial dolichoectasia. Ann Neurol 2010;67:508-515.


47. Rempe RG, Hartz AMS, Bauer B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: versatile breakers and makers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2016;36:1481-1507.



48. De Luca C, Papa M. Matrix metalloproteinases, neural extracellular matrix, and central nervous system pathology. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2017;148:167-202.


49. Zhang M, Zhu W, Yun W, Wang Q, Cheng M, Zhang Z, et al. Correlation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 single nucleotide polymorphisms with the risk of small vessel disease (SVD). J Neurol Sci 2015;356:61-64.


50. Zhang DP, Peng YF, Zhang HL, Ma JG, Zhao M, Yin S, et al. Basilar artery tortuosity is associated with white matter hyperintensities by TIMP-1. Front Neurosci 2019;13:836.



51. Kato T, Hattori H, Yorifuji T, Tashiro Y, Nakahata T. Intracranial aneurysms in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV in early childhood. Pediatr Neurol 2001;25:336-339.


52. Giannantoni NM, Broccolini A, Frisullo G, Pilato F, Profice P, Morosetti R, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 1 associated with vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia and pontine ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging 2015;25:505-506.


53. Manara R, Carlier RY, Righetto S, Citton V, Locatelli G, Colas F, et al. Basilar artery changes in fabry disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2017;38:531-536.



54. Finney LH, Roberts TS, Anderson RE. Giant intracranial aneurysm associated with Marfan’s syndrome. Case report. J Neurosurg 1976;45:342-347.


55. Montagnese F, Granata F, Musumeci O, Rodolico C, Mondello S, Barca E, et al. Intracranial arterial abnormalities in patients with late onset Pompe disease (LOPD). J Inherit Metab Dis 2016;39:391-398.



56. Laforêt P, Petiot P, Nicolino M, Orlikowski D, Caillaud C, Pellegrini N, et al. Dilative arteriopathy and basilar artery dolichoectasia complicating late-onset Pompe disease. Neurology 2008;70:2063-2066.


57. Cartwright MS, Hickling WH, Roach ES. Ischemic stroke in an adolescent with arterial tortuosity syndrome. Neurology 2006;67:360-361.


58. Cuadrado-Godia E, Dwivedi P, Sharma S, Ois Santiago A, Roquer Gonzalez J, Balcells M, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease: a review focusing on pathophysiology, biomarkers, and machine learning strategies. J Stroke 2018;20:302-320.




59. Giau VV, Bagyinszky E, Youn YC, An SSA, Kim SY. Genetic factors of cerebral small vessel disease and their potential clinical outcome. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:4298.



60. Traylor M, Zhang CR, Adib-Samii P, Devan WJ, Parsons OE, Lanfranconi S, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of cerebral white matter hyperintensities in patients with stroke. Neurology 2016;86:146-153.



61. Rutten-Jacobs LCA, Rost NS. Emerging insights from the genetics of cerebral small-vessel disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2019;Jan. 8. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13998.

63. Renard D, Miné M, Pipiras E, Labauge P, Delahaye A, Benzacken B, et al. Cerebral small-vessel disease associated with COL4A1 and COL4A2 gene duplications. Neurology 2014;83:1029-1031.


64. Miyatake S, Schneeberger S, Koyama N, Yokochi K, Ohmura K, Shiina M, et al. Biallelic COLGALT1 variants are associated with cerebral small vessel disease. Ann Neurol 2018;84:843-853.


65. Gunda B, Mine M, Kovács T, Hornyák C, Bereczki D, Várallyay G, et al. COL4A2 mutation causing adult onset recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage and leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol 2014;261:500-503.



66. Verbeek E, Meuwissen ME, Verheijen FW, Govaert PP, Licht DJ, Kuo DS, et al. COL4A2 mutation associated with familial porencephaly and small-vessel disease. Eur J Hum Genet 2012;20:844-851.




67. Kearns KN, Yagmurlu K, Chen CJ, Jane J Jr, Park MS, Kalani MYS. Deletion of 6p25.3 is associated with cerebrovascular dolichoectasia: report of 2 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 2019;54:196-200.


68. Gupta D, George UB, Pandian JD. Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia and a tale of two brothers. Neurol India 2010;58:810-812.


69. Pico F, Labreuche J, Hauw JJ, Seilhean D, Duyckaerts C, Amarenco P. Coronary and basilar artery ectasia are associated: results from an autopsy case-control study. Stroke 2016;47:224-227.