 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 23(3); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Mechanical thrombectomy renders the occluding clot available for analysis. Insights into thrombus composition could help establish the stroke cause. We aimed to investigate the value of clot composition analysis as a complementary diagnostic tool in determining the etiology of large vessel occlusion (LVO) ischemic strokes (International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews [PROSPERO] registration # CRD42020199436). Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, we ran searches on Medline (using the PubMed interface) and Web of Science for studies reporting analyses of thrombi retrieved from LVO stroke patients subjected to mechanical thrombectomy (January 1, 2006 to September 21, 2020). The PubMed search was updated weekly up to February 22, 2021. Reference lists of included studies and relevant reviews were hand-searched. From 1,714 identified studies, 134 eligible studies (97 cohort studies, 31 case reports, and six case series) were included in the qualitative synthesis. Physical, histopathological, biological, and microbiological analyses provided information about the gross appearance, mechanical properties, structure, and composition of the thrombi. There were non-unanimous associations of thrombus size, structure, and composition (mainly proportions of fibrin and blood formed elements) with the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) etiology and underlying pathologies, and similarities between cryptogenic thrombi and those of known TOAST etiology. Individual thrombus analysis contributed to the diagnosis, mainly in atypical cases. Although cohort studies report an abundance of quantitative rates of main thrombus components, a definite clot signature for accurate diagnosis of stroke etiology is still lacking. Nevertheless, the qualitative examination of the embolus remains an invaluable tool for diagnosing individual cases, particularly regarding atypical stroke causes.
Mechanical thrombectomy has not only become the standard of care in the management of most large vessel occlusion (LVO) strokes, but it also renders the occluding clot available for lab bench analysis [1]. Insights into thrombus composition and properties could help determine its relationships with the clot signs on imaging, stroke cause, resistance to thrombectomy, procedural complications, and outcome measures [2].
A previous systematic review of studies published between January 2005 and December 2015 on imaging and histologic characteristics of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) concluded that the hyperdense artery sign was associated with red blood cell (RBC)-rich thrombi and improved recanalization rates. However, there was no association between the histopathological characteristics of thrombi, stroke etiology, and angiographic outcomes [3]. Another recent scoping systematic review focused on the impact of thrombus composition on the efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy and thrombolysis [4]. However, assessing the value of clot analysis in the diagnosis of stroke etiology and thus guiding secondary prevention strategies seems more challenging.
This systematic review aimed to evaluate the value of clot composition analysis as a complementary diagnostic tool in determining the LVO ischemic stroke etiology. Specifically, we addressed the following research questions: (1) What types of physical, histological, or other biological analyses have been carried out on thrombi retrieved from LVO stroke patients subjected to mechanical thrombectomy?; (2) What kind of information about the structure, and molecular and cellular composition of stroke thrombi has resulted from laboratory analyses?; (3) Could laboratory analyses of clot structure and composition be used as complementary diagnostic tools to determine stroke etiology, and thus reduce the proportion of cryptogenic strokes?; (4) Could specific findings in clot composition be used as ancillary information to diagnose atypical stroke etiologies due to underlying pathologies?
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
This systematic review was carried out according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [5]. The protocol was registered in the CRD-NIHR International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) with registration number CRD42020199436 [6].
We searched the published literature reporting the analysis of thrombi retrieved from LVO stroke patients subjected to mechanical thrombectomy and performed a qualitative assessment of the available evidence.
We carried out electronic searches on Medline (using the PubMed interface) and Web of Science from January 1, 2006, up to and including September 21, 2020. The search syntax was (stroke AND (thrombus OR thrombi OR clot)) AND (thrombectomy OR endovascular). The search fields were [Title/Abstract] in Medline (PubMed) and [Topic] in Web of Science. There were no language restrictions. The PubMed search was updated weekly through My NCBI up to February 22, 2021. References were added to a Mendeley Reference Manager library dedicated to this review’s topic, checked for duplicates, and completed with Mendeley’s feedback-delivering personalized suggestions for related articles. Reference lists of included studies and relevant reviews were hand-searched. The electronic database search was supplemented by searching for trial protocols through ClinicalTrials.gov Advanced Search syntax: condition or disease (ischemic stroke) and other terms ((thrombus OR thrombi OR clot) AND (thrombectomy OR composition)). The search was not extended to unpublished studies or other sources of grey literature.
The current review considered observational cohort studies, case series and case report studies reporting any kind of physical, histological, or other biological analyses carried out on thrombi retrieved from LVO stroke patients subjected to mechanical thrombectomy. We included studies published as full-length original research articles in any language, provided that the English abstract was available, and abstracts of conference proceedings in English language. In cases of studies with duplicate or overlapping patient populations, only the publication with the most complete dataset was included. Protocol articles, review articles and abstracts later published in full were also excluded.
Titles and abstracts yielded by the search were independently screened against the inclusion criteria by two reviewers. Full reports were obtained for all titles that appeared to meet the inclusion criteria or where there was any uncertainty. Reviewer pairs then screened the full-text reports of potentially eligible studies and decided whether these met the inclusion criteria. Disagreements were resolved through discussion and consensus involving a third reviewer.
The following information was collected from the eligible studies and extracted to tables independently by two reviewers: general information (first author name, year of publication, source, and type of study), type(s) of physical, histological, or other biological analyses carried out on thrombi, sample size(s), qualitative and quantitative features about thrombus composition, and diagnostic information regarding typical LVO ischemic stroke Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) etiologies or atypical etiologies with underlying pathologies.
Heterogeneity in study design, outcome measuring, and reporting precluded a meta-analysis of the association between thrombus composition and typical or atypical stroke etiology. Instead, a systematic narrative synthesis is provided with information presented in the text and tables to summarize and explain the characteristics and findings of the included studies.
A detailed study selection flow chart is shown in Figure 1. Briefly, a total of 2,665 records were identified electronically in the Web of Science and Medline (through PubMed) databases up to and including September 21, 2020. After removing duplicate and irrelevant records, and adding relevant records identified through an updated search on PubMed (up to and including February 22, 2021) and other sources, 152 full-text articles and congress abstracts were assessed for eligibility. Subsequent reasoned exclusions rendered 134 studies which were included in the qualitative synthesis (Supplementary Table 1).
A summary of the study characteristics is shown in Table 1. Most of them (72.39%) were observational cohort studies with a wide range of cohort sizes, varying from four to 1,022 patients with thrombus samples subjected to analysis (median, 65 [interquartile range, IQR, 37 to 105]). Thirty-one (23.13%) case reports and six (4.48%) case series were also included. In 108 out of the 134 studies, the retrieved thrombi were subjected to one or more types of histopathological examinations. Physical, biological, and/or microbiological analyses were carried out in 62 studies. A relationship between thrombus structure/composition and TOAST or atypical etiologies was reported in 54.48% of the studies. In 46.27% of the studies, the stroke etiology was not taken into consideration, or non-conclusive results were obtained.
The publication chronology of the studies is shown in Figure 2. Although Marder’s pioneering study was published 15 years ago [7], 75.37% of the studies have been published in the last 5 complete years (2016 to 2020). Of note, 80% of the studies assessing thrombus composition by means of biological analyses using biochemical or molecular biology techniques have been published in the last 3 complete years (2018 to 2020). Since 11 studies have been published in 2021 up to and including February 22, around 75 studies are estimated to be published in the present year.
The search for clinical trial protocols identified five ongoing studies in which thrombi and blood samples are being collected for histopathological and/or other biological analyses [8-12]. Concurrently, active multi-institutional registries like RESTORE (National University of Ireland) and Stroke Thromboembolism Registry of Imaging and Pathology, Mayo Clinic (STRIP) are compiling clinical, procedural, imaging, and histopathological data from patients with AIS.
Procedures for thrombus retrieval and subsequent analysis have been reviewed [1,13]. Briefly, after retracting the thrombectomy device, the retrieved clot material is gently removed from the device and transferred into saline solution. If clot per-pass analysis is desired, clot material from each pass can be processed separately. The macroscopic appearance and other physical properties of the retrieved thrombus can be freshly examined; otherwise, the clot can be flash-frozen for storage and later biological analyses. For histological analysis, the specimens are fixed, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and stained depending on the component of interest. Both manual quantifications and color-based segmentation analysis of thrombus components are used.
Supplementary Table 1 summarizes whether physical, histological, or biological analyses were carried out in each of the 134 included studies [7,14-146].
In 33 studies, thrombi were subjected to some kind of physical analysis. The gross appearance of the retrieved thrombus was reported in 29 studies. In case reports (20 studies) and case series (two studies), the macroscopic aspect of the thrombus was shown mostly through photographs. Mechanical behavior of the thrombi was analyzed in two studies using custom-made platforms and marketed devices, respectively. In one study the thrombi were scanned using high spatial-resolution three-dimensional (3D) T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to reveal morphological and other physical characteristics. Finally, advanced synchrotron-based imaging techniques were used in one study to map thrombus composition.
Different types of histopathological examinations, including conventional histology, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy, were carried out in 108 studies. The most frequently used conventional stains were hematoxylin and eosin (H&E, 86 studies), Martius Scarlet Blue (MSB, 18 studies), Elastica van Gieson (14 studies), Prussian blue (eight studies), Masson’s trichrome (five studies), and Von Kossa (four studies). Other seldom-used stains were periodic-acid Schiff, Carstairs’ staining, Picro-Mallory, Alcian blue, Luna, Mallory’s phosphotungstic acid-hematoxylin, Ladewig trichrome, naphthol AS-D chloroacetate, and Feulgen’s reaction. Immunohistochemistry was carried out in 45 studies with specific antibodies against cellular and biomolecular thrombus components. Finally, the thrombi composition and organization were analyzed at the ultrastructural level through electron microscopy in six studies.
Regarding biological analyses, thrombus composition was assessed through different biochemical, biomolecular, and cellular techniques, such as enzymatic assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), transcriptomics (real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction [qRT-PCR]), proteomics, metabolomics, and flow cytometry in 15 studies. Finally, microbiological analysis of the thrombi was performed through classical culture techniques, specific staining for bacteria/fungi and/or metagenomics (qPCR) in 20 studies.
Case reports and case series, usually presenting thrombectomies of LVOs of atypical etiologies, showed mostly photographic images of the thrombus, and described whether single or multiple clots were retrieved, as well as their gross appearance, including size, shape, consistency, visual texture, color, and homo/heterogeneous aspect [14-34].
Macroscopic analysis of retrieved thrombi was also carried out in some cohort studies and one case series. The clot color was categorized using three different terminologies. Two cohort studies classified the thrombus as “red-black” or “white,” showing similar results: 94.2% red-black thrombi versus 5.8% white thrombi [35]; and 91.4% red/black thrombi versus 8.6% white thrombi [36]. Another cohort study categorized the thrombi by visual assessment as pinkish (17.3%), red (53.8%), or dark red (28.8%) [37]. A fourth cohort study described the thrombi as slightly white, darker, or reddish, but did not report percentages [38]. Regarding thrombus size, other cohort studies focused on the total extracted clot area (ECA) for each case, defined as the sum of the clot areas from all clot fragments within a case [39]. In a cohort of 550 patients, the mean ECA for all cases was 64 mm2 and the median number of fragments per case was 3 [40]. Of note, bridging therapy was associated with the retrieval of significantly smaller clots [41,42]. Median ECA was 0.33 cm2 (IQR, 0.16 to 0.59) in patients pre-treated with alteplase (recombinant tissue plasminogen activator [rtPA]), versus 0.39 cm2 (IQR, 0.22 to 0.82) in patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy alone [41]. Finally, in a case series of five patients the median volume of the thrombus, calculated using the ellipsoid formula (4/3πr1r2r3), was 10.47 mm3 [43].
Only two studies with limited sample sizes evaluated the mechanical behavior of the thrombi. The specimens were mechanically heterogeneous, in line with the histological heterogeneity. Stiffness and elasticity were measured with a dynamic mechanical analyzer, showing that red thromboemboli composed mainly of fibrin (FBR) and RBC were much softer than the calcified and cholesterol-rich material [44]. The tensile strength and response to stress were measured with a quasistatic uniaxial tensile test using a custom-made platform. The ultimate tensile strain of the emboli increased with a higher platelet (PLT) percentage, and the ultimate tensile stress increased with a higher FBR percentage and decreased with a higher RBC percentage [45].
Multiparametric MRI has been used to characterize retrieved cerebral thrombi. Preliminary results showed that T1-weighted images with the corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (water mobility) and T2 maps (relaxation time) could be used to assess thrombus compactness and microstructure, which in turn reflect RBC and PLT/FBR meshwork content [46]. Advanced synchrotron-based imaging techniques, including X-ray fluorescence and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, have been used in freshly retrieved thrombi to map the distribution of biological elements and metabolites, respectively [47].
Most histopathology studies focused on the presence and relative abundance of FBR, and blood formed elements (RBCs, PLTs, and white blood cells [WBCs]) in the thrombus. Classical H&E staining was almost always used to visualize the general structure of the thrombus. Although H&E staining and machine learning software allowed reproducible quantification of the three major clot components (RBCs, WBCs, and FBR) [48], the more specific MSB staining was used in many studies for the selective quantification of RBCs and FBR [28,37,39,43,44,49-61]. The Picro-Mallory stain was used to assess the maturity of FBR in thrombi, based on its age-dependent differential staining [62]. Immunohistochemical staining procedures allowed the best visualization and reliable separate quantification of RBCs (glycophorin A, also designated CD235a antigen) [63-65], WBCs (CD45 antigen) [66-70], PLTs (CD41, CD42b, and CD61 antigens) [38,45,49,51,53,56,57,60,63,65,66,71-73], and fibrinogen/FBR [49,53,63,65,66,74]. Depending on the discriminatory capability of the staining procedures used, the studies expressed the ratios of clot components according to four different classifications, as shown in Table 2. A number of studies categorized the clots according to the dominant component (usually with a 60% cut-off) [48] as RBCrich, FBR-rich, PLT-rich, or mixed [7,50,52,54,58,59,64,75-91]. Some studies identified and/or quantified WBC types and subtypes by immunohistochemical staining using specific antibodies against neutrophil elastase (NE) [66,76,92-94], neutrophil myeloperoxidase (MPO) [65,66,76,95], Ly6G (monocyte, granulocyte, and neutrophil) [94], CD3 (T lymphocyte) [66,68-70,90,96], CD4 (T lymphocyte) [52,53], CD14 (monocyte) [66], CD15 (neutrophil, eosinophil, and monocyte) [97], CD20 (B lymphocyte) [66,68-70,96], CD66b (neutrophil) [76,93], and CD68 (monocyte and macrophage) [30,52,67-70,96,98].
Neutrophils were the predominant leukocyte subset in stroke thrombi [66,93]. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) have been identified as part of the clot scaffold by using antibodies against NETosis biomarkers (citrullinated histones) and histochemical staining of extracellular DNA [63,65,66,76,93-95,99]. NETs were visualized in almost all (79.1% to 100%) of the analyzed thrombi in different studies [63,65,66,76,93,95], in amounts ranging from 0.21% to 13.45% of total thrombus area [93], and 1.1%±2.7% on average [76]. NET signals were observed as being confined within cells, filopodia-like structures, or web-like structures [65], especially in the outer thrombus layers [63,95], and almost exclusively within FBR-rich areas [76]. Inside the NETs, citrullinated histones were co-localized with inflammasome proteins (caspase-1 and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase-recruitment domain [ASC]) [99], granular neutrophil proteins (MPO) and extracellular DNA released from neutrophils [93,95]. The addition of histone-DNA complexes to FBR resulted in thicker fibers accompanied by increased rigidity, which contributed to the structural complexity and stabilization of the thrombi [76]. Of interest, monocytes could also form extracellular traps, but to a lesser extent than neutrophils [66,94].
Coagulation system proteins other than fibrinogen/FBR were immunohistochemically identified by using specific antibodies against von Willebrand factor (VWF) [52-56,60,63,74,97,100], and two PLT-derived direct inhibitors of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA): plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [63,74] and protease nexin-1 [63]. The proportion of VWF varied from 0.1% to 94.3% of the total clot area [60], with mean values between 11.8% and 29.8% in different studies [56,60,100], and higher content in thrombi retrieved after unsuccessful intravenous thrombolysis [74]. VWF levels were correlated with those of FBR and PLTs [97]. White FBR-rich thrombi showed higher percentages of VWF+ areas co-localized with regions of FBR/collagen [52]. Similarly, PLT-rich areas were characterized by dense FBR structures aligned with VWF [53].
The presence of other thrombus components has been assessed using specific staining procedures. Some cohort studies used standard protocols including H&E and one or more of the following staining procedures to visualize elastic collagen fibers (Elastica van Gieson), hemosiderin/iron (Prussian blue), calcifications (Von Kossa), and collagen (Masson’s trichro me) [67-70,78,81,86,88,89,91,96,101]. However, positive results showing the occasional presence of intimal collagen fibers, cholesterol clefts, and smooth muscle cells (immunohistochemically stained for α-smooth muscle actin) were reported only in three studies assessing thrombectomy-induced wall damage, which identified vascular wall components or atheromatous gruel in a low proportion (2.6% to 20%) of the retrieved thrombi [78,91,101]. Case reports also used these specific stainings to identify elastic fibers, hemosiderin granules, collagen fibrous stalks, calcium deposits, and myofibroblast-like cells, usually in atypical thrombi [15,23,30,43,102].
The presence of foreign bodies in thrombi has also been evaluated. Delaminated polymer coating particulates were readily detected in 33% of H&E-stained preparations [103]. Thread or sheet-like structures were found in 25% of thrombi scanned by electron microscopy [104].
Classical descriptions of thrombus histological patterns based on light microscopy categorized their organized structure as layered (PLT bands arranged in layers), serpentine (PLT bands arranged in a serpentine way), or erythrocytic (with RBCs and nucleated cells interspersed) [7,52,75,105,106]. The molecular and cellular organization revealed distinct features between clots as well as among different regions within a clot. Thrombi were composed of two main area types: RBC-rich and PLT-rich areas. RBC-rich areas had limited complexity and consisted of RBCs entangled in a meshwork of thin FBR. Conversely, PLT-rich areas were characterized by dense FBR structures aligned with VWF and abundant amounts of WBCs and DNA that accumulate around [53]. Similarly, serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed a thrombus 3D ultrastructure that varied greatly depending on the region analyzed. RBC-rich areas were composed mainly of tightly packed RBCs deformed into polyhedrocytes with scant FBR fibers interwoven between cells. The regions with mixed composition showed thick FBR fibers along with PLTs, WBCs, and RBC clusters. FBR-rich areas contained dense FBR masses with sparse RBCs [56]. High-resolution SEM and transmission electron microscopy revealed a dense, sealed, rtPA-resistant external shell encapsulating a loose RBC-rich core. Shell components were densely compacted and agglomerated and formed a continuous layer, in which individual cells could hardly be detected. This was in stark contrast to the clearly identifiable RBCs, FBR fibers, and aggregated PLTs in the inner core [63,107]. Other ultrastructural studies showed morphologic features consistent with the presence of NETs, calcified deposits and cholesterol crystals in the clots [44,99].
Regarding septic cerebral emboli, Marder’s pioneering study reported one case of mycotic embolus [7]. However, both real-time and standard PCR demonstrated no expression of bacterial 16S rDNA in any of the 20 clot samples. Gram staining results also showed no evidence of bacteria [108]. Contrastingly, bacteria were detected in Gram-stained clots of four out of 65 patients (6.2%) [109]. A larger cohort of 75 patients showed DNA signatures of oral streptococcal bacteria in 84% of the retrieved thombi [110]. Metagenomics analysis also showed the presence of bacterial DNA in all four thrombi originated from symptomatic carotid plaques [111].
Clot homogenates subjected to qRT-PCR showed the expression of inflammatory cytokines (interleukin 1β [IL-1β], IL-6, IL-8, IL18, tumor necrosis factor α [TNF-α], and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 [MCP-1]), matrix metalloproteinases-2, -9 [112], and endothelial CD31 [75]. Four-plex assay showed the expression of cytokines (IL-1β and IL-18) and other inflammasome signaling proteins such as caspase-1 and ASC. Moreover, the presence of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor protein-1 and absent in melanoma-2, two receptors that interact with caspase-1 and ASC to form an inflammasome complex, was shown by immunoblot analysis [99].
Proteomic analysis has been used to characterize the protein cargo of thrombi (thousands) and commonly present proteins (hundreds). Functional bioinformatics analyses revealed protein clusters related to inflammation [113]; immunological functions, blood cell dependent functions, and peripheral vascular processes [114]; metabolic processes, inflammatory track, and cell proliferation, activation, or motility [115]; primary hemostasis, integrin and kinase signaling linked to integrins, glycolysis, and acute phase reactants [116]. Nevertheless, metabolomics analysis suggested clot sorbitol content as a surrogate marker reflecting blood glucose level at stroke onset [117].
PLT, RBC, and WBC content of AIS thrombi could be estimated through biochemical quantification of glycoprotein (GP) VI (immunoassay), heme (formic acid-based colorimetric assay), and DNA (dsDNA fluorescence assay kit) in thrombus homogenates [118]. Hemoglobin (ELISA) and heme content were highly correlated with RBC content determined by flow cytometry [119]. Different lymphocyte profiles were identified in cell suspensions of clots subjected to flow cytometry [120].
The presence of NETs was confirmed in intact thrombus samples subjected to endonuclease treatment to release NE activity [95], and by incubating with DNase-I to produce ex vivo thrombolysis [71]. Thrombin elution pattern assessed by measuring secreted thrombin activity along serial washings has been suggested as a biomarker of clot content [121].
Analysis of thrombus size, structure and composition in patient cohorts found associations with TOAST etiology (large-artery atherosclerosis [LAA; TOAST 1]; cardioembolism [CE; TOAST 2]; stroke of other determined cause [ODC; TOAST 4]; cryptogenic [CRY] stroke of undetermined etiology [TOAST 5]), embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS), or underlying pathologies (Supplementary Table 2). LAA thrombi showed a larger ECA [39,40] and higher number of fragments [40]. Eight studies, reporting results from 1,183 thrombi (median 73), showed higher RBC proportions in thrombi from LAA or non-CE (LAA+ODC) sources [39,57,64,82,96,122-124]. Contrastingly, three studies (119 thrombi, median 37) showed higher RBC proportions in CE thrombi [72,84,125]. Seven studies (1,061 thrombi, median 58) showed higher FBR proportions in CE [39,57,76,82,96,123,124], while in two studies (82 thrombi, median 41) the FBR proportion was higher in LAA [72,125]. CE thrombi also showed a higher FP (FBR+PLTs) proportion in one study (137 thrombi) [122]. PLT proportion was higher in LAA in two studies (1,127 thrombi, median 563.5) [50,59], but higher in CE in another two studies (697 thrombi, median 348.5) [39,67]. Further support for higher PLT proportions in non-CE thrombi came from higher GP VI content in thrombus homogenates [118]. LAA thrombi showed mostly peripheral PLT distribution patterns (PDPs), while mostly clustering PDP was observed in CE [51]. Non-CE thrombi showed higher RBC/PLT ratio [73], in line with lower FP/RBC ratio [126]. Results from the large multicentric STRIP registry (1,350 thrombi), published during the preparation of this manuscript, showed that LAA thrombi had a higher mean RBC density (46%±23% vs. 42%±22%, P=0.01) and a lower PLT density (24%±18% vs. 27%±18%, P=0.03) than CE thrombi [147]. Regarding WBCs, three studies (358 thrombi, median 137) showed higher proportions in CE [89,96,122], while one study (37 thrombi) reported higher proportions in LAA [84]. Another study supported higher WBC proportions in CE, as estimated by DNA content in thrombus homogenates [118]. When WBC subtypes were analyzed, CE thrombi showed higher contents of neutrophils [76], NETs [66,93], and netting neutrophils [66], as well as more macrophages [67]. As for lymphocytes, CE thrombi contained more suppressor-cytotoxic T-cells [120], while LAA thrombi showed higher T-cell [90], helper T-cell, and natural killer (NK)-cell contents [120]. Finally, higher IL-1β expression was measured in LAA thrombi [112], while coagulation factor XIII was associated with CE [115].
Some studies aimed to compare the features of CRY thrombi with those of known TOAST etiology. Most of them found similar proportions of RBCs [39,57,64,96,122-124,127], FBR, PLTs (or both together) [57,76,96,122-124,127], and WBCs between CRY and CE thrombi [96,122,127]. CRY and CE thrombi also shared smaller ECA and number of retrieved fragments [39,40], clustering PDP [51], higher neutrophil counts [76], and NETosis [66], temporal profile of eluted thrombin activity [121], and low expression of IL-1β [112]. ESUS and CE thrombi showed similar RBC/PLTs ratios [73]. Conversely, a few studies found similar proportions of RBCs [84], PLTs [50], and WBCs [84,89] in CRY and LAA thrombi. Finally, ESUS and LAA thrombi shared low macrophage proportions [67].
Regardless of TOAST etiology, some thrombus features have been associated with the patient’s age and underlying pathologies. The clots from elderly subjects had higher FBR proportions compared to younger patients [128]. As for gross appearance, white thrombi were much more frequent in the context of pathologies like active cancer (AC) or infective endocarditis (IE) [36,38]. Furthermore, thrombi showed lower RBC proportions, and higher FBR and/or PLT proportions, with underlying AC [38,65] or diabetes mellitus (DM) [55]. Other composition characteristics were lower WBC proportion in AC [38], and higher NETosis in DM [94]. Direct presence of tumor cells in the thrombus was rare in AC [129]. Contrastingly, bacteria or fungi were present with underlying IE [7,109] or other systemic infections [109].
Thrombus analysis in individual cases was a valuable complementary tool in diagnosing the stroke etiology, especially atypical ones (Supplementary Table 3). Proteomic analysis determined a common origin for tandem occlusions after traumatic carotid thrombosis and embolization [130]. Macroscopic and thorough histopathological examination confirmed the occlusion by an intracranial atherosclerotic plaque, revealing the atherothrombotic etiology [19]. Identification of cocci or bacilli in the thrombus confirmed septic emboli in cases of bacterial IE [14,18,31,32,102,131-135], including a rare case of Whipple’s endocarditis [26]. Similarly, the presence of Candida confirmed septic embolus in a case of fungal IE [136]. Observation of fungal hyphae confirmed cases of septic embolus [137] and angioinvasive mucormycosis secondary to sinusitis [138]. Identification of papillary fronds or myxomatous tissue helped diagnose embolization secondary to cardiac papillary fibroelastoma [15,16,20] and myxoma [29], respectively. Visual assessment and histopathology identified valve tissue [24], calcifications [27,30], chordae tendineae [21], and aortic wall tissue [23] as embolism sources, which detached spontaneously or periprocedurally during valve replacement surgery. Immunohistopathology contributed to diagnose the embolism of a Libman-Sacks vegetation in systemic lupus erythematosus-associated endocarditis [22]. Thrombus calcification, cholesterol crystal cleft and foamy cells confirmed the aortogenic embolic stroke due to atheromatous lesion in the aortic arch [139,140]. Embolizations of carotid free-floating and carotid web thrombi were determined by assessing the clot aspect and blood cell content [28,141]. Clot visual appearance and high FBR content indicated thromboembolism secondary to coronavirus disease 2019-associated hypercoagulability [34] and cancer-related Trousseau syndrome [33]. Finally, thrombus examination confirmed periprocedural catheter-related thromboembolism during valve implantation [17] and inadvertent embolization of foreign bodies during aneurysm treatment [25].
In response to the four research questions posed in this study, our results show that:
(1) Thrombi were subjected to physical analyses (macroscopic appearance, mechanical behavior, MRI, and synchrotron-based imaging), histopathological analyses (conventional histology, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy), biological analyses (biochemical, biomolecular, and cellular techniques, such as enzymatic assay, ELISA, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and flow cytometry), and microbiological analyses (culture, histological staining, and metagenomics).
(2) The information obtained about thrombi included gross appearance (size, shape, consistency, visual texture, color, and homo/heterogeneous aspect), mechanical properties (stiffness, elasticity, tensile strength, and response to stress), structure (compactness, molecular and cellular organization, and ultrastructure), and composition (FBR, other coagulation factors, blood formed elements, NETs, vessel wall and plaque components, microbial pathogens, inflammatory mediators, protein cargo, metabolites, elements, and even foreign bodies).
(3) There were associations of thrombus size, structure and composition (mainly proportions of FBR and blood formed elements) with TOAST etiology and underlying pathologies, and similarities between cryptogenic thrombi and those of known TOAST etiology.
(4) Individual thrombus analysis proved to be a valuable complementary tool in the diagnosis of stroke etiology, particularly in atypical cases.
The first endovascular device clearance by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration occurred in 2004 [148], and the first report describing a systematic histological analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries was published in 2006 [7]. Since then, a total of 134 eligible studies have been identified in this systematic review. Of note, there has been a surge of reports in the last 5 years, just after the publication of Brinjikji’s systematic review [3]. Although most studies carried out histopathological analyses, studies reporting biochemical or biomolecular analyses have been increasing in the last 3 years. Almost 10,000 thrombi/emboli retrieved from LVO stroke patients have been analyzed predominantly in cohort studies but also in case reports.
Physical, histopathological and biological analyses provided a considerable amount of information about the gross appearance, mechanical properties, structure, and composition of thrombi in patient cohorts. However, assessments of possible associations of thrombus features with stroke causes have been carried out mainly based on thrombus size, color, and proportions of FBR and blood formed elements. LAA thrombi were larger and more fragmented. Regarding composition, non-unanimous evidence supported higher RBC contents in thrombi from LAA or non-CE (LAA+ODC) sources, and higher FBR contents in thrombi of CE origin. WBC content, neutrophil count, and NETosis were also higher in CE thrombi. As for the PLT proportion, controversial histopathological evidence did not support a clear association with the CE or non-CE cause, although non-CE thrombi showed higher GP VI content (PLT marker), and peripheral PDP. Cryptogenic mechanisms account for 10% to 40% of all ischemic strokes [149]. Most evidence pointed to similar features in CRY and CE thrombi, mainly regarding proportions of RBCs, FBR, PLTs, and WBCs, and smaller size and number of retrieved fragments, clustering PDP, and higher NETosis. This could aid the etiologic investigation and reduce the percentage of CRY strokes. Of note, the large multicentric STRIP registry found statistically significant but clinically insignificant differences between clots of CE and LAA etiologies [147]. Although LAA clots had a higher mean RBC density and a lower mean PLT density than CE clots, the receiver operating characteristics analysis showed that identification of a reliable threshold with a high area under the curve for differentiating clots of these two etiologies based on composition analysis alone was not possible; this suggests that conventional histological analyses of the cellular composition do not provide insights into stroke etiology in cryptogenic cases. Regardless of TOAST etiology, a few studies found associations of thrombus color and composition with underlying pathologies like cancer, diabetes, and IE.
Macroscopic, histopathological, biomolecular, and microbiological analyses of thrombi were useful in the diagnosis of the stroke cause in individual cases. Thrombus features confirmed cases of typical intracranial and carotid thromboembolism, and atypical free-floating and web thrombi. Histopathology also contributed to diagnose embolisms due to cardiac tumor fragments, sterile endocarditis vegetations, aortogenic lesions, and tissue fragments detached during valve replacement surgery. Microbiological analysis revealed septic emboli secondary to IE, allowing appropriate antibiotic therapy. Finally, thromboembolisms due to secondary hypercoagulable states were diagnosed based on clot features.
Current methods of assessing thrombus features vary widely. Despite a consensus statement on the analyses of thrombi in AIS [1] and recommendations for thrombus handling and procedures [13], the results in this review show a lack of standardization in the research and reporting of thrombus characteristics and parameters. Heterogeneity in study designs, outcome measuring, and reporting precluded a meta-analysis of the association between thrombus composition and stroke etiology. Hopefully, ongoing multi-institutional registers, larger cohorts, and homogenous protocols will overcome this limitation. Although traditional histopathological techniques seem of limited value, the application of pathophysiological classifications show promise in differentiating between CE and LAA emboli [150]. Nevertheless, focusing on immunohistochemical analysis and more advanced techniques could help increase the knowledge on the composition and structure of thrombi. Advanced analysis of microRNA signatures [151], proteomic analysis [152], and combined “omic” analysis (proteome and metabolome) [153] are promising molecular approaches to elucidate the composition of emboli. Moreover, ultrastructural analysis using high-resolution SEM shows the finely organized clot components [56]. The role of all these advanced techniques in identifying stroke etiology could be further explored.
Although cohort studies report an abundance of quantitative rates of main thrombus components, a definite clot signature for accurate diagnosis of stroke etiology is still lacking. Nevertheless, qualitative examination of the embolus remains an invaluable tool in the diagnostic work-up of individual cases, particularly regarding atypical stroke causes. Beyond conventional histopathological and immunohistochemical clot analyses, future studies should emphasize the analysis of biomolecular composition and structural organization to provide insights about reliable links between clot features and stroke etiology.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2021.02306.
Supplementary Table 2.
Cohort studies: thrombus composition and TOAST stroke etiology or underlying pathology
Supplementary Table 3.
Case reports: thrombus/embolus composition and stroke etiologies or underlying pathologies
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by RETICS research network INVICTUS+ from Spanish ‘Instituto de Salud Carlos III’ (co-financed with European Regional Development Fund), through grant RD16/0019/0008. The funding source had no further role in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
The authors acknowledge the help rendered by Marta Méndez Debaets in manuscript preparation and reference management.
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flowchart of the literature search results and selection of studies at each stage.

Figure 2.
Chronology of study publication. Number of yearly-published studies from January 1, 2006, to February 22, 2021. Faded colors indicate incomplete year 2021.
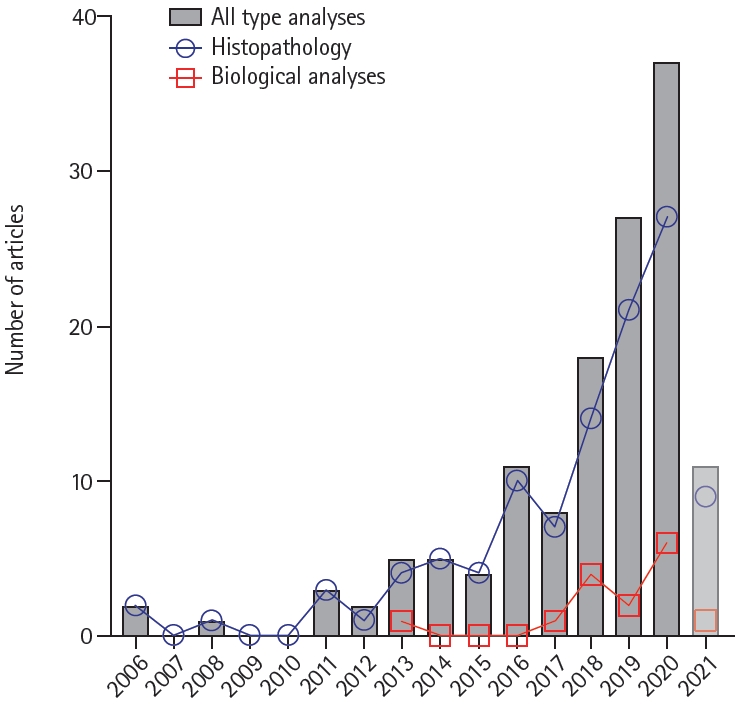
Table 1.
Study characteristics summary
Table 2.
Average proportions of fibrin and blood formed elements in stroke thrombi
| PLT | FBR | PLT+FBR | RBC | WBC | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59%±138%, 166 | 41%±25%, 166 | 38%±25%, 166 | 4%±5%, 166 | [56,57,67,72] | |
| 52%±19%, 1,025 | 41%±19%, 1,045 | 5%±3%, 944 | [38,81,84,92,122,142-146] | ||
| 27%±16%, 287 | 38%±37%, 287 | 41%±91%, 287 | [54,55,64,65,123] | ||
| 52%±25%, 441 | 47%±25%, 441 | [78,87,101] |
References
1. De Meyer SF, Andersson T, Baxter B, Bendszus M, Brouwer P, Brinjikji W, et al. Analyses of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke: a consensus statement on current knowledge and future directions. Int J Stroke 2017;12:606-614.


2. Bacigaluppi M, Semerano A, Gullotta GS, Strambo D. Insights from thrombi retrieved in stroke due to large vessel occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2019;39:1433-1451.



3. Brinjikji W, Duffy S, Burrows A, Hacke W, Liebeskind D, Majoie CB, et al. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome: a systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg 2017;9:529-534.


4. Jolugbo P, Ariëns RA. Thrombus composition and efficacy of thrombolysis and thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2021;52:1131-1142.



5. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000100.



6. Salom JB, Aliena-Valero A, Torregrosa G, Baixauli-Martín J. Clot composition analysis as complementary diagnostic tool to gain insight into ischemic stroke etiology: A systematic review of clinical studies and case reports. National Institute for Health Reearch https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42020199436. August 17, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021.
7. Marder VJ, Chute DJ, Starkman S, Abolian AM, Kidwell C, Liebeskind D, et al. Analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2006;37:2086-93.


8. Multimodal Investigation of Intracranial Clot Environment (MISO). ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04421326. 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021.
9. Investigation of Clot in Ischemic Stroke and Hematoma Evacuation (INSIGHT). ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04693767. 2021. Accessed September 27, 2021.
10. Thrombus Composition in Ischemic Stroke: Analysis of the Correlation With Plasma Biomarkers, Efficacy of Treatment, Etiology and Prognosis (COMPO-CLOT). ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03268668. 2021. Accessed September 27, 2021.
11. Blood And Clot Thrombectomy Registry And Collaboration (BACTRAC). ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03153683. 2021. Accessed September 27, 2021.
12. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT031536RNA Sequencing Analysis in Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke DATA Bank (RNASA-LVOSB). ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03490552. 2018. Accessed September 27, 2021.
13. Staessens S, Fitzgerald S, Andersson T, Clarençon F, Denorme F, Gounis MJ, et al. Histological stroke clot analysis after thrombectomy: technical aspects and recommendations. Int J Stroke 2020;15:467-476.


14. Abdel-Wahed L, Shaban A, Hayakawa M, Limaye K. Retrieved arterial clot helps guide antibiotic therapy in infective endocarditis. Am J Med 2019;132:e795-e796.


15. Biraschi F, Diana F, Alesini F, Guidetti G, Peschillo S. Effective ADAPT thrombectomy in a patient with acute stroke due to cardiac papillary elastofibroma: histological thrombus confirmation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2016;25:e185-e187.


16. Salam KA, Rafeeque M, Hashim H, Mampilly N, Noone ML. Histology of thrombectomy specimen reveals cardiac tumor embolus in cryptogenic young stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2018;27:e70-e72.


17. Salinas P, Moreno R, Frutos R, Lopez-Sendon JL. Neurovascular rescue for thrombus-related embolic stroke during transcatheter aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2013;6:981-982.


18. Scharf EL, Chakraborty T, Rabinstein A, Miranpuri AS. Endovascular management of cerebral septic embolism: three recent cases and review of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg 2017;9:463-465.


19. Semerano A, Genchi A, Callea M, Sanvito F, Simionato F, Panni P, et al. Thrombus hallmarks reveal atherothrombotic stroke aetiology. J Neurol 2019;266:1533-1535.


20. Tejada J, Galiana A, Balboa O, Clavera B, Redondo-Robles L, Alonso N, et al. Mechanical endovascular procedure for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke caused by total detachment of a papillary fibroelastoma. J Neurointerv Surg 2014;6:e37.


21. Thomas MC, Delgado Almandoz JE, Todd AJ, Young ML, Fease JL, Scholz JM, et al. A case of right middle cerebral artery ‘tendonectomy’ following mitral valve replacement surgery. J Neurointerv Surg 2017;9:e35.


22. Valente M, Saab J, Cordato D, Manning N, Cappelen-Smith C. The diagnostic utility of routine clot analysis after endovascular thrombectomy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. J Clin Neurosci 2019;70:247-249.


23. Wollenweber FA, Remi J, Bauer A, Theiss H, Massberg S, Patzig M, et al. Thrombectomy recovers an aortic wall fragment from middle cerebral artery immediately after TAVI. Neurology 2016;86:2111-2112.


24. Anuwatworn A, Raizada A, Kelly S, Stys T, Jonsson O, Stys A. Stroke with valve tissue embolization during transcatheter aortic valve replacement treated with endovascular intervention. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2015;8:1261-1263.


25. Chapot R, Wassef M, Bisdorff A, Rogopoulos A, Merland JJ, Houdart E. Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery due to synthetic fibers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:148-150.


26. Elodie O, Labeyrie PE, Aubry M, Cecile D, Roux S, Ferry T, et al. Whipple’s endocarditis diagnosed by thrombus analysis retrieved by successful mechanical thrombectomy. J Neurol Sci 2019;400:42-43.


27. Fassa AA, Mazighi M, Himbert D, Deschamps L, Ducrocq G, Cheong AP, et al. Successful endovascular stroke rescue with retrieval of an embolized calcium fragment after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2014;7:125-126.


28. Fitzpatrick N, Motyer R, Gibney B, Duffy S, Murphy S, O’Brien P, et al. Expanding the role of stent-retriever endovascular thrombectomy: a case series of free-floating thrombus. J Neurointerv Surg 2018;10:1164-1167.


29. Garcia-Ptacek S, Matias-Guiu JA, Valencia-Sánchez C, Gil A, Bernal-Becerra I, De las Heras-Revilla V, et al. Mechanical endovascular treatment of acute stroke due to cardiac myxoma. J Neurointerv Surg 2014;6:e1.


30. Genchi A, Schwarz G, Semerano A, Callea M, Sanvito F, Simionato F, et al. Large vessel occlusion stroke due to dislodged aortic valve calcification revealed by imaging and histopathology. J Neurol Sci 2020;408:116573.


31. Kan P, Webb S, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI. First reported use of retrievable stent technology for removal of a large septic embolus in the middle cerebral artery. World Neurosurg 2012;77:591.

32. Kim JM, Jeon JS, Kim YW, Kang DH, Hwang YH, Kim YS. Forced arterial suction thrombectomy of septic embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion due to infective endocarditis: an illustrative case and review of the literature. Neurointervention 2014;9:101-5.



33. Matsumoto N, Fukuda H, Handa A, Kawasaki T, Kurosaki Y, Chin M, et al. Histological examination of trousseau syndrome-related thrombus retrieved through acute endovascular thrombectomy: report of 2 cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2016;25:e227-e230.


34. Pisano TJ, Hakkinen I, Rybinnik I. Large vessel occlusion secondary to COVID-19 hypercoagulability in a young patient: a case report and literature review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2020;29:105307.



35. Bourcier R, Duchmann Z, Sgreccia A, Desal H, Carità G, Desilles JP, et al. Diagnostic performances of the susceptibility vessel sign on MRI for the prediction of macroscopic thrombi features in acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2020;29:105245.


36. Sgreccia A, Duchmann Z, Desilles JP, Lapergue B, Labreuche J, Kyheng M, et al. Association between acute ischemic stroke etiology and macroscopic aspect of retrieved clots: is a clot’s color a warning light for underlying pathologies? J Neurointerv Surg 2019;11:1197-1200.


37. Choi MH, Park GH, Lee JS, Lee SE, Lee SJ, Kim JH, et al. Erythrocyte fraction within retrieved thrombi contributes to thrombolytic response in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2018;49:652-659.


38. Fu CH, Chen CH, Lin YH, Lee CW, Tsai LK, Tang SC, et al. Fibrin and platelet-rich composition in retrieved thrombi hallmarks stroke with active cancer. Stroke 2020;51:3723-3727.


39. Fitzgerald S, Rossi R, Mereuta OM, Jabrah D, Okolo A, Douglas A, et al. Per-pass analysis of acute ischemic stroke clots: impact of stroke etiology on extracted clot area and histological composition. J Neurointerv Surg 2020 Dec 9 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016966.

40. Fitzgerald S, Rossi R, Mereuta OM, Molina S, Okolo A, Douglas A, et al. Large artery atherosclerotic clots are larger than clots of other stroke etiologies and have poorer recanalization rates. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2021;30:105463.


41. Rossi R, Fitzgerald S, Molina S, Mereuta OM, Douglas A, Pandit A, et al. The administration of rtPA before mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke patients is associated with a significant reduction of the retrieved clot area but it does not influence revascularization outcome. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2021;51:545-551.


42. Horie N, Shobayashi K, Morofuji Y, Sadakata E, Iki Y, Matsunaga Y, et al. Impact of mechanical thrombectomy device on thrombus histology in acute embolic stroke. World Neurosurg 2019;132:e418-e422.


43. Almekhlafi MA, Hu WY, Hill MD, Auer RN. Calcification and endothelialization of thrombi in acute stroke. Ann Neurol 2008;64:344-348.


44. Chueh JY, Wakhloo AK, Hendricks GH, Silva CF, Weaver JP, Gounis MJ. Mechanical characterization of thromboemboli in acute ischemic stroke and laboratory embolus analogs. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:1237-1244.



45. Liu Y, Zheng Y, Reddy AS, Gebrezgiabhier D, Davis E, Cockrum J, et al. Analysis of human emboli and thrombectomy forces in large-vessel occlusion stroke. J Neurosurg 2020;134:893-901.


46. Vidmar J, Bajd F, Milosevic ZV, Kocijancic IJ, Jeromel M, Sersa I. Retrieved cerebral thrombi studied by T2 and ADC mapping: preliminary results. Radiol Oncol 2019;53:427-433.



47. Meher V, Pushie J, Sylvain N, Weese Maley S, Hou H, Peeling L, et al. Analysis of retrieved stroke thrombi from mechanical thrombectomy using X-ray fluorescence imaging and fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Int J Stroke 2018;13:150.
48. Fitzgerald S, Wang S, Dai D, Murphree DH Jr, Pandit A, Douglas A, et al. Orbit image analysis machine learning software can be used for the histological quantification of acute ischemic stroke blood clots. PLoS One 2019;14:e0225841.



49. Fitzgerald ST, Wang S, Dai D, Douglas A, Kadirvel R, Gounis MJ, et al. Platelet-rich clots as identified by Martius Scarlet Blue staining are isodense on NCCT. J Neurointerv Surg 2019;11:1145-1149.



50. Fitzgerald S, Dai D, Wang S, Douglas A, Kadirvel R, Layton KF, et al. Platelet-rich emboli in cerebral large vessel occlusion are associated with a large artery atherosclerosis source. Stroke 2019;50:1907-1910.



51. Kim B, Kim YM, Jin SC, Lee JW, Lee BI, Kim SE, et al. Development of a predictive scale for cardioembolic stroke using extracted thrombi and angiographic findings. J Clin Neurosci 2020;73:224-230.


52. Schuhmann MK, Gunreben I, Kleinschnitz C, Kraft P. Immunohistochemical analysis of cerebral thrombi retrieved by mechanical thrombectomy from patients with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Mol Sci 2016;17:298.



53. Staessens S, Denorme F, Francois O, Desender L, Dewaele T, Vanacker P, et al. Structural analysis of ischemic stroke thrombi: histological indications for therapy resistance. Haematologica 2020;105:498-507.



54. Ye G, Qi P, Chen K, Tan T, Cao R, Chen J, et al. Risk of secondary embolism events during mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: a single-center study based on histological analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2020;193:105749.


55. Ye G, Gao Q, Qi P, Wang J, Hu S, Chen K, et al. The role of diabetes mellitus on the thrombus composition in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Interv Neuroradiol 2020;26:329-336.



56. Mereuta OM, Fitzgerald S, Christensen TA, Jaspersen AL, Dai D, Abbasi M, et al. High-resolution scanning electron microscopy for the analysis of three-dimensional ultrastructure of clots in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg 2021;13:906-911.


57. Ahn SH, Hong R, Choo IS, Heo JH, Nam HS, Kang HG, et al. Histologic features of acute thrombi retrieved from stroke patients during mechanical reperfusion therapy. Int J Stroke 2016;11:1036-1044.


58. Benson JC, Fitzgerald ST, Kadirvel R, Johnson C, Dai D, Karen D, et al. Clot permeability and histopathology: is a clot’s perviousness on CT imaging correlated with its histologic composition? J Neurointerv Surg 2020;12:38-42.


59. Brinjikji W, Fitzgerald S, Kallmes DF, Layton K, Hanel R, Pereira VM, et al. Outcomes of the stroke thromboembolism registry of imaging and pathology: a multicenter international study. Stroke 2020;51(Suppl 1):A147.
60. Douglas A, Fitzgerald S, Mereuta OM, Rossi R, O’Leary S, Pandit A, et al. Platelet-rich emboli are associated with von Willebrand factor levels and have poorer revascularization outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg 2020;12:557-562.


61. Duffy S, McCarthy R, Farrell M, Thomas S, Brennan P, Power S, et al. Per-pass analysis of thrombus composition in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. Stroke 2019;50:1156-1163.


62. Khismatullin RR, Shakirova AZ, Weisel JW, Litvinov RI. Agedependent differential staining of fibrin in blood clots and thrombi. BioNanoScience 2020;10:370-374.

63. Di Meglio L, Desilles JP, Ollivier V, Nomenjanahary MS, Di Meglio S, Deschildre C, et al. Acute ischemic stroke thrombi have an outer shell that impairs fibrinolysis. Neurology 2019;93:e1686-e1698.



64. Niesten JM, van der Schaaf IC, van Dam L, Vink A, Vos JA, Schonewille WJ, et al. Histopathologic composition of cerebral thrombi of acute stroke patients is correlated with stroke subtype and thrombus attenuation. PLoS One 2014;9:e88882.



65. Park H, Kim J, Ha J, Hwang IG, Song TJ, Yoo J, et al. Histological features of intracranial thrombi in stroke patients with cancer. Ann Neurol 2019;86:143-149.


66. Novotny J, Oberdieck P, Titova A, Pelisek J, Chandraratne S, Nicol P, et al. Thrombus NET content is associated with clinical outcome in stroke and myocardial infarction. Neurology 2020;94:e2346-e2360.


67. Goebel J, Gaida BJ, Wanke I, Kleinschnitz C, Koehrmann M, Forsting M, et al. Is histologic thrombus composition in acute stroke linked to stroke etiology or to interventional parameters? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2020;41:650-657.



68. Sporns PB, Krähling H, Psychogios MN, Jeibmann A, Minnerup J, Broocks G, et al. Small thrombus size, thrombus composition, and poor collaterals predict pre-interventional thrombus migration. J Neurointerv Surg 2021;13:409-414.


69. Sporns PB, Jeibmann A, Minnerup J, Broocks G, Nawabi J, Schön G, et al. Histological clot composition is associated with preinterventional clot migration in acute stroke patients. Stroke 2019;50:2065-2071.


70. Sporns PB, Hanning U, Schwindt W, Velasco A, Buerke B, Cnyrim C, et al. Ischemic stroke: histological thrombus composition and pre-interventional CT attenuation are associated with intervention time and rate of secondary embolism. Cerebrovasc Dis 2017;44:344-350.


71. Peña-Martínez C, Durán-Laforet V, García-Culebras A, Ostos F, Hernández-Jiménez M, Bravo-Ferrer I, et al. Pharmacological modulation of neutrophil extracellular traps reverses thrombotic stroke tPA (tissue-type plasminogen activator) resistance. Stroke 2019;50:3228-3237.


72. Kim SK, Yoon W, Kim TS, Kim HS, Heo TW, Park MS. Histologic analysis of retrieved clots in acute ischemic stroke: correlation with stroke etiology and gradient-echo MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015;36:1756-1762.



73. Nouh A, Mehta T, Hussain M, Song X, Ollenschleger M. Clot composition of embolic strokes of undetermined source: a feasibility study. BMC Neurol 2020;20:383.



74. López-Cancio E, Millán M, Pérez de la Ossa N, Dávalos A, Ribó M, Morancho A, et al. Immunohistochemical study of clot composition in thrombi retrieved from MCA with mechanical thrombectomy. Cerebrovasc Dis 2013;35:255.
75. Elijovich L, Arthur A, Hoit D, Nickele C, Morris D, Vachhani J, et al. Thrombus composition is associated with endothelial injury and stroke etiology in patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy for emergent large vessel occlusion. Stroke 2018;49(Suppl 1):A145.
76. Essig F, Kollikowski AM, Pham M, Solymosi L, Stoll G, Haeusler KG, et al. Immunohistological analysis of neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in human thrombemboli causing acute ischemic stroke. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:7387.



77. Gurkas E, Asif A, Akpinar CK, Shoukat M, Aytac E, Aydin MC, et al. Thrombus composition and success of thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke patients: a histopathological analysis. Stroke 2019;50(Suppl 1):AWP36.
78. Hashimoto T, Hayakawa M, Funatsu N, Yamagami H, Satow T, Takahashi JC, et al. Histopathologic analysis of retrieved thrombi associated with successful reperfusion after acute stroke thrombectomy. Stroke 2016;47:3035-3037.


79. Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Yong WH, Starkman S, Tsang MP, Moya AL, et al. CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke 2011;42:1237-1243.



80. Liu M, Hao Z, Li R, Cai J, Jiang C, Li Y. Erythrocyte-rich thrombi related to serum iron contribute to single stent retrieval and favorable clinical outcomes in acute ischemic stroke by endovascular treatment. Thromb Res 2020;195:8-15.


81. Maegerlein C, Friedrich B, Berndt M, Lucia KE, Schirmer L, Poppert H, et al. Impact of histological thrombus composition on preinterventional thrombus migration in patients with acute occlusions of the middle cerebral artery. Interv Neuroradiol 2018;24:70-75.


82. Maekawa K, Shibata M, Nakajima H, Mizutani A, Kitano Y, Seguchi M, et al. Erythrocyte-rich thrombus is associated with reduced number of maneuvers and procedure time in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra 2018;8:39-49.



83. Qureshi AI, Qureshi MH, Lobanova I, Bashir A, Khan AA, Bologna SM, et al. Histopathological characteristics of IV recombinant tissue plasminogen-resistant thrombi in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Vasc Interv Neurol 2016;8:38-45.


84. Shin JW, Jeong HS, Kwon HJ, Song KS, Kim J. High red blood cell composition in clots is associated with successful recanalization during intra-arterial thrombectomy. PLoS One 2018;13:e0197492.



85. Simons N, Mitchell P, Dowling R, Gonzales M, Yan B. Thrombus composition in acute ischemic stroke: a histopathological study of thrombus extracted by endovascular retrieval. J Neuroradiol 2015;42:86-92.


86. Singh P, Doostkam S, Reinhard M, Ivanovas V, Taschner CA. Immunohistochemical analysis of thrombi retrieved during treatment of acute ischemic stroke: does stent-retriever cause intimal damage? Stroke 2013;44:1720-1722.


87. Darcourt J, Garcia C, Phuong DM, Michelozzi C, Bellanger G, Adam G, et al. Absence of susceptibility vessel sign is associated with aspiration-resistant fibrin/platelet-rich thrombi. Int J Stroke 2021 Jan 12 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493020986626.

88. Hanning U, Sporns PB, Psychogios MN, Jeibmann A, Minnerup J, Gelderblom M, et al. Imaging-based prediction of histological clot composition from admission CT imaging. J Neurointerv Surg 2021 Jan 22 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016774.

89. Boeckh-Behrens T, Schubert M, Förschler A, Prothmann S, Kreiser K, Zimmer C, et al. The impact of histological clot composition in embolic stroke. Clin Neuroradiol 2016;26:189-197.


90. Dargazanli C, Rigau V, Eker O, Riquelme Bareiro C, Machi P, Gascou G, et al. High CD3+ cells in intracranial thrombi represent a biomarker of atherothrombotic stroke. PLoS One 2016;11:e0154945.



91. Donnerstag F, Götz F, Dadak M, Raab P, Iglesias EC, Werlein C, et al. Interventional stroke treatment: is it also safe for arteries?: looking at thrombectomy wall damage through clot histology. Interv Neuroradiol 2021;27:404-410.


92. Kaesmacher J, Boeckh-Behrens T, Simon S, Maegerlein C, Kleine JF, Zimmer C, et al. Risk of thrombus fragmentation during endovascular stroke treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2017;38:991-998.



93. Laridan E, Denorme F, Desender L, François O, Andersson T, Deckmyn H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic stroke thrombi. Ann Neurol 2017;82:223-232.


94. Deng J, Zhao F, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Xu X, Zhang X, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps increased by hyperglycemia exacerbate ischemic brain damage. Neurosci Lett 2020;738:135383.


95. Ducroux C, Di Meglio L, Loyau S, Delbosc S, Boisseau W, Deschildre C, et al. Thrombus neutrophil extracellular traps content impair tPA-induced thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2018;49:754-757.


96. Sporns PB, Hanning U, Schwindt W, Velasco A, Minnerup J, Zoubi T, et al. Ischemic stroke: what does the histological composition tell us about the origin of the thrombus? Stroke 2017;48:2206-2210.


97. Prochazka V, Jonszta T, Czerny D, Krajca J, Roubec M, Macak J, et al. The role of von Willebrand factor, ADAMTS13, and cerebral artery thrombus composition in patient outcome following mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. Med Sci Monit 2018;24:3929-3945.



98. Krajíčková D, Krajina A, Šteiner I, Vyšata O, Herzig R, Lojík M, et al. Fibrin clot architecture in acute ischemic stroke treated with mechanical thrombectomy with stent-retrievers: cohort study. Circ J 2018;82:866-873.


99. Chen SH, Scott XO, Ferrer Marcelo Y, Almeida VW, Blackwelder PL, Yavagal DR, et al. Netosis and inflammasomes in large vessel occlusion thrombi. Front Pharmacol 2021;11:607287.



100. Mereuta OM, Fitzgerald S, Abbasi M, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Kallmes DF, et al. Von Willebrand factor expression in various subtypes of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2020;51(Suppl 1):AWP268.
101. Funatsu N, Hayakawa M, Hashimoto T, Yamagami H, Satow T, Takahashi JC, et al. Vascular wall components in thrombi obtained by acute stroke thrombectomy: clinical significance and related factors. J Neurointerv Surg 2019;11:232-236.


102. Bhaskar S, Saab J, Cappelen-Smith C, Killingsworth M, Wu XJ, Cheung A, et al. Clot histopathology in ischemic stroke with infective endocarditis. Can J Neurol Sci 2019;46:331-336.


103. Mehta RI, Rai AT, Vos JA, Solis OE, Mehta RI. Intrathrombus polymer coating deposition: a pilot study of 91 patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute large vessel stroke. Part I: Histologic frequency. J Neurointerv Surg 2019;11:1191-1196.



104. Hund HM, Taha A, Ramlal SA, Hansen D, Autar ASA, van de Lugt A, et al. Foreign bodies are present in thrombi mechanically extracted from patients suffering acute ischemic stroke and who underwent endovascular treatment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2019;39:261.
105. Sallustio F, Arnò N, Di Legge S, Koch G, Martorana A, Rossi C, et al. Histological features of intracranial thrombo-emboli predict response to endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Disord Stroke 2015;3:1105.
106. Cline B, Vos J, Carpenter J, Rai A. Pathological analysis of extracted clots in embolectomy patients with acute ischaemic stroke. J NeuroInterv Surg 2013;5(Suppl 2):A15-A16.
107. Li Y, Wang H, Zhao L, Jian Y, Dang M, Jiang Y, et al. A case report of thrombolysis resistance: thrombus ultrastructure in an ischemic stroke patient. BMC Neurol 2020;20:135.



108. Khashim Z, Fitzgerald S, Kadirvel R, Dai D, Doyle KM, Brinjikji W, et al. Clots retrieved by mechanical thrombectomy from acute ischemic stroke patients show no evidence of bacteria. Interv Neuroradiol 2019;25:502-507.



109. Hernández-Fernández F, Rojas-Bartolomé L, García-García J, Ayo-Martín Ó, Molina-Nuevo JD, Barbella-Aponte RA, et al. Histopathological and bacteriological analysis of thrombus material extracted during mechanical thrombectomy in acute stroke patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2017;40:1851-1860.


110. Patrakka O, Pienimäki JP, Tuomisto S, Ollikainen J, Lehtimäki T, Karhunen PJ, et al. Oral bacterial signatures in cerebral thrombi of patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with thrombectomy. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8:e012330.



111. Vajpeyee A, Chauhan PS, Pandey S, Tiwari S, Yadav LB, Shroti AK, et al. Metagenomics analysis of thrombus samples retrieved from mechanical thrombectomy. Neurointervention 2021;16:39-45.



112. Baek BH, Kim HS, Yoon W, Lee YY, Baek JM, Kim EH, et al. Inflammatory mediator expression within retrieved clots in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2018;5:273-279.



113. Rao NM, Capri J, Cohn W, Abdaljaleel M, Restrepo L, Gornbein JA, et al. Peptide composition of stroke causing emboli correlate with serum markers of atherosclerosis and inflammation. Front Neurol 2017;8:427.



114. Muñoz R, Santamaría E, Rubio I, Ausín K, Ostolaza A, Labarga A, et al. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic profiling of thrombotic material obtained by endovascular thrombectomy in patients with ischemic stroke. Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:498.



115. Dargazanli C, Zub E, Deverdun J, Decourcelle M, de Bock F, Labreuche J, et al. Machine learning analysis of the cerebrovascular thrombi proteome in human ischemic stroke: an exploratory study. Front Neurol 2020;11:575376.



116. Lopez-Pedrera C, Ibañez-Costa A, Perez-Sanchez C, Luque-Tevar M, Patiño-Trives AM, Abalos-Aguilera MDC, et al. Characterization of the protein profile in thrombi of patients with ischemic stroke and identification of potential biomarkers as predictors of negative clinical evolution. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2020;4(Suppl 1):OC08.5.
117. Suissa L, Guigonis JM, Graslin F, Doche E, Osman O, Chau Y, et al. Metabolome of cerebral thrombi reveals an association between high glycemia at stroke onset and good clinical outcome. Metabolites 2020;10:483.



118. Di Meglio L, Desilles JP, Solonomenjanahary M, Labreuche J, Ollivier V, Dupont S, et al. DNA content in ischemic stroke thrombi can help identify cardioembolic strokes among strokes of undetermined cause. Stroke 2020;51:2810-2816.


119. Di Meglio L, Derraz I, Solonomenjanahary M, Daly D, Chodraui Filho S, Ben Maacha M, et al. Two-layered susceptibility vessel sign is associated with biochemically quantified thrombus red blood cell content. Eur J Neurol 2020;27:1264-1271.


120. Juega J, Pagola J, Palacio C, Camacho J, Cardona P, Quesada H, et al. Etiology of stroke based on early analysis of clot cytometry obtained through first pass technique for mechanical thrombectomy. Stroke 2019;50(Suppl 1):AWMP70.
121. Itsekson Hayosh Z, Abu Bandora E, Shelestovich N, Nulman M, Bakon M, Yaniv G, et al. In-thrombus thrombin secretion: a new diagnostic marker of atrial fibrillation in cryptogenic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg 2021;13:799-804.


122. Boeckh-Behrens T, Kleine JF, Zimmer C, Neff F, Scheipl F, Pelisek J, et al. Thrombus histology suggests cardioembolic cause in cryptogenic stroke. Stroke 2016;47:1864-1871.


123. Liao Y, Guan M, Liang D, Shi Y, Liu J, Zeng X, et al. Differences in pathological composition among large artery occlusion cerebral thrombi, valvular heart disease atrial thrombi and carotid endarterectomy plaques. Front Neurol 2020;11:811.



124. Xue Y, Zhao Y, Cao J, Zhu XC, Shao HM, Chen RH, et al. Exploration of thrombus histological composition and clinical effect in mechanical thrombectomy of acute ischemic stroke. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018;98:3697-3700.

125. Gong L, Zheng X, Feng L, Zhang X, Dong Q, Zhou X, et al. Bridging therapy versus direct mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke due to middle cerebral artery occlusion: a clinical- histological analysis of retrieved thrombi. Cell Transplant 2019;28:684-690.



126. Berndt M, Prothmann S, Maegerlein C, Oberdieck P, Zimmer C, Hegge B, et al. Artificial stroke clots: how wide is the gap to the real world? World Neurosurg 2018;110:e90-e99.


127. Bhaskar S, Saab J, Cappelen-Smith C, Cordato D, Cheung A, Manning N, et al. Cryptogenic stroke is linked to cardioembolic aetiology: a histopathological study of thrombus retrieved after endovascular thrombectomy. Eur J Neurol 2019;26:20.
128. Meng L, Wang H, Yang H, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Dong Q, et al. Nomogram to predict poor outcome after mechanical thrombectomy at older age and histological analysis of thrombus composition. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020;2020:8823283.



129. Wolpert F, Kulcsár Z, Hänsel M, Rushing E, Seystahl K, Schweizer J, et al. Embolization of tumor cells is rare in patients with systemic cancer and cerebral large vessel occlusion. Eur J Neurol 2020;27:2041-2046.


130. Hinman JD, Rao NM, Yallapragada A, Capri J, Souda P, Whitelegge J, et al. Drip, ship, and grip, then slice and dice: comprehensive stroke center management of cervical and intracranial emboli. Front Neurol 2013;4:104.



131. Ambrosioni J, Urra X, Hernández-Meneses M, Almela M, Falces C, Tellez A, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke secondary to infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 2018;66:1286-1289.


132. Bain MD, Hussain MS, Gonugunta V, Katzan I, Gupta R. Successful recanalization of a septic embolus with a balloon mounted stent after failed mechanical thrombectomy. J Neuroimaging 2011;21:170-172.


133. Distefano M, Calandrelli R, Arena V, Pedicelli A, Della Marca G, Pilato F. A puzzling case of cryptogenic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2019;28:e33-e35.


134. Nakanishi K, Kawano H, Amano T, Omori Y, Kanma H, Hirano T. Stroke due to infective endocarditis diagnosed by the retrieved thrombus: a case report. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2018;58:35-40.


135. Sukumaran S, Jayadevan ER, Mandilya A, Sreedharan SE, Harikrishnan S, Radhakrishnan N, et al. Successful mechanical thrombectomy of acute middle cerebral artery occlusion due to vegetation from infective endocarditis. Neurol India 2012;60:239-240.


136. Sgreccia A, Carità G, Coskun O, Maria FD, Benamer H, Tisserand M, et al. Acute ischemic stroke treated with mechanical thrombectomy and fungal endocarditis: a case report and systematic review of the literature. J Neuroradiol 2020;47:386-392.


137. Katano T, Sakamoto Y, Kunugi S, Nishiyama Y, Shimizu A, Kimura K. A fungus in a thrombus by mechanical thrombectomy in acute cerebral infarction: a case report. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2020;60:340-345.


139. Matsumoto N, Takahashi M, Katano T, Kutsuna A, Kanamaru T, Sakamoto Y, et al. Cholesterol crystal in thrombus removed by mechanical thrombectomy should be a strong marker for aortogenic embolic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2020;29:105178.


140. Usui G, Hashimoto H, Sugiura Y, Nishi Y, Kusakabe M, Horiuchi H, et al. Aortogenic embolic stroke diagnosed by a pathological examination of endovascularly removed thrombus: an autopsy report. Intern Med 2019;58:2851-2855.



141. Koneru S, Nogueira RG, Osehobo E, Oprea-Ilies G, Al-Bayati AR, Brinjikji W, et al. Clot composition in retrieved thrombi after mechanical thrombectomy in strokes due to carotid web. J Neurointerv Surg 2021;13:530-533.



142. Mönch S, Boeckh-Behrens T, Berndt M, Maegerlein C, Wunderlich S, Zimmer C, et al. Angiographic baseline proximal thrombus appearance of M1/M2 occlusions in mechanical thrombectomy. Clin Neuroradiol 2021;31:189-196.


143. Wei L, Zhu Y, Deng J, Li Y, Li M, Lu H, et al. Visualization of thrombus enhancement on thin-slab maximum intensity projection of CT angiography: an imaging sign for predicting stroke source and thrombus compositions. Radiology 2021;298:374-381.


144. Patel TR, Fricano S, Waqas M, Tso M, Dmytriw AA, Mokin M, et al. Increased perviousness on CT for acute ischemic stroke is associated with fibrin/platelet-rich clots. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2021;42:57-64.



145. Berndt M, Poppert H, Steiger K, Pelisek J, Oberdieck P, Maegerlein C, et al. Thrombus histology of basilar artery occlusions : are there differences to the anterior circulation? Clin Neuroradiol 2021;31:753-761.



146. Berndt M, Friedrich B, Maegerlein C, Moench S, Hedderich D, Lehm M, et al. Thrombus permeability in admission computed tomographic imaging indicates stroke pathogenesis based on thrombus histology. Stroke 2018;49:2674-2682.


147. Brinjikji W, Nogueira RG, Kvamme P, Layton KF, Delgado Almandoz JE, Hanel RA, et al. Association between clot composition and stroke origin in mechanical thrombectomy patients: analysis of the Stroke Thromboembolism Registry of Imaging and Pathology. J Neurointerv Surg 2021;13:594-598.



148. Smith WS, Furlan AJ. Brief history of endovascular acute ischemic stroke treatment. Stroke 2016;47:e23-e26.


150. Roessler FC, Kalms N, Jann F, Kemmling A, Ribbat-Idel J, Stellmacher F, et al. First approach to distinguish between cardiac and arteriosclerotic emboli of individual stroke patients applying the histological THROMBEX-classification rule. Sci Rep 2021;11:8433.




151. Kim JM, Byun JS, Kim J, Park MS, Hong SA, Nam TK, et al. Analysis of microRNA signatures in ischemic stroke thrombus. J Neurointerv Surg 2021 Jul 8 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017597.