 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 25(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Advances in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) treatment have been contingent on innovations in neuroimaging. Neuroimaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and prognosis of ischemic stroke and large vessel occlusion, enabling triage decisions in the emergent care of the stroke patient. Current imaging protocols for acute stroke are dependent on the available resources and clinicians’ preferences and experiences. In addition, differential application of neuroimaging in medical decision-making, and the rapidly growing evidence to support varying paradigms have outpaced guideline-based recommendations for selecting patients to receive intravenous or endovascular treatment. In this review, we aimed to discuss the various imaging modalities and approaches used in the diagnosis and treatment of AIS.
Neuroimaging is an integral part of acute stroke management. It can be used to confirm the diagnosis and to guide acute treatment options by excluding acute hemorrhage, confirming vessel occlusion or stenosis, assessing tissue viability with perfusion estimates, and evaluating collateral circulation [1]. Recent advances in neuroimaging modalities have helped identify patients who may or may not benefit from endovascular treatment (EVT) [2-4].
Imaging played a critical role in the selection of patients into acute ischemic stroke (AIS) randomized controlled trials (RCTs), both in the early and late windows of patient presentation [5]. After their publication, the 2019 American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA), the European Stroke Organization, Korean Stroke Guidelines, Chinese Stroke Association, and Canadian Stroke Guidelines were updated to recommend obtaining advanced or multimodal imaging for EVT patient triage and selection especially for late window treatment [6-10]. Other guidelines, such as from the Society of Vascular and Interventional Neurology, have not been as stringent [11]. However, advanced imaging is not widely available, particularly in low- or middle-income countries and primary stroke centers [12], and is potentially associated with treatment delay and increased cost [13,14]. In addition, there is a lack of standardized imaging protocols and a variety of qualitative and quantitative (automated) methods for assessing cerebral perfusion in AIS [15]. These varying algorithms and technology can provide different estimates of tissue destined to infarct (termed ischemic core) and tissue at risk of infarction (termed ischemic penumbra). In this review, we discuss the advantages and limitations of the current state of neuroimaging in the diagnosis and treatment of AIS.
Computed tomography (CT)-based imaging remains the most common imaging modality to evaluate patients presenting with acute stroke symptoms. It is easily available, safe, and fast which is critical in acute stroke management. CT has high sensitivity for the detection of intracerebral hemorrhage. However, apart from hyperdense arteries that may indicate acute thrombus, the brain parenchyma is often normal on CT in the early few hours after AIS [16]. Early ischemic changes (loss of the grey-white matter differentiation or effacement of the cortical sulci) can be seen in approximately 30% of patients with anterior circulation large vessel occlusion (LVO) within the first 3 hours [16], and 60% within the first 6 hours after symptom onset (Figure 1) [17]. The Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) is a semi-quantitative score used to summate the extent of early ischemic changes in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory on non-contrast CT (NCCT) scan (Figure 2) [18]. Most EVT RCTs published in 2015 (except MR CLEAN [Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Netherlands]) required an ASPECTS of 6 or greater to be eligible for inclusion in the trial [19]. A meta-analysis of the pooled data from the five landmark studies published in 2015 showed a benefit of thrombectomy in patients with ASPECTS ≥6 and therefore an ASPECTS 6-10 is considered a surrogate marker of small infarct volume and a strong predictor of favorable clinical outcome after EVT for LVO [20]. The AHA/ASA guidelines recommend mechanical thrombectomy for patients with LVO and ASPECTS ≥6 who present within 6 hours of last known well time based on pre-specified inclusion criteria from randomized trials, without additional advanced imaging [6].
Moreover, the benefit of EVT over medical management was observed in patients with ASPECTS scores ranging from 3 to 5 after central adjudication of imaging from the early window EVT trials [21]. The RESCUE-Japan LIMIT (Recovery by Endovascular Salvage for Cerebral Ultra-acute Embolism Japan Large IscheMIc core Trial) was the first published randomized clinical trial that evaluated the efficacy and safety of EVT in patients with LVO and an established large infarct (ASPECTS of 3 to 5). Patients selected within 6 hours of arrival were eligible with a CT ASPECTS of 3-5, while patients in the 6 to 24 hour window were eligible if their diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI)-ASPECTS was 3-5 and they had no fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) correlate. In this population, better outcomes were observed at 90 days in patients who underwent EVT versus medical management (rate of modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0-3, 31.0% vs. 12.7%, P=0.002) [22].
Despite its widespread use, the limitations of ASPECTS include its relatively low sensitivity and inter-rater reliability for the detection of early ischemic changes [23]. CT angiogram (CTA) source image and DWI-ASPECTS are more sensitive than NCCT ASPECTS in the detection of early ischemic changes and prediction of final infarct volume (Figure 1) [24].
A posterior circulation version of the ASPECTS has been developed (the pc-ASPECTS), and has been shown to predict functional outcome in posterior circulation stroke (Figure 3) [25]. While the pc-ASPECTS can be calculated from an NCCT brain, beam hardening artifact in the posterior fossa and poor spatial resolution of brainstem structures are major limiting factors, but accuracy is improved when calculated based on CTA source images [25,26].
Recently, two RCTs (ATTENTION [Endovascular Treatment For Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion] and BAOCHE [Basilar Artery Occlusion Chinese Endovascular]) evaluating EVT versus best medical therapy in patients presenting with acute basilar artery occlusion (BAO) showed high rates of successful recanalization, improved outcome, and decreased mortality up to 24 hours after estimated symptom onset [27,28]. These two trials were the first to use an imaging scoring system in the selection of patients into the trial [29]. In ATTENTION, BAO was confirmed on CTA, magnetic resonance angiography, or digital subtraction angiography (DSA) within 12 hours after the estimated time of stroke onset and patients were included if they had a pc-ASPECTS of ≥6 points among patients younger than 80 years of age and a score of ≥8 points among those 80 years of age or older. In BAOCHE, patients were included if they had a pc-ASPECTS of ≥6 on NCCT, CTA-source images or DWI, or Pons-Midbrain Index of ≤2 points. In both the ATTENTION and BAOCHE trials, the extent of early ischemic changes was limited. In ATTENTION, the median pc-ASPECTS was 9 in the EVT group and 10 in the control group. In BAOCHE, the median pc-ASPECTS was 8 in both EVT and control groups [27,28].
In addition to the evaluation of the brain parenchyma, the NCCT brain is also helpful to determine the thrombus location, density, composition, and length. The “hyperdense artery sign” represents the red blood cell (RBC) rich intra-luminal thrombus and is considered a surrogate of arterial obstruction (Figure 4). The hyperdense artery sign is highly specific (95%) for MCA occlusion according to some reports [30] but can only be visualized in 30%-52% of MCA occlusions on routine 3-5 mm source images [30,31]. Thin slice reformats (1 mm) increase this sensitivity to approximately 90% [32]. In clinical practice, a hyperdense vessel can appear similar to calcified intracranial atherosclerosis and sometimes be misinterpreted as hemoconcentration, therefore it must be interpreted in the appropriate clinical context. The hyperdense vessel sign can also be identified in M2 occlusions (known as the “dot sign”), BAO, or any newly occluded blood vessel (Figure 4) [33-36]. For patients who are unable to undergo non-invasive vascular imaging, the “hyperdense vessel sign” can guide decisions for EVT [7]. Knowledge of these clot factors can provide insights into stroke etiology and can impact the choice of revascularization techniques. The RBC rich thrombi are easier to retrieve by stent retriever technique and have higher chance of recanalization with fibrinolytic therapies due to their decreased stiffness, greater permeability, and less friction with the vessel wall. This contrasts with fibrin-rich thrombi which are more adherent and have higher friction with the vessel wall [37]. RBC rich thrombi are also more prone to fragmentation, highlighting the potential need for proximal flow arrest with balloon guide catheters [38,39].
CTA plays a critical role in the detection of LVO for AIS and the historical success of RCTs published after 2014. The 2013 LVO RCTs did not demonstrate a benefit of EVT for LVO, in part, due to inclusion of patients who did not harbor an intracranial occlusion despite elevated National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) on presentation [40-42]. The subsequent AIS clinical trials required inclusion of patients with LVO that was confirmed by non-invasive vascular imaging (usually CTA), thus enriching the population to those who might benefit from EVT [19]. CTA informs the presence, site, permeability, and length of vessel occlusion, as well as the collateral circulation (Figure 5) [43-45]. Collateral vessel status is a valuable and sometimes underappreciated surrogate for infarct growth, and can be useful for the early identification of “rapid progressors” or patients with a high probability of rapid growth of irreversible tissue injury [43,46]. However, single phase CTA is often timed at peak arterial phase when the contrast may not have yet opacified collateral vessels and may therefore underestimate the extent of collateral blood flow. CTA can aid in understanding the underlying pathophysiology of the stroke, including arterial dissection, carotid or intracranial atherosclerosis, carotid web, and intracranial vasculopathy (Figure 6) [35,36,47-49]. The ability to discern carotid pseudo-occlusion from a carotid terminus occlusion versus tandem proximal internal carotid artery (ICA) atherosclerotic occlusion remains a limitation of CTA, even when adjudicated by experienced radiologists [50]. CTA evaluating the head and neck vessels informs neurointerventionalists who are planning an endovascular procedure on the access of an intracranial target, including bovine or hostile aortic arch and whether radial or femoral arterial access is more appropriate [51,52]. CTA source images are also better to adjudicate ASPECTS in the anterior and posterior circulations [24]. However, radiation exposure, cost, and ionized contrast media are to be considered, especially when CT perfusion (CTP) is added to the protocol [53,54].
CTA (also using thin-section CT) is also useful in clot imaging. Thrombus perviousness (also known as permeability), the degree to which contrast agents penetrate the thrombus on CTA, has been associated with cardioembolic source of clot [55] and with improved functional and angiographic outcomes after EVT and increased reperfusion after tissue plasminogen activator administration [56,57].
Multiphase CTA can be used to evaluate the collateral circulation with greater accuracy than single phase CTA as it is less dependent on contrast timing [58,59]. The cerebral collateral circulation is a network of vascular channels that sustains blood flow to the ischemic regions in case of failure of the principal conduits (Figure 5) [1,60]. Collateral blood vessels comprise extracranial (external carotid artery branches), and intracranial routes (communicating arteries of the circle of Willis and leptomeningeal collaterals). Leptomeningeal collaterals consist of pre-existing collateral routes between the cortical vessels that may be recruited in the event of a proximal occlusion). Collateral circulation has an important role in the AIS evolution, management, and prognosis [61,62]. Good collateral circulation maintains the blood supply to the penumbral area in the acute stage and is associated with higher recanalization rate, smaller infarct volume, lower rate of hemorrhagic transformation, and better neurological outcome after medical treatment or EVT [63,64].
Although DSA is considered the gold standard for dynamic evaluation of the collateral circulation, CTA is a commonly used modality to evaluate the collateral status before EVT. Several collateral scores on single or multiphase CTA have been described in AIS [65,66]. The collaterals on the affected side are usually compared to the contralateral side and they are generally categorized as absent, less, equal, or greater collaterals compared to the other side. These scores have been shown to be predictors of clinical outcomes after EVT. Several societal guidelines recommend assessing collateral status when selecting patients for EVT [9,67]. The use of collateral-based imaging using multiphase CTA compared well with CTP-based blood flow measurements in predicting final tissue fate [68] and in selecting patients for EVT in the late window [69]. The “Endovascular Treatment for Small Core and Proximal Occlusion Ischemic Stroke (ESCAPE)” trial showed that a collateral-based imaging paradigm was capable of selecting patients with LVO who would benefit from EVT up to 12 hours from onset/last known well. However, it is important to note patients with no or minimal collaterals on multiphase CTA were excluded from the ESCAPE trial [70].
Multiphase CTA is readily available at many centers which utilize CTA and requires no additional contrast material or post-processing software. It may improve the sensitivity to detect vessel occlusion, the length of clot and potentially the extent of ischemic core [71]. The typical 3-timepoint multiphase CTA requires rescanning of the patient’s head twice after the initial CTA acquisition, increasing the radiation dose. However, the mean effective dose of multi-phase CTA was estimated approximately 20% above that of single phase CTA, compared with 70% added dose for CTP [59,72]. Additional limitations of multiphase CTA include the suboptimal assessment of collateral status in case of poor hemodynamics (e.g., heart failure) and in case of flow-limiting stenosis in the neck vessels that can potentially delay opacification of pial vessels in both ischemic and non-ischemic tissue [71].
The main goal of perfusion imaging in patients with AIS is to identify patients with small regions of critical hypoperfusion (often termed “ischemic core”), which is commonly estimated using a relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF) threshold of <30% of that in normally perfused brain tissue. Differentiating the ischemic core from the surrounding penumbra is crucial for tailoring treatment strategy for patients with AIS. The estimation of irreversible injury based on reduced blood flow relies on assumptions about the duration of reduced flow. In clinical practice, the reduced flow has generally been present sufficiently long to induce irreversible injury. However, in patients with fluctuating blood flow or very fast reperfusion, the rCBF <30% threshold may overestimate the extent of irreversible injury [73]. This is more common in regions of white matter [74], which may remain viable for longer periods when compared to grey matter although it is designated as “ischemic core” on perfusion maps. In addition to identifying regions of critical hypoperfusion, perfusion imaging may also estimate regions of tissue at risk of infarction in the absence of reperfusion (termed the ischemic penumbra). Penumbra is the hypoperfused area surrounding the ischemic core (critically hypoperfused region with irreversible damage). The penumbra can be salvaged if perfusion is improved, or it can progress to tissue infarction if blood flow is not restored. Penumbra is identified using a threshold of >6 seconds in time-to-maximum residue function (Tmax) [75]. This improves estimates compared to visual assessments as the perfusion abnormality includes benign oligemia that is not at risk of infarction. However, this too is a probabilistic threshold. Generally, such a delay in contrast transit is insufficient to cause irreversible ischemia, but it may be sufficient to cause focal cerebral dysfunction until perfusion may be restored. The more severe the delay, the greater the risk of infarction without reperfusion. Of note, perfusion imaging is increasingly automated, with volumetric outputs generated minutes following image acquisition. Several automated CTP software applications have been developed to provide support in the definition of ischemic core and penumbra in AIS. However, the available software packages can vary substantially in their output [76]. In addition to estimating tissue viability, perfusion imaging increases the diagnostic accuracy for acute stroke and provides prognostic information regarding functional outcome [75].
The presence of a favorable perfusion profile (mismatch between small rCBF <30% volume and large Tmax >6 seconds lesion or severe clinical presentation) indicates that rapid reperfusion is likely to salvage substantial brain tissue and was the basis of selection in the DAWN (DWI or CTP Assessment with Clinical Mismatch in the Triage of Wake-Up and Late Presenting Strokes Undergoing Neurointervention with Trevo), DEFUSE-3 (Endovascular Therapy Following Imaging Evaluation for Ischemic Stroke), and EXTEND (Extending the Time for Thrombolysis in Emergency Neurological Deficits) trials that extended EVT and intravenous thrombolytic beyond standard time windows. An alternative approach for patients with unknown onset time is to use a mismatch between abnormal diffusion but normal FLAIR magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to infer that a patient is likely to be in the first 4.5 hours after stroke onset. DWI-FLAIR mismatch was used in the WAKE-UP (Efficacy and Safety of MRI-Based Thrombolysis in Wake-Up Stroke) trial to extend thrombolytic eligibility in patients with stroke on awakening [77,78].
Perfusion imaging was used in two of the early window LVO trials [79,80] but became more widespread after the release of the DAWN and DEFUSE-3 trial results which used perfusion for selection of patients for thrombectomy versus medical management [12].
When added to unenhanced imaging, perfusion imaging can facilitate the diagnosis and triage of AIS in several ways. Perfusion imaging can enable the detection of distal and posterior circulation vessel steno-occlusive disease using the Tmax maps [36,48,81,82]. Perfusion imaging may further help identify a subset of patients with a large region of established infarct who may benefit from EVT when there remains considerable tissue at risk [83]. In the event of multiple intracranial occlusions or stenosis, perfusion imaging may identify the symptomatic site (Figure 7), provided the reference artery selected for the arterial input function is physiologically appropriate [84]. Importantly, partial or complete reperfusion of infarcted tissue may elevate CBF above the threshold for ischemic core and this can be recognized if there is NCCT hypodensity [85].
CTP radiation exposure is a consideration in younger patients but is reducing with hardware advances (e.g., use of lower CT tube voltage, 70 kV). If using CTP, it is important to make treatment decisions in parallel to avoid treatment delay. Thrombolytic decisions within 4.5 hours can be made on clinical and NCCT grounds in many cases, but the additional diagnostic and prognostic information from CTP can assist in cases of uncertainty. Likewise, EVT decisions can often be initiated based on a severe clinical syndrome with a hyperdense proximal artery, but the additional information from CTA and CTP can assist in procedural planning and more finely balanced risk and benefit scenarios, such as in patients with moderate or large core infarct, distal vessel occlusion, or co-morbidities. Cost related to post-processing software is a consideration in some environments and availability varies widely. In some regions (e.g., Australia), CTP is routine at primary stroke centers but in the United States, as well as low- and middle-income countries, it is less used outside comprehensive stroke centers [8,9,12]. The value of the additional diagnostic information gained by perfusion imaging should be weighed against potential treatment delays, cost of CTP, and added radiation exposure [43].
MRI-based imaging offers some advantages over CT in the evaluation of patients presenting with stroke-like symptoms [86,87]. Because DWI-MRI identifies acute cytotoxic edema as tissue progresses toward infarction, this modality is highly sensitive for detecting infarction and can aid in the selection of patients for intravenous thrombolytic or EVT, particularly those presenting in the late window [88,89]. Despite the high sensitivity of DWI to detect AIS (up to 92%), DWI-negative stroke can be seen in approximately 8% of AIS patients, especially those with hyper acute strokes or small brainstem ischemic lesions [90]. DWI hyperintensity can also be reversible, at least temporarily, within 24 hours after acute reperfusion treatment. Partial sustained reversibility, when there is no evidence of permanent tissue injury on T2 or FLAIR imaging in a component of the lesion, may occur in up to 26.5% of AIS cases [91,92].
In contrast to DWI signal changes, T2/FLAIR prolongation (or hyperintensity) results from the increased concentration of water in the interstitial spaces (interstitial edema) and it is usually present after 4.5-6 hours after stroke onset [93,94]. This mismatch between positive DWI and negative FLAIR has been used to estimate the stroke onset and to select patients who may benefit from intravenous thrombolysis in wake up stroke and patients with unknown stroke onset [95,96].
The use of MRI as the primary modality in patients presenting with AIS has increased over the years [97]. MRI is as accurate as CT for the detection of hyperacute hemorrhage using susceptibility-weighted images (SWI) [98]. MRI is also more sensitive than CT to detect subtle hemorrhagic changes within the ischemic lesion [99]. Acute intra-arterial thrombus can cause significant blooming on SWI suggestive of LVO (Figure 8). The “susceptibility vessel sign” on MRI, similar to the “hyperdense vessel sign” on CT scan, reflects the dense RBC presence in acute thrombus, and these lesions may have better response to stent retriever thrombectomy compared to contact aspiration [100,101]. Absence of these signs may indicate a fibrin-predominant thrombus [100]. MRI may also predict underlying intracranial atherosclerotic disease in LVO in case of the presence of smaller infarct volume and scattered or borderzone infarcts [102,103].
There are no randomized trials comparing MRI versus CT-based imaging for selecting acute stroke patients for EVT. Analysis of the SWIFT PRIME patients showed a comparable benefit of EVT between MRI-based and CTP-based selection despite significantly longer time metrics in MRI-selected patients [104]. In an analysis of over 1,200 patients, MRI-based selection was associated with reduced risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (SICH) after EVT but without improved functional outcome compared with CT-based selection [105]. The reduced risk of SICH is likely related to the higher sensitivity of MRI to detect occult hemorrhage, as well as the better estimation of the ischemic core before intravenous thrombolysis in unknown or unwitnessed stroke [2]. In a study of 2,011 patients (690 patients selected by MRI and 1,321 patients selected by CT), MRI-based selection was associated with decreased futile recanalization and improved clinical outcomes compared to CT-based selection [2]. However, it is not known how many patients who were excluded from treatment as triaged by MRI might have benefited from EVT. Studies comparing CT, CTP, versus MRI-based selection should therefore be interpreted with caution.
There are several limitations associated with MRI in the setting of AIS. While acquisition protocols can be short (e.g., 6 min), MRI is less widely available. Some patients have metallic implants or are too unstable to be imaged with MRI and screening for metallic implants in stroke patients is challenging. Given the predominance of CT over MRI in the endovascular trials, the role of MRI as first imaging tool should remain limited to sites who can perform such studies while maintaining door to reperfusion times that are comparable to NCCT/CTA as the first imaging approach.
Acute stroke guidelines do not recommend the routine use of advanced imaging in the early time-window (less than 6 hrs) because multiple randomized clinical trials on EVT in the early time window did not use advanced imaging for patient selection and showed a large treatment benefit in this population [6,106]. Of note, in the SWIFT PRIME trial (Solitaire With the Intention for Thrombectomy as Primary Endovascular Treatment), the use of perfusion imaging was associated with time delays and did not demonstrate improved efficacy of MT. [104].
The optimal imaging selection for stroke patients presenting in the late window (beyond 6 hours from last seen well) remains controversial. Two RCTs (DEFUSE-3 and DAWN) have shown overwhelming benefit of EVT in patients presenting up to 16 and 24 hours from last seen well, respectively [15,95,96,99,102,103,107]. Recent guidelines have not been as restrictive in the imaging selection aradigms for late window presenting patients [4,7,8,11,108,109]. Both the DEFUSE-3 and DAWN trials used CTP over MRI perfusion due to its wider availability, faster acquisition, fewer contraindications, and decreased cost of CT-based images [5,107,110]. Both trials also used an automated program (RAPID, iSchemaView, Menlo Park, CA, USA) to estimate volumes of ischemic core (rCBF <30%) and critical hypoperfusion (using Tmax >6 s). This software is known to reduce imaging processing/interpretation times and reduce inter-operator variability. DEFUSE-3 used perfusion mismatch to assess the imaging profiles while DAWN used clinical-core mismatch that was adjusted by age and stroke severity. Despite the advantages of advanced imaging demonstrated in DEFUSE-3 and DAWN, these benefits were also demonstrated for patients who met DEFUSE-3 and DAWN eligibility criteria and for the subgroups who did not [111,112]. Furthermore, the eligibility criteria of the DEFUSE-3 and DAWN trials were strict and excluded patients from receiving a potentially effective therapy given the large treatment effect size [113]. In a single comprehensive center study, of all patients presenting with AIS, only 1.7% of patients met DAWN inclusion criteria with an additional 0.6% to 1% qualifying for the DEFUSE-3 trial [114]. Other observational cohort studies have since corroborated the positive outcomes following EVT in extended window trial-ineligible patients [4,109,112,115,116].
Given the limitations of advanced imaging, more simplified imaging protocols could potentially result in the treatment of a larger proportion of stroke patients presenting in the late window while still maintaining the benefit of EVT. Many studies have shown that patient selection using ASPECTS on NCCT scan and/or the collateral circulation on multi-phase CTA can be a reasonable alternative to advanced imaging to select patients for EVT in the late window [4,13,69,109,117,118].
In a multinational cohort of 1,604 patients presenting with LVO in the extended window, patients selected by NCCT had comparable clinical and safety outcomes with patients selected by CTP or MRI [13]. A real-world observational study found that EVT may be safe and effective in patients with wake-up stroke and late-presenting stroke selected using clinical-core mismatch (high NIHSS/high ASPECTS in NCCT) [117]. MR CLEAN-LATE (MR CLEAN for late arrivals) is a multicenter randomized trial that investigated the efficacy of EVT in patients with AIS presenting between 6 and 24 hours from time last known well based on collateral scoring (poor, moderate, or good) on single phase CTA. Preliminary data presented at the October 2022 World Stroke Congress showed better functional outcomes by 90-day mRS in the EVT compared to the medical management group (adjusted odds ratio 1.68 [95% confidence interval 1.21-2.33]) after selection based on the presence of CTA collaterals [119]. The pooled data from another study that evaluated 608 patients from multiple trials and registries showed comparable functional outcomes in patients selected for EVT in the late window using collateral imaging alone compared with patients selected using perfusion and collateral imaging. Of the 608 patients included in the study, 229/608 patients had only collateral imaging and 379/608 patients had collateral and perfusion imaging. Independent functional outcome was achieved in 45.5% in the perfusion cohort versus 43.9% in the collateral cohort (P=0.71) [120]. The adoption of NCCT and CTA-based imaging selection for the 6- to 24-hour time window would also have implications for stroke systems of care because this simplified imaging paradigm can be used at centers that lack CTP and acute phase MRI capabilities to triage patients for EVT without the need for implementing perfusion imaging [12,121]. While this would expand access, it may not identify all patients who could benefit from EVT. ASPECTS has limited correlation with lesion volume and many patients with low ASPECTS can have relatively small ischemic core volumes and would be eligible for treatment using a mismatch paradigm. ASPECTS also has limited applicability outside patients with M1 occlusion [122].
The safety and clinical outcome of EVT beyond the 24-hour time window from ischemic stroke have been reported [123,124]. It has been shown that EVT can be safely performed in properly selected patients beyond 24-hours from stroke symptoms onset. These patients should have a favorable target mismatch perfusion profile that is persistent beyond 24-hours and characterized by a lower hypoperfusion intensity ratio and favorable collaterals [124]. However, the optimal imaging selection paradigm for patient selection beyond 24 hours remains uncertain. In our experience, patients with good ASPECTS scores (clinical-ASPECTS mismatch) and/or robust collateral circulation achieve good functional outcomes at discharge and 90-days. A recent study showed no difference in functional and safety outcomes between patients presenting beyond 24 hours and selected by NCCT/CTA only versus perfusion-based imaging [123]. Randomized trials to assess the safety and efficacy of EVT beyond 24 hours are warranted.
Several clinical trials are currently examining alternative imaging modalities in the selection of patients for EVT in the 6-to-24-hour window. The RESILIENT-Extend (Randomization of Endovascular Treatment with Stent-retriever and/or Thromboaspiration vs. Best Medical Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke due to Large VEssel OcclusioN Trial in the Extended Time Window) (NCT02216643) trial will examine the efficacy of thrombectomy for anterior circulation LVO stroke, as compared to medical therapy, within 8 to 24 hours from last known well. The study will use modified clinical ASPECTS Mismatch (mCAM); defined as ASPECTS 5-10 with criteria based on cortical involvement (M1-6). Eligible patients must have intracranial ICA or MCA occlusion, with NIHSS ≥8 for entry. The study was reported completed in February 2022.
The NO-CTP (NOn-contrast Computed Tomography Versus Computed Tomography Perfusion Selection in Stroke Patients for Endovascular Treatment) study (NCT05230914) is a non-inferiority randomized clinical trial in China evaluating NCCT compared to CTP in achieving functional independence for patients with anterior circulation LVO presenting in the greater than 6-hour time window from last known well to randomization.
Machine and deep learning algorithms are advanced automated algorithms that have been adopted in the management of acute stroke patients in some centers. Commercially available machine learning algorithms have been integrated into clinical setting to support the time-sensitive decision-making for rapid diagnosis and image analysis; no significant differences have been observed between software [125]. These algorithms are useful to detect LVO, delineate the core, penumbra size and target mismatch [126], score collaterals [127], classify stroke mechanisms [128], and predict outcomes and risk of hemorrhagic transformation after EVT in ischemic stroke patients [129,130]. The role of machine learning is evolving and will continue to play a role in the diagnosis and management of cerebrovascular diseases in the future. Further integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in acute stroke care is inevitable.
There is no standardization for the imaging protocols for acute stroke patients. Efforts to offer endovascular reperfusion therapies to all appropriate candidates may be facilitated by the use of simplified imaging selection paradigms with widely available basic imaging techniques, such as NCCT and CTA. Advanced imaging is not required in the early windows in the acute stroke guidelines but may assist in patients with diagnostic uncertainty and co-morbidities. In the late window, the decision for intravenous thrombolysis should be based on advanced imaging modalities. Patients with LVO and target mismatch as assessed by multimodal imaging and/or clinical imaging mismatch should receive EVT. CT alone in patients presenting with high ASPECTS and high NIHSS may indicate sufficient eligibility for EVT but may not identify all patients who are likely to benefit from reperfusion.
Figure 1.
Early ischemic changes seen on (A) axial non-contrast head computed tomography (CT) as loss of the grey matter density of the right insula, part of the lenticular nucleus, and the right fronto-temporal regions. These changes are better seen on (B) the axial CT angiogram (CTA) source images and (C) the diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging images as areas of reduced diffusion. Scarce collaterals are noted in the right middle cerebral artery territory on (B) the CTA source images.
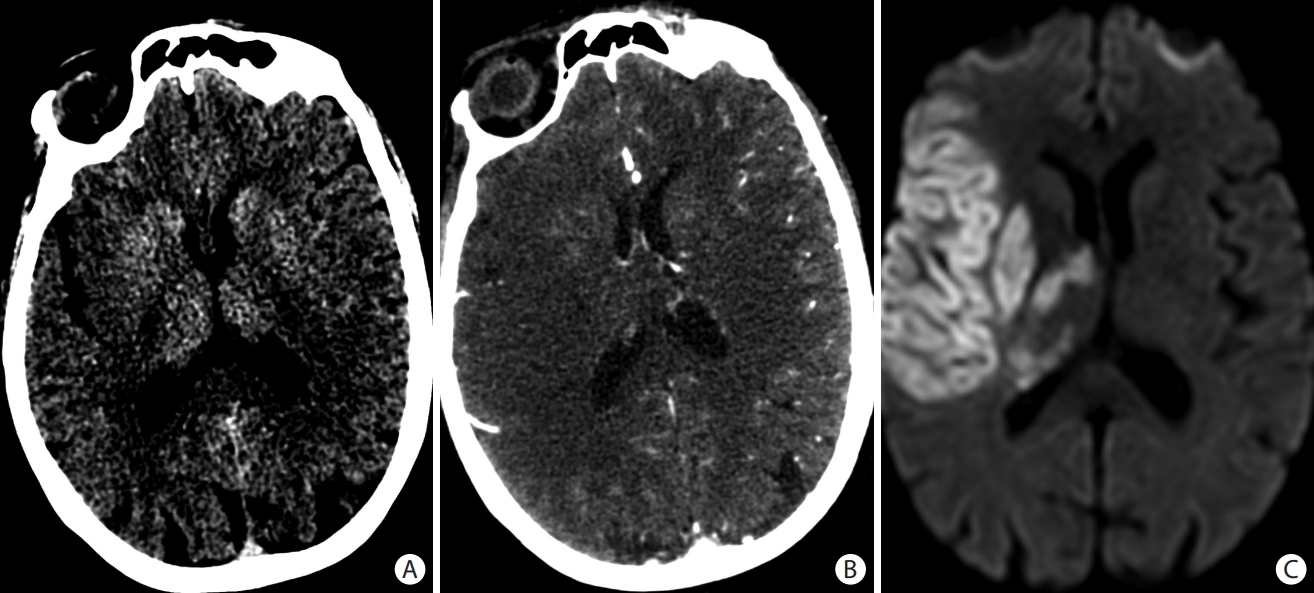
Figure 2.
The Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) consists of 10 specific regions of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory on a non-contrast axial head computed tomography at two levels: (A) the basal ganglia level and (B) the body of the lateral ventricles level. At the basal ganglia level, the following regions are assessed: caudate (C), internal capsule (IC), lentiform nucleus (L), insula (I), frontal MCA cortex (M1), anterior temporal MCA cortex (M2), and posterior temporal MCA cortex (M3). At the supraganglionic level, the following regions are assessed: anterior frontal MCA cortex (M4), lateral frontal MCA cortex (M5), and posterior frontal MCA cortex (M6).
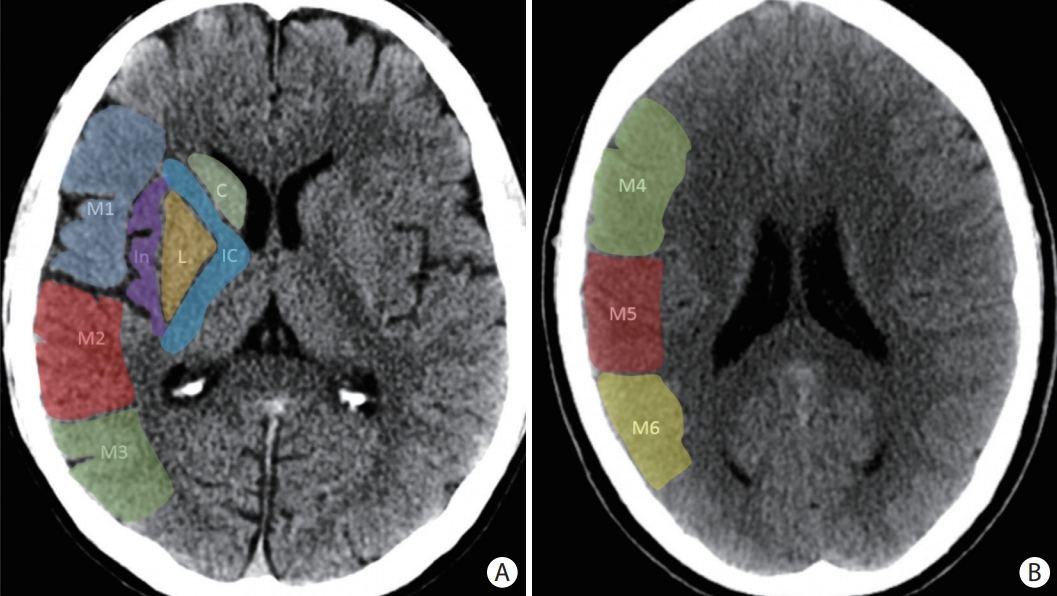
Figure 3.
The posterior circulation Acute Stroke Prognosis Early Computed Tomography Score (pc-ASPECTS) is a score derived from evaluating eight distinct regions for evidence of early ischemic changes in the posterior circulation territories as shown on (A-C) three axial slices of a non-contrast head computed tomography. The superimposed numbers indicate the point values assigned to each region. Specifically, the midbrain and pons each account for two points in the scoring system, while the bilateral cerebellar hemispheres, bilateral thalami, and bilateral occipital lobes account for one point each.
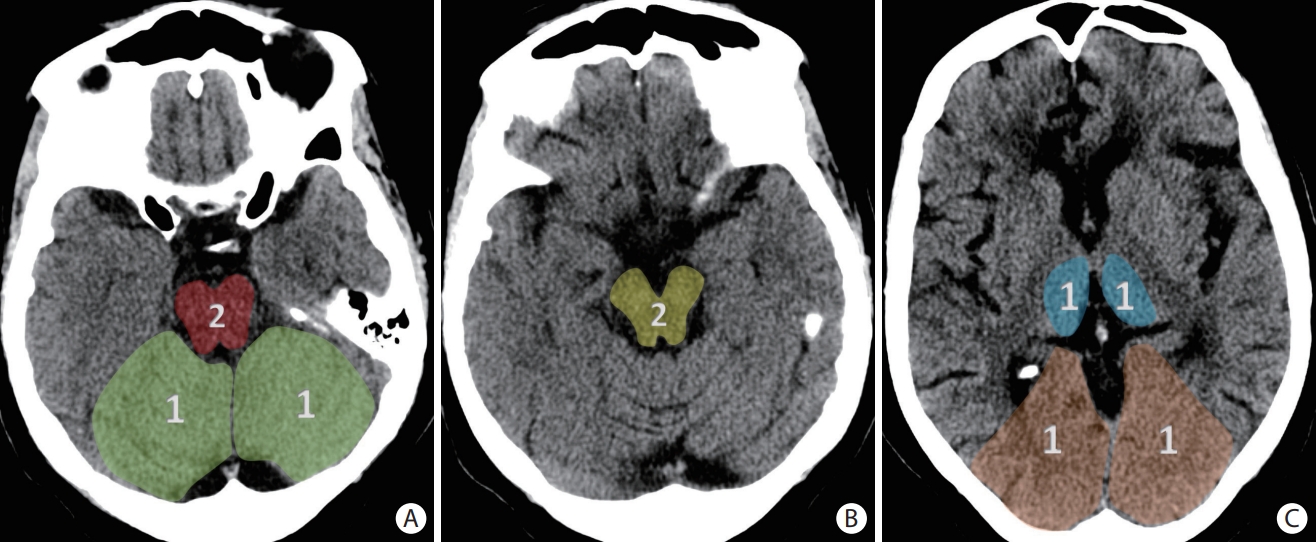
Figure 4.
Examples of hyperdense vessel signs (white circles) on non-contrast axial head computed tomography in (A) the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery, (B) M2 segment of the left middle cerebral artery, (C) the basilar artery, and (D) the anterior cerebral artery.

Figure 5.
Collateral circulation in acute ischemic stroke. (A) CT angiograpy source images in a patient with left M1 occlusion showing dark left middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory due to lack of collaterals that were confirmed on (B) angiogram. Despite (C) complete recanalization, (D) there was progression to large left MCA infarct. Paucity of collaterals indicates a high probability of tissue infarction despite successful recanalization, and correlates strongly with hypoperfusion estimates on advanced neuroimaging. (E) Anteroposterior angiogram of a right internal carotid artery injection showing an abrupt cut-off of the M1 segment of the right MCA. There are significant leptomeningeal collaterals (white circle) from the right anterior cerebral artery to the right MCA territory. (F) Complete reperfusion was achieved with (G) very small infarction of the lenticular nucleus.
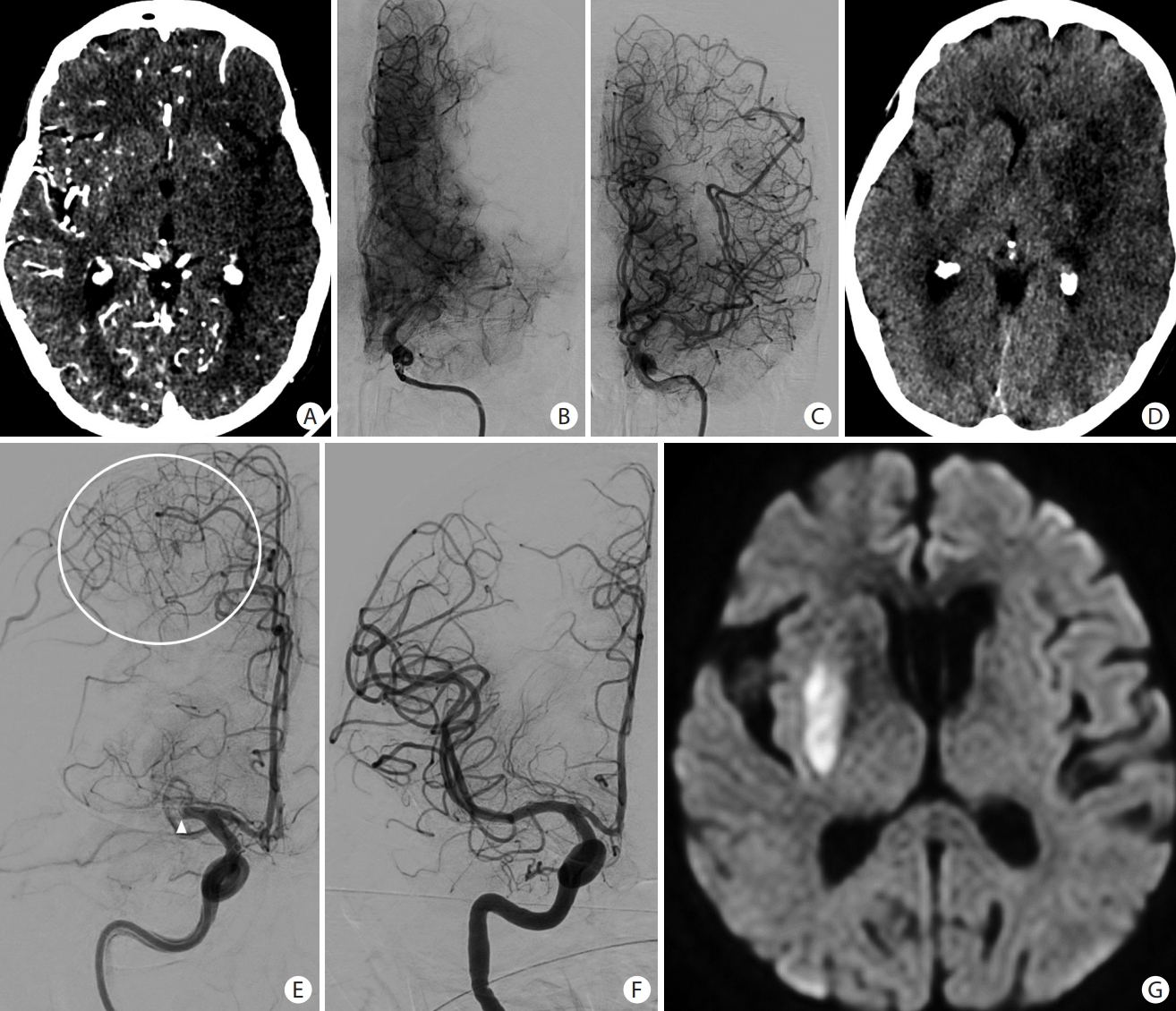
Figure 6.
Patient presented with an acute occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (arrowheads on A and C). There is also a shelf-like filling defect of the posterior aspect of the carotid bifurcation (white arrows on A and B), consistent with a carotid web which is an underappreciated cause of embolic stroke. Image on (A) is a 3D volume rendering reconstruction of a CT angiogram of the neck. Images on (B), (C), and (D) consist of cerebral angiograms.

Figure 7.
A patient presented with slurred speech, right arm and leg plegia and numbness. (A) Coronal computed tomography angiogram of the head and (C) anteroposterior angiogram showing an occlusion of the A2 segment of the left anterior cerebral artery (ACA) (white arrows) and critical stenosis of the M1 segment of the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) (white circle). (B) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) perfusion images with mean transient time (MTT), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and cerebral blood volume (CBV) showing a core infarct (prolonged MTT with significantly reduced CBF and CBV) in the left ACA territory and an area of penumbra (prolonged MTT with mildly reduced CBF and preserved CBV) in the left MCA territory. (D) Based on the patient’s clinical presentation and perfusion images, decision was to proceed with MCA recanalization to salvage the left MCA territory at risk. Intracranial stenting was performed with restoration of flow of the left MCA territory. No endovascular treatment was performed of the A2 occlusion because of the complete irreversible infarction of the ACA territory. (E and F) Follow-up MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging showing an infarction of the left ACA territory with a small focus of infarction of the lenticular nucleus.
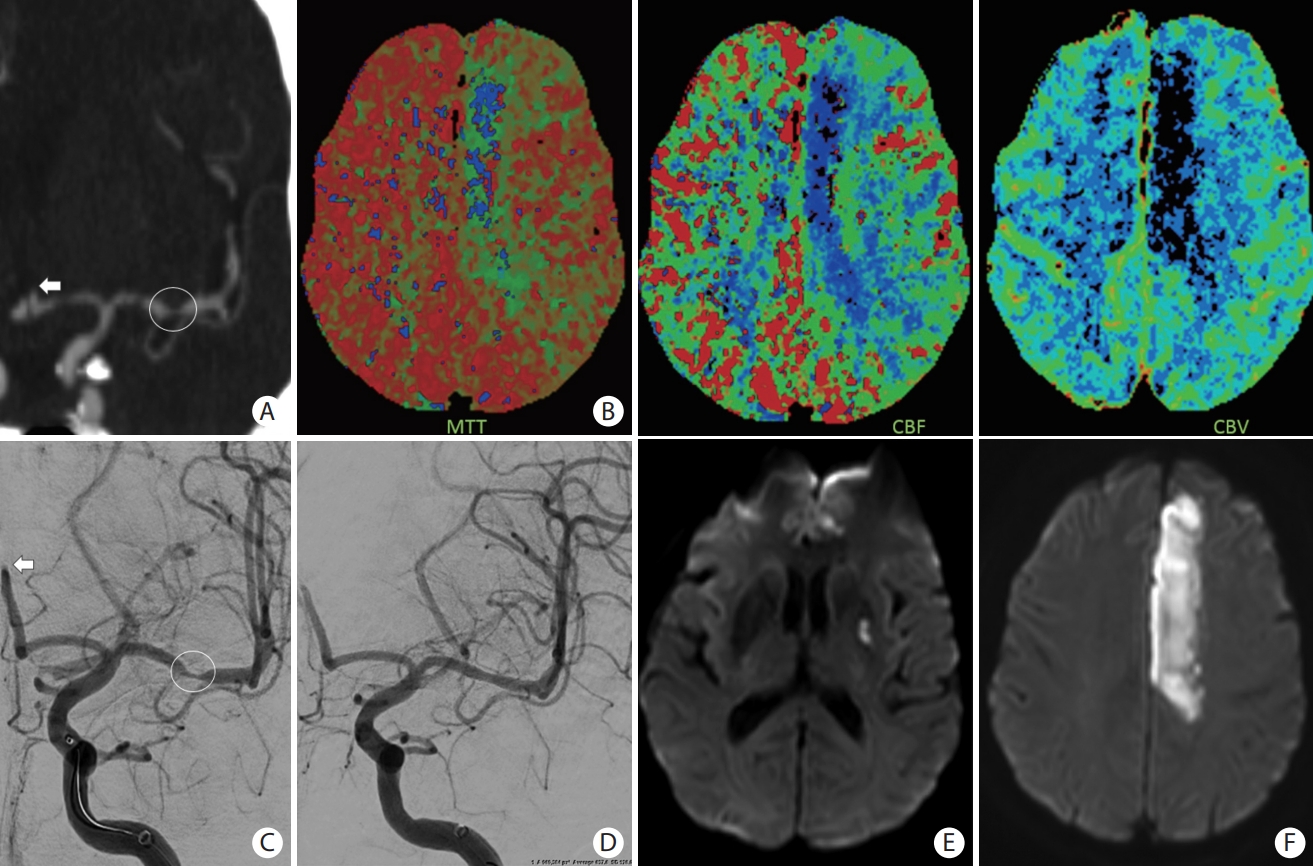
Figure 8.
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in acute ischemic stroke. (A) Axial susceptibility-weighted images showing blooming (white circle) in the right Sylvian fissure due to (D) an M2 occlusion (white arrow) that was confirmed on the cerebral angiogram. (B) Axial diffusion-weighted images (DWI) showing areas of restricted diffusion with (C) no significant fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) hyperintensities (DWI-FLAIR mismatch). (C) Note of “hyperintense vessels sign” seen on FLAIR as a result of slow or retrograde flow (arrowheads). (E) Mechanical thrombectomy was performed with recanalization of the distal M2 occlusion.

References
1. Romero JR, Pikula A, Nguyen TN, Nien YL, Norbash A, Babikian VL. Cerebral collateral circulation in carotid artery disease. Curr Cardiol Rev 2009;5:279-288.



2. Meinel TR, Kaesmacher J, Mosimann PJ, Seiffge D, Jung S, Mordasini P, et al. Association of initial imaging modality and futile recanalization after thrombectomy. Neurology 2020;95:e2331-e2342.



3. Linfante I, Starosciak AK, Walker GR, Dabus G, Castonguay AC, Gupta R, et al. Predictors of poor outcome despite recanalization: a multiple regression analysis of the NASA registry. J Neurointerv Surg 2016;8:224-229.


4. Seker F, Qureshi MM, Möhlenbruch MA, Nogueira RG, Abdalkader M, Ribo M, et al. Reperfusion without functional independence in late presentation of stroke with large vessel occlusion. Stroke 2022;53:3594-3604.


5. Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S, Christensen S, Tsai JP, Ortega-Gutierrez S, et al. Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med 2018;378:708-718.



6. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018;49:e46-e110.


7. Ko SB, Park HK, Kim BM, Heo JH, Rha JH, Kwon SU, et al. 2019 update of the Korean clinical practice guidelines of stroke for endovascular recanalization therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke 2019;21:231-240.




8. Liu L, Chen W, Zhou H, Duan W, Li S, Huo X, et al. Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular disorders: executive summary and 2019 update of clinical management of ischaemic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2020;5:159-176.



9. Casaubon LK, Boulanger JM, Blacquiere D, Boucher S, Brown K, Goddard T, et al. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: hyperacute stroke care guidelines, update 2015. Int J Stroke 2015;10:924-940.



10. Turc G, Bhogal P, Fischer U, Khatri P, Lobotesis K, Mazighi M, et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) - European Society for Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy (ESMINT) guidelines on mechanical thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic StrokeEndorsed by Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE). Eur Stroke J 2019;4:6-12.




11. Nguyen TN, Castonguay AC, Siegler JE, Nagel S, Lansberg MG, de Havenon A, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in the late presentation of anterior circulation large vessel occlusion stroke: a guideline from the Society of Vascular and Interventional Neurology guidelines and Practice Standards Committee. Stroke Vasc Interv Neurol 2023;3:e000512.

12. Nguyen TN, Klein P, Berberich A, Nagel S, Abdalkader M, Herning A, et al. Late window imaging selection for endovascular therapy of large vessel occlusion stroke: an international survey. Stroke Vasc Interv Neurol 2023;3:e000595.

13. Nguyen TN, Abdalkader M, Nagel S, Qureshi MM, Ribo M, Caparros F, et al. Noncontrast computed tomography vs computed tomography perfusion or magnetic resonance imaging selection in late presentation of stroke with large-vessel occlusion. JAMA Neurol 2022;79:22-31.



14. Sheth KN, Terry JB, Nogueira RG, Horev A, Nguyen TN, Fong AK, et al. Advanced modality imaging evaluation in acute ischemic stroke may lead to delayed endovascular reperfusion therapy without improvement in clinical outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg 2013;5 Suppl 1:i62-i65.



15. Goyal M, Menon BK, Derdeyn CP. Perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke: let us improve the science before changing clinical practice. Radiology 2013;266:16-21.


16. Gao J, Parsons MW, Kawano H, Levi CR, Evans TJ, Lin L, et al. Visibility of CT early ischemic change is significantly associated with time from stroke onset to baseline scan beyond the first 3 hours of stroke onset. J Stroke 2017;19:340-346.




17. Demchuk AM, Hill MD, Barber PA, Silver B, Patel SC, Levine SR; NINDS rtPA Stroke Study Group. Importance of early ischemic computed tomography changes using ASPECTS in NINDS rtPA Stroke Study. Stroke 2005;36:2110-2115.


18. Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, Buchan AM. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. Lancet 2000;355:1670-1674.


19. Yu W, Jiang WJ. A simple imaging guide for endovascular thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke: from time window to perfusion mismatch and beyond. Front Neurol 2019;10:502.



20. Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016;387:1723-1731.


21. Román LS, Menon BK, Blasco J, Hernández-Pérez M, Dávalos A, Majoie CBLM, et al. Imaging features and safety and efficacy of endovascular stroke treatment: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data. Lancet Neurol 2018;17:895-904.

22. Yoshimura S, Sakai N, Yamagami H, Uchida K, Beppu M, Toyoda K, et al. Endovascular therapy for acute stroke with a large ischemic region. N Engl J Med 2002;386:1303-1313.

23. Schröder J, Cheng B, Ebinger M, Köhrmann M, Wu O, Kang DW, et al. Validity of acute stroke lesion volume estimation by diffusion-weighted imaging-Alberta stroke program early computed tomographic score depends on lesion location in 496 patients with middle cerebral artery stroke. Stroke 2014;45:3583-3588.



24. Coutts SB, Lev MH, Eliasziw M, Roccatagliata L, Hill MD, Schwamm LH, et al. ASPECTS on CTA source images versus unenhanced CT: added value in predicting final infarct extent and clinical outcome. Stroke 2004;35:2472-2476.


25. Puetz V, Khomenko A, Hill MD, Dzialowski I, Michel P, Weimar C, et al. Extent of hypoattenuation on CT angiography source images in basilar artery occlusion: prognostic value in the Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study. Stroke 2001;42:3454-3459.

26. Puetz V, Sylaja PN, Coutts SB, Hill MD, Dzialowski I, Mueller P, et al. Extent of hypoattenuation on CT angiography source images predicts functional outcome in patients with basilar artery occlusion. Stroke 2008;39:2485-2490.


27. Jovin TG, Li C, Wu L, Wu C, Chen J, Jiang C, et al. Trial of thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke due to basilar-artery occlusion. N Engl J Med 2022;387:1373-1384.


28. Tao C, Nogueira RG, Zhu Y, Sun J, Han H, Yuan G, et al. Trial of endovascular treatment of acute basilar-artery occlusion. N Engl J Med 2022;387:1361-1372.


29. Abdalkader M, Hu W. Endovascular therapy for stroke due to basilar artery occlusion: challenges and opportunities. J Neuroradiol 2022;Dec. 14. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2022.12.004.

30. Mair G, Boyd EV, Chappell FM, von Kummer R, Lindley RI, Sandercock P, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the hyperdense artery sign for arterial obstruction in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2015;46:102-107.



31. Leys D, Pruvo JP, Godefroy O, Rondepierre P, Leclerc X. Prevalence and significance of hyperdense middle cerebral artery in acute stroke. Stroke 1992;23:317-324.


32. Riedel CH, Zoubie J, Ulmer S, Gierthmuehlen J, Jansen O. Thin-slice reconstructions of nonenhanced CT images allow for detection of thrombus in acute stroke. Stroke 2012;43:2319-2323.


33. Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME, Pexman JH, Hill MD, Buchan AM. Hyperdense sylvian fissure MCA “dot” sign: a CT marker of acute ischemia. Stroke 2001;32:84-88.


34. Goldmakher GV, Camargo EC, Furie KL, Singhal AB, Roccatagliata L, Halpern EF, et al. Hyperdense basilar artery sign on unenhanced CT predicts thrombus and outcome in acute posterior circulation stroke. Stroke 2009;40:134-139.


35. Abdalkader M, Sahoo A, Shulman JG, Sader E, Takahashi C, Kaliaev A, et al. Acute occlusion of the fetal posterior cerebral artery: diagnosis and management paradigms. Neuroradiol J 2021;Jun. 6. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1177/19714009211019383.

36. Abdalkader M, Sahoo A, Dmytriw AA, Brinjikji W, Dabus G, Raz E, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy of the fetal posterior cerebral artery. Stroke Vasc Interv Neurol 2021;1:e000115.

37. Brinjikji W, Duffy S, Burrows A, Hacke W, Liebeskind D, Majoie CBLM, et al. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome: a systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg 2017;9:529-534.



38. Brouwer PA, Brinjikji W, De Meyer SF. Clot pathophysiology: why is it clinically important? Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2018;28:611-623.


39. Nguyen TN, Castonguay AC, Nogueira RG, Haussen DC, English JD, Satti SR, et al. Effect of balloon guide catheter on clinical outcomes and reperfusion in Trevo thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg 2019;11:861-865.


40. Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM, Yeatts SD, Khatri P, Hill MD, et al. Endovascular therapy after intravenous t-PA versus t-PA alone for stroke. N Engl J Med 2013;368:893-903.



41. Ciccone A, Valvassori L; SYNTHESIS Expansion Investigators. Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2013;368:2433-2434.



42. Qureshi AI, Abd-Allah F, Aleu A, Connors JJ, Hanel RA, Hassan AE, et al. Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke patients: implications and interpretation of IMS III, MR RESCUE, and SYNTHESIS EXPANSION trials: a report from the working group of international congress of interventional neurology. J Vasc Interv Neurol 2014;7:56-75.
43. Lee JS, Bang OY. Collateral status and outcomes after thrombectomy. Transl Stroke Res 2022;Jun. 10. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-022-01046-z.

44. Lee SU, Hong JM, Kim SY, Bang OY, Demchuk AM, Lee JS. Differentiating carotid terminus occlusions into two distinct populations based on Willisian collateral status. J Stroke 2016;18:179-186.




45. Lee SJ, Hwang YH, Hong JM, Choi JW, Kang DH, Kim YW, et al. Predictors and prognoses of Willisian collateral failure during mechanical thrombectomy. Sci Rep 2020;10:20874.




46. Rocha M, Jovin TG. Fast versus slow progressors of infarct growth in large vessel occlusion stroke: clinical and research implications. Stroke 2017;48:2621-2627.


47. Berberich A, Finitsis S, Strambo D, Michel P, Herweh C, Meyer L, et al. Endovascular therapy versus no endovascular therapy in patients receiving best medical management for acute isolated occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol 2022;29:2664-2673.

48. Herweh C, Abdalkader M, Nguyen TN, Puetz V, Schöne D, Kaiser D, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in isolated occlusion of the proximal posterior cerebral artery. Front Neurol 2021;12:697348.



49. Lee JS, Lee SJ, Hong JM, Alverne FJAM, Lima FO, Nogueira RG. Endovascular treatment of large vessel occlusion strokes due to intracranial atherosclerotic disease. J Stroke 2022;24:3-20.




50. Diouf A, Fahed R, Gaha M, Chagnon M, Khoury N, Kotowski M, et al. Cervical internal carotid occlusion versus pseudo-occlusion at CT angiography in the context of acute stroke: an accuracy, interobserver, and intraobserver agreement study. Radiology 2018;286:1008-1015.


51. Alverne FJAM, Lima FO, Rocha FA, Bandeira DA, Lucena AF, Silva HC, et al. Unfavorable vascular anatomy during endovascular treatment of stroke: challenges and bailout strategies. J Stroke 2020;22:185-202.




52. Abdalkader M, Sahoo A, Lee J, Kiley N, Masoud HE, Norbash AM, et al. Balloon gliding technique: a novel use of balloon guiding catheters in accessing challenging circulations when treating acute ischemic stroke. Interv Neuroradiol 2022;Mar. 14. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1177/15910199221082473.

53. Cohnen M, Wittsack HJ, Assadi S, Muskalla K, Ringelstein A, Poll LW, et al. Radiation exposure of patients in comprehensive computed tomography of the head in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:1741-1745.


54. Kaiser DPO, Abdalkader M, Berberich A, Sporns PB, Nguyen TN. Acute shortage of iodinated contrast media: implications and guidance for neurovascular imaging and intervention. Neuroradiology 2002;64:1715-1718.




55. Kufner A, Erdur H, Endres M, Nolte CH, Scheel M, Schlemm L. Association between thrombus perviousness assessed on computed tomography and stroke cause. Stroke 2020;51:3613-3622.


56. Kappelhof M, Tolhuisen ML, Treurniet KM, Dutra BG, Alves H, Zhang G, et al. Endovascular treatment effect diminishes with increasing thrombus perviousness: pooled data from 7 trials on acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2021;52:3633-3641.



57. Borst J, Berkhemer OA, Santos EMM, Yoo AJ, den Blanken M, Roos YBWEM, et al. Value of thrombus CT characteristics in patients with acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2017;38:1758-1764.



58. Wiegers EJA, Mulder MJHL, Jansen IGH, Venema E, Compagne KCJ, Berkhemer OA, et al. Clinical and imaging determinants of collateral status in patients with acute ischemic stroke in MR CLEAN trial and registry. Stroke 2020;51:1493-1502.

59. Menon BK, d’Esterre CD, Qazi EM, Almekhlafi M, Hahn L, Demchuk AM, et al. Multiphase CT angiography: a new tool for the imaging triage of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Radiology 2015;275:510-520.


61. Bang OY, Goyal M, Liebeskind DS. Collateral circulation in ischemic stroke: assessment tools and therapeutic strategies. Stroke 2015;46:3302-3309.



62. Wang YJ, Wang JQ, Qiu J, Li W, Sun XH, Zhao YG, et al. Association between collaterals, cerebral circulation time and outcome after thrombectomy of stroke. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2022;Dec. 16. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.51718.

63. Marks MP, Lansberg MG, Mlynash M, Olivot JM, Straka M, Kemp S, et al. Effect of collateral blood flow on patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2014;45:1035-1039.



64. Vagal A, Aviv R, Sucharew H, Reddy M, Hou Q, Michel P, et al. Collateral clock is more important than time clock for tissue fate: a natural history study of acute ischemic strokes. Stroke 2018;49:2102-2107.



65. Souza LC, Yoo AJ, Chaudhry ZA, Payabvash S, Kemmling A, Schaefer PW, et al. Malignant CTA collateral profile is highly specific for large admission DWI infarct core and poor outcome in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33:1331-1336.



66. Maas MB, Lev MH, Ay H, Singhal AB, Greer DM, Smith WS, et al. Collateral vessels on CT angiography predict outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2009;40:3001-3005.



67. Venema E, Mulder MJHL, Roozenbeek B, Broderick JP, Yeatts SD, Khatri P, et al. Selection of patients for intra-arterial treatment for acute ischaemic stroke: development and validation of a clinical decision tool in two randomised trials. BMJ 2017;357:j1710.



68. d’Esterre CD, Trivedi A, Pordeli P, Boesen M, Patil S, Ahn SH, et al. Regional comparison of multiphase computed tomographic angiography and computed tomographic perfusion for prediction of tissue fate in ischemic stroke. Stroke 2017;48:939-945.


69. Almekhlafi MA, Kunz WG, McTaggart RA, Jayaraman MV, Najm M, Ahn SH, et al. Imaging triage of patients with late-window (6-24 hours) acute ischemic stroke: a comparative study using multiphase CT angiography versus CT perfusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2020;41:129-133.



70. Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1019-1030.


71. Dundamadappa S, Iyer K, Agrawal A, Choi DJ. Multiphase CT angiography: a useful technique in acute stroke imaging—collaterals and beyond. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2021;42:221-227.



72. Yang CY, Chen YF, Lee CW, Huang A, Shen Y, Wei C, et al. Multiphase CT angiography versus single-phase CT angiography: comparison of image quality and radiation dose. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29:1288-1295.



73. Martins N, Aires A, Mendez B, Boned S, Rubiera M, Tomasello A, et al. Ghost infarct core and admission computed tomography perfusion: redefining the role of neuroimaging in acute ischemic stroke. Interv Neurol 2018;7:513-521.




74. Hoving JW, Marquering HA, Majoie CBLM, Yassi N, Sharma G, Liebeskind DS, et al. Volumetric and spatial accuracy of computed tomography perfusion estimated ischemic core volume in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2018;49:2368-2375.


75. Demeestere J, Wouters A, Christensen S, Lemmens R, Lansberg MG. Review of perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke: from time to tissue. Stroke 2020;51:1017-1024.


76. Austein F, Riedel C, Kerby T, Meyne J, Binder A, Lindner T, et al. Comparison of perfusion CT software to predict the final infarct volume after thrombectomy. Stroke 2016;47:2311-2317.


77. Thomalla G, Simonsen CZ, Boutitie F, Andersen G, Berthezene Y, Cheng B, et al. MRI-guided thrombolysis for stroke with unknown time of onset. N Engl J Med 2018;379:611-622.


78. Ma H, Campbell BCV, Parsons MW, Churilov L, Levi CR, Hsu C, et al. Thrombolysis guided by perfusion imaging up to 9 hours after onset of stroke. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1795-1803.


79. Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2285-2295.


80. Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1009-1018.


81. Amukotuwa SA, Wu A, Zhou K, Page I, Brotchie P, Bammer R. Distal medium vessel occlusions can be accurately and rapidly detected using Tmax maps. Stroke 2021;52:3308-3317.


82. Becks MJ, Manniesing R, Vister J, Pegge SAH, Steens SCA, van Dijk EJ, et al. Brain CT perfusion improves intracranial vessel occlusion detection on CT angiography. J Neuroradiol 2019;46:124-129.


83. Kerleroux B, Janot K, Dargazanli C, Daly-Eraya D, Ben-Hassen W, Zhu F, et al. Perfusion imaging to select patients with large ischemic core for mechanical thrombectomy. J Stroke 2020;22:225-233.




84. Chiu FY, Teng MM, Kao YH, Chen YD, Luo CB, Chang FC, et al. Selection of arterial input function for postprocessing of cerebral CT perfusion in chronic unilateral high-grade stenosis or occlusion of the carotid or middle cerebral artery. Acad Radiol 2012;19:8-16.


85. Marchal G, Young AR, Baron JC. Early postischemic hyperperfusion: pathophysiologic insights from positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999;19:467-482.



86. Burke JF, Kerber KA, Iwashyna TJ, Morgenstern LB. Wide variation and rising utilization of stroke magnetic resonance imaging: data from 11 states. Ann Neurol 2012;71:179-185.



87. Brazzelli M, Sandercock PA, Chappell FM, Celani MG, Righetti E, Arestis N, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography for detection of acute vascular lesions in patients presenting with stroke symptoms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;4:CD007424.

88. Matsumoto K, Lo EH, Pierce AR, Wei H, Garrido L, Kowall NW. Role of vasogenic edema and tissue cavitation in ischemic evolution on diffusion-weighted imaging: comparison with multiparameter MR and immunohistochemistry. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16:1107-1115.


89. Campbell BC, Purushotham A, Christensen S, Desmond PM, Nagakane Y, Parsons MW, et al. The infarct core is well represented by the acute diffusion lesion: sustained reversal is infrequent. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2012;32:50-56.




90. Edlow BL, Hurwitz S, Edlow JA. Diagnosis of DWI-negative acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. Neurology 2017;89:256-262.



91. Labeyrie MA, Turc G, Hess A, Hervo P, Mas JL, Meder JF, et al. Diffusion lesion reversal after thrombolysis: a MR correlate of early neurological improvement. Stroke 2012;43:2986-2991.


92. Kranz PG, Eastwood JD. Does diffusion-weighted imaging represent the ischemic core? An evidence-based systematic review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:1206-1212.



93. Makkat S, Vandevenne JE, Verswijvel G, Ijsewijn T, Grieten M, Palmers Y, et al. Signs of acute stroke seen on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002;179:237-243.


94. Thomalla G, Cheng B, Ebinger M, Hao Q, Tourdias T, Wu O, et al. DWI-FLAIR mismatch for the identification of patients with acute ischaemic stroke within 4·5 h of symptom onset (PREFLAIR): a multicentre observational study. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:978-986.


95. Emeriau S, Serre I, Toubas O, Pombourcq F, Oppenheim C, Pierot L. Can diffusion-weighted imaging-fluid-attenuated inversion recovery mismatch (positive diffusion-weighted imaging/negative fluid-attenuated inversion recovery) at 3 tesla identify patients with stroke at <4.5 hours? Stroke 2013;44:1647-1651.


96. Cho AH, Sohn SI, Han MK, Lee DH, Kim JS, Choi CG, et al. Safety and efficacy of MRI-based thrombolysis in unclear-onset stroke. A preliminary report. Cerebrovasc Dis 2008;25:572-579.



97. Fischer U, Branca M, Bonati LH, Carrera E, Vargas MI, Platon A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography for suspected acute stroke: association of admission image modality with acute recanalization therapies, workflow metrics, and outcomes. Ann Neurol 2022;92:184-194.


98. Kidwell CS, Chalela JA, Saver JL, Starkman S, Hill MD, Demchuk AM, et al. Comparison of MRI and CT for detection of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA 2004;292:1823-1830.


99. Arnould MC, Grandin CB, Peeters A, Cosnard G, Duprez TP. Comparison of CT and three MR sequences for detecting and categorizing early (48 hours) hemorrhagic transformation in hyperacute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:939-944.


100. Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Yong WH, Starkman S, Tsang MP, Moya AL, et al. CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke 2011;42:1237-1243.



101. Mohammaden MH, Haussen DC, Perry da Camara C, Pisani L, Olive Gadea M, Al-Bayati AR, et al. Hyperdense vessel sign as a potential guide for the choice of stent retriever versus contact aspiration as first-line thrombectomy strategy. J Neurointerv Surg 2021;13:599-604.


102. Suh HI, Hong JM, Lee KS, Han M, Choi JW, Kim JS, et al. Imaging predictors for atherosclerosis-related intracranial large artery occlusions in acute anterior circulation stroke. J Stroke 2016;18:352-354.




103. Lee JS, Hong JM, Kim JS. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for acute intracranial atherosclerosis-related occlusions. J Stroke 2017;19:143-151.




104. Menjot de Champfleur N, Saver JL, Goyal M, Jahan R, Diener HC, Bonafe A, et al. Efficacy of stent-retriever thrombectomy in magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomographic perfusion-selected patients in SWIFT PRIME trial (solitaire FR with the intention for thrombectomy as primary endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke). Stroke 2017;48:1560-1566.


105. Kim JT, Cho BH, Choi KH, Park MS, Kim BJ, Park JM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography angiography based selection for endovascular therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2019;50:365-372.

106. Eskey CJ, Meyers PM, Nguyen TN, Ansari SA, Jayaraman M, McDougall CG, et al. Indications for the performance of intracranial endovascular neurointerventional procedures: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018;137:e661-e689.


107. Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RF, Bhuva P, et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med 2018;378:11-21.

108. Yamagami H, Hayakawa M, Inoue M, Iihara K, Ogasawara K, Toyoda K, et al. Guidelines for mechanical thrombectomy in japan, the fourth edition, March 2020: a guideline from the Japan Stroke Society, the Japan Neurosurgical Society, and the Japanese Society for Neuroendovascular Therapy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2021;61:163-192.



109. Siegler JE, Qureshi MM, Nogueira RG, Tanaka K, Nagel S, Michel P, Vigilante N, Ribo M, Yamagami H, Yoshimura S, et al. Endovascular versus medical management for late-window anterior large vessel occlusion with pre-stroke disability: Patient-level analysis from the CLEAR and RESCUE-Japan studies. Neurology 2022;Nov. 4. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000201543.

110. Kim Y, Lee S, Abdelkhaleq R, Lopez-Rivera V, Navi B, Kamel H, et al. Utilization and availability of advanced imaging in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2021;14:e006989.


111. Leslie-Mazwi TM, Hamilton S, Mlynash M, Patel AB, Schwamm LH, Lansberg MG, et al. DEFUSE 3 non-DAWN patients. Stroke 2019;50:618-625.



112. Siegler JE, Messé SR, Sucharew H, Kasner SE, Mehta T, Arora N, et al. Thrombectomy in DAWN- and DEFUSE-3-ineligible patients: a subgroup analysis from the best prospective cohort study. Neurosurgery 2020;86:E156-E163.



113. Nguyen TN, Raymond J, Nogueira RG, Fischer U, Siegler JE. The problem of restrictive thrombectomy trial eligibility criteria. Stroke 2022;53:2988-2990.


114. Jadhav AP, Desai SM, Kenmuir CL, Rocha M, Starr MT, Molyneaux BJ, et al. Eligibility for endovascular trial enrollment in the 6- to 24-hour time window: analysis of a single comprehensive stroke center. Stroke 2018;49:1015-1017.


115. Desai SM, Rocha M, Molyneaux BJ, Starr M, Kenmuir CL, Gross BA, et al. Thrombectomy 6-24 hours after stroke in trial ineligible patients. J Neurointerv Surg 2018;10:1033-1037.


116. Ducroux C, Khoury N, Lecler A, Blanc R, Chetrit A, Redjem H, et al. Application of the DAWN clinical imaging mismatch and DEFUSE 3 selection criteria: benefit seems similar but restrictive volume cut-offs might omit potential responders. Eur J Neurol 2018;25:1093-1099.



117. Santos T, Carvalho A, Cunha AA, Rodrigues M, Gregório T, Paredes L, et al. NCCT and CTA-based imaging protocol for endovascular treatment selection in late presenting or wakeup strokes. J Neurointerv Surg 2019;11:200-203.


118. DiBiasio EL, Jayaraman MV, Goyal M, Yaghi S, Tung E, Hidlay DT, et al. Dismantling the ability of CT and MRI to identify the target mismatch profile in patients with anterior circulation large vessel occlusion beyond six hours from symptom onset. Emerg Radiol 2019;26:401-408.



119. Pirson FAVA, Hinsenveld WH, Goldhoorn RB, Staals J, de Ridder IR, van Zwam WH; MR CLEAN-LATE investigators. MR CLEAN-LATE, a multicenter randomized clinical trial of endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke in the Netherlands for late arrivals: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2021;22:160.




120. Almekhlafi MA, Thornton J, Casetta I, Goyal M, Nannoni S, Herlihy D, et al. Stroke imaging prior to thrombectomy in the late window: results from a pooled multicentre analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2022;93:468-474.


121. Almekhlafi MA, Kunz WG, Menon BK, McTaggart RA, Jayaraman MV, Baxter BW, et al. Imaging of patients with suspected large-vessel occlusion at primary stroke centers: available modalities and a suggested approach. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2019;40:396-400.



122. Demeestere J, Scheldeman L, Cornelissen SA, Heye S, Wouters A, Dupont P, et al. Alberta stroke program early CT score versus computed tomographic perfusion to predict functional outcome after successful reperfusion in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2018;49:2361-2367.



123. Dhillon PS, Butt W, Podlasek A, Barrett E, McConachie N, Lenthall R, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy beyond 24 hours from ischemic stroke onset: a propensity score matched cohort study. J Neurointerv Surg 2022;Feb. 15. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-018591.

124. Christensen S, Mlynash M, Kemp S, Yennu A, Heit JJ, Marks MP, et al. Persistent target mismatch profile >24 hours after stroke onset in DEFUSE 3. Stroke 2019;50:754-757.



125. Stanton RJ, Wang LL, Smith MS, Aziz Y, Zhang B, Grossman AW, et al. Differences in automated perfusion software: do they matter clinically? Stroke Vasc Interv Neurol 2022;2:e000424.

126. Murray NM, Unberath M, Hager GD, Hui FK. Artificial intelligence to diagnose ischemic stroke and identify large vessel occlusions: a systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg 2020;12:156-164.


127. Grunwald IQ, Kulikovski J, Reith W, Gerry S, Namias R, Politi M, et al. Collateral automation for triage in stroke: evaluating automated scoring of collaterals in acute stroke on computed tomography scans. Cerebrovasc Dis 2019;47:217-222.




128. Kamel H, Navi BB, Parikh NS, Merkler AE, Okin PM, Devereux RB, et al. Machine learning prediction of stroke mechanism in embolic strokes of undetermined source. Stroke 2020;51:e203-e210.