 |
 |
- Search
| J Stroke > Volume 25(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background and Purpose
Various mechanisms are involved in the etiology of stroke caused by atherosclerosis of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Here, we compared differences in plaque nature and hemodynamic parameters according to stroke mechanism in patients with MCA atherosclerosis.
Methods
Consecutive patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic MCA atherosclerosis (Ōēź50% stenosis) were enrolled. MCA plaque characteristics (location and plaque enhancement) and wall shear stress (WSS) were measured using high-resolution vessel wall and four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging, respectively, at five points (initial, upstream, minimal lumen, downstream, and terminal). These parameters were compared between patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic MCA atherosclerosis with infarctions of different mechanisms (artery-to-artery embolism vs. local branch occlusion).
Results
In total, 110 patients (46 asymptomatic, 32 artery-to-artery embolisms, and 32 local branch occlusions) were investigated. Plaques were evenly distributed in the MCA of patients with asymptomatic MCA atherosclerosis, more commonly observed in the distal MCA of patients with artery-to-artery embolism, and in the middle MCA of patients with local branch occlusion. Maximum WSS and plaque enhancement were more prominent in the minimum lumen area of patients with asymptomatic MCA atherosclerosis or those with local branch occlusion, and were more prominent in the upstream area in those with artery-to-artery embolism. The elevated variability in the maximum WSS was related to stroke caused by artery-to-artery embolism.
Atherosclerosis in intracranial arteries, including the middle cerebral artery (MCA), is commonly observed in patients with ischemic stroke and has a particularly high prevalence in Asians. Various mechanisms are involved in stroke caused by MCA atherosclerosis: artery-to-artery embolism (AAE), which is the most common in patients with intracranial arterial stenosis, local branch occlusion (LBO), in situ thrombosis, and combined mechanisms [1-3]. The lesion pattern is affected by the mechanism of ischemic stroke with MCA disease [4]. Efforts have been made to explain the differences in platelet reactivity extent, plaque nature, and plaque location in the MCA depending on stroke mechanisms [4-6].
Wall shear stress (WSS) is a direct mechanical frictional force generated by cerebral blood flow acting on the plaque inside the stenotic artery [7]. A low WSS enhances the development and progression of atherosclerosis in the cerebral arteries [8,9], while a high WSS inside the vasculature provokes plaque rupture [7,10,11]. Furthermore, areas with a high or alternating WSS commonly experience shear-induced platelet activation, which may result in distal embolization and ischemic stroke [12-14]. However, studies to date have mostly used vascular geometry or computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to presume or indirectly measure the hemodynamics and analyze the association between hemodynamic parameters and the development of atherosclerosis or ischemic stroke.
Four-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a useful tool for directly measuring blood flow and hemodynamic parameters of individual patients using in vivo quantification. We hypothesized that WSS measured by four-dimensional MRI would influence vessel wall pathology and be associated with the occurrence and mechanisms of ischemic stroke. Thus, in this study, we compared the plaque nature and WSS characteristics between patients with asymptomatic MCA stenosis (aMCA), symptomatic MCA stenosis with infarction due to AAE (sMCA-AAE), and symptomatic MCA stenosis with infarction due to LBO (sMCA-LBO).
All data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
This was a retrospective analysis of consecutive prospectively recruited patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic atherosclerotic MCA stenosis (M1 portion), diagnosed using high-resolution vessel wall MRI (HRVWI) between January 2018 and December 2020. Symptomatic stenosis was defined as significant stenosis (Ōēź50%) with acute ischemic stroke (within 7 days of stroke onset) in the corresponding vascular territory defined on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Asymptomatic stenosis was defined as significant stenosis (Ōēź50%) in the MCA confirmed on magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) performed for evaluation of reasons other than stroke (i.e., headache or dizziness).
We excluded patients with (1) tandem stenotic lesions at the carotid artery and MCA branch (significant stenosis or occlusion); (2) another embolic source (e.g., cardioembolic source or coagulopathy); or (3) other etiologies of MCA steno-occlusive disease, such as dissection, vasculitis, or moyamoya disease. We further excluded patients whose MRA data did not allow WSS assessment (e.g., near or complete occlusion of the MCA, poor MRA quality), those who underwent reperfusion treatment prior to the MRI, and those who did not provide consent. As many patients with in situ thrombosis, combined mechanisms, or embolism from the proximal arteries showed complete occlusion, patients with these mechanisms were not included in the analysis. Finally, among patients with symptomatic MCA stenosis, those with stroke due to AAE and LBO were included in the analysis.
Demographic characteristics, vascular risk factors, and concurrent medications were also recorded. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kyung Hee University Hospital (KHUH IRB 2018-07-065), which waived the requirement for informed consent owing to its retrospective nature and the minimal risk to patients.
Patients with symptomatic MCA stenosis underwent 3-T MRI and MRA (Intera; Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands) on the first day of admission to the stroke unit, including the following sequences: DWI, T1- and T2-weighted imaging, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging, susceptibilitay-weighted imaging, time-of-flight (TOF) MRA (intracranial), and contrast-enhanced MRA (extracranial). Patients with aMCA underwent 3-T MRI and MRA within two weeks of the first visit to the outpatient clinic.
If significant stenosis (Ōēź50%) in the MCA was suspected on TOF MRA, the patients further underwent HRVWI, which was performed using a 3-T Philips scanner (Philips Healthcare, Eindhoven, the Netherlands) with a standard 16-channel neurovascular coil. The recorded sequences included TOF MRA, maximum-intensity projection, T1-weighted imaging, proton-density black blood imaging (PD-BBI), and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging with turbo/fast spin-echo sequences. T1-weighted spin echo was obtained using the following parameters (in-plane resolution=0.5├Ś0.5 mm, slice thickness/spacing=0.5/0.5 mm, repetition time [TR]/echo time [TE]=650/16 ms, field-of-view [FOV]=180├Ś180 mm, matrix=360├Ś360, time=7 min 20 s), voxel size=0.35├Ś0.35├Ś0.5 mm3. PD-BBI was obtained using the following parameters along the MCA axis: TR/TE=2,000/30 ms, FOV=180├Ś180 mm, matrix=360├Ś360, slice thickness/spacing=0.5/0.5 mm. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging was performed following injection of intravenous gadolinium (Gadovist; Bayer Schering Pharma, Berlin, Germany). A pre-regional 80-mm-thick saturation pulse was used to saturate the incoming arterial flow.
Four-dimensional flow MRI was acquired using three-dimensional fast field-echo velocity-encoded phase contrast MRI sequence with the following parameters: TR/TE=4.3/2.2 ms, flip angle=10┬░, FOV=211├Ś181 mm, matrix size=140├Ś118, acquisition voxel size=1.5├Ś1.5├Ś1.5 mm3, reconstructed voxel size=0.9├Ś0.9├Ś1.5 mm3, and sensitivity encoding (SENSE) factor=2.0, velocity encoding (VENC)=80 cm/s, and reconstructed cardiac phases=20. We used a commercially available four-dimensional flow software (GT-Flow ver. 3.0.23; GyroTools LLC, Zurich, Switzerland) to evaluate the WSS of each enrolled patient. GT-Flow software, which was recently used to estimate the WSS of intracranial arteries and carotid artery, is well agreed with CFD, which is currently regarded as the gold standard for measuring cerebral hemodynamics [15-18]. A semiautomatic filter was applied to mask static tissue, including the brain parenchyma and skull. Two-dimensional analysis planes were positioned perpendicular to the long axis of the vessels in the M1 segment of the MCA. For each analysis plane, the region of interest was placed on the vessels using a semi-automatic iso-contour method with the GT-Flow software. The WSS (maximum and mean) of the vessel through a cardiac cycle was measured as previous study [17-19].
The mechanism of stroke triggered by MCA stenosis was classified by the lesion pattern on DWI, decided by consensus. First, patients with small scattered cortical lesions were classified by AAE. Second, patients with a small (lesion diameter, <2 cm) single subcortical lesion with a spatial relationship between the perforating arteries and the margin of plaque on HRVWI were classified as LBO. Third, patients with territorial infarction due to MCA occlusion, except those with MCA occlusion due to combined mechanisms or embolism from the proximal arteries, were classified as having in situ thrombosis. Fourth, patients with small scattered cortical lesions and a single subcortical lesion were classified as having other combined mechanisms [20].
The plaque characteristics were evaluated using HRVWI. The plaque location was assessed from the MCA M1 portion between the MCA and anterior cerebral artery bifurcation point and MCA M2 bifurcation point, and plaque location inside the MCA was sub-classified as either proximal, middle, or distal.
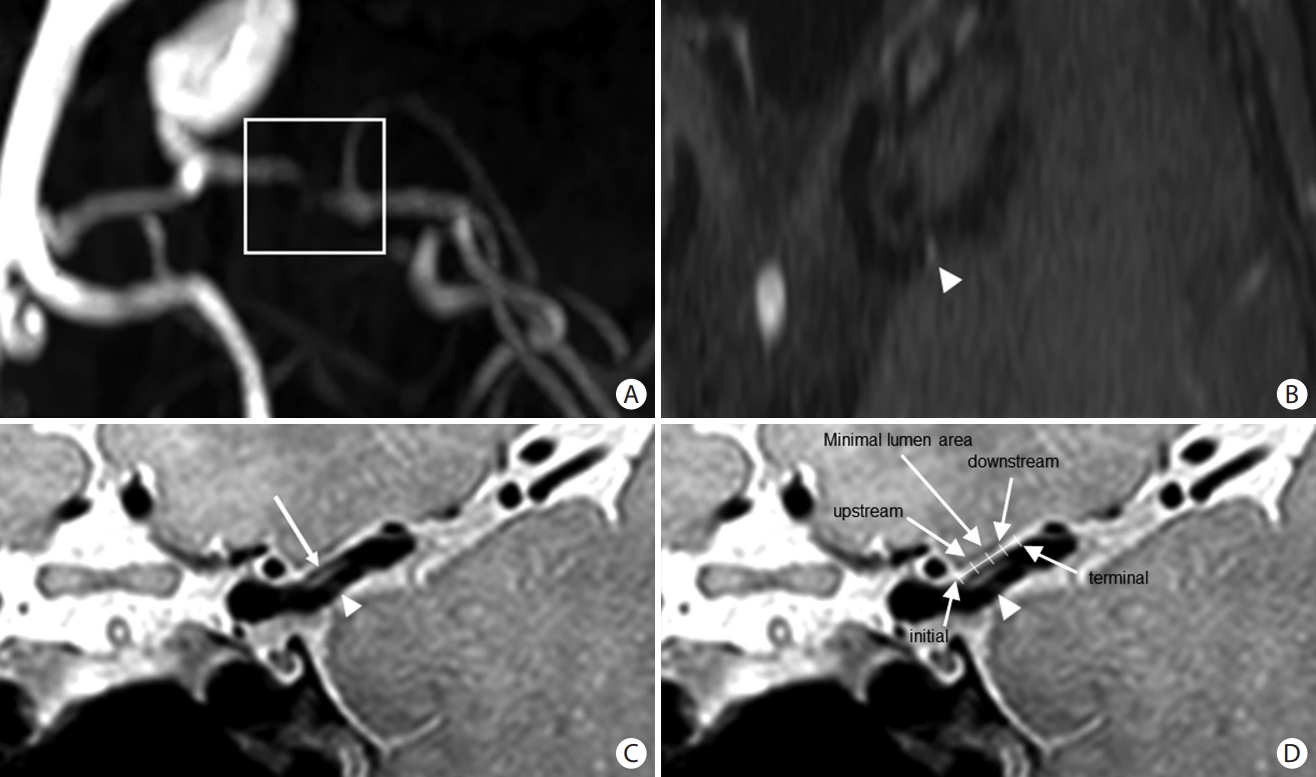
Plaque enhancement was defined as a higher signal intensity on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging than on T1-weighted imaging, assessed to be within the MCA with an atherosclerotic plaque. Within the plaque, the location of enhancement was measured at five points; initial, upstream, minimal lumen area, downstream, and terminal [21,22]. These five points were defined as follows: The point with the most severe stenosis was defined as the minimal lumen area. The most proximal and distal points with atherosclerotic plaques were defined as the initial and terminal points, respectively. The middle points located between the initial or terminal point and the minimal lumen area were defined as the upstream and downstream points, respectively (Figure 1).
The degree of stenosis of the MCA was calculated on TOF MRA and HRVWI using the following formula: [1 - (the diameter of the artery at minimal lumen area/the diameter of the proximal normal artery)] ├Ś 100%. Two independent researchers blinded to the patientsŌĆÖ clinical information (H.G.W. and H.K.) evaluated the characteristics of the MCA plaques on HRVWI. If any discrepancies occurred between two independent researchers, a consensus meeting was held with more than three researchers (including B.J.K.) to decide on a final characterization of the MCA plaque characteristics.
The WSS of the atherosclerotic MCA was measured using GT-Flow software at five points. The time-averaged WSS during the cardiac cycle was measured from each slice perpendicular to the MCA at five points. The maximum and mean time-averaged WSS within the slice along the circumferential vessel wall are presented as the maximal and mean time-averaged WSS at a particular point. The maximal WSS was used for the main analysis.
To evaluate the spatial variability of the WSS, we calculated the standard deviation (SD) and coefficient of variation (CoV) of the maximal WSS measured from the five points. The location of the highest maximal WSS among the five points was also investigated in each group. Because the flow status was estimated on a patient-specific basis, we normalized the maximal WSS to the relative values, such as the highest/initial maximal WSS ratio (highest value of maximal WSS among five locations/value of maximal WSS on initial location) or the lowest/initial maximal WSS ratio (lowest value of maximal WSS among five locations/value of maximal WSS on initial location).
Kappa statistics were applied to calculate the inter-rater reliability between the two researchers for the identification of MCA plaque enhancement. Patient demographics, vascular risk factors, concurrent medication, MCA plaque characteristics, and WSS of the atherosclerotic MCA were compared between patients with aMCA, sMCA-AAE, and sMCA-LBO. Pearson chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance, or the Kruskal-Wallis test were used as appropriate. Spearman rank-correlation analyses were used to investigate the association between the highest maximal WSS location and the plaque enhancement location.
Subsequently, we analyzed the association between the stroke mechanism and plaque and WSS characteristics. Multivariable logistic regression analysis included age, sex, and all potential predictors with values of P<0.1 in the univariable analyses. Binary logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate the independent association between sMCA-AAE and maximal WSS. Odds ratios (ORs) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 22.0 for Windows (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
From our initial database of 2,284 patients who had experienced acute ischemic stroke during the study period, 578 (25.3%) were classified as having large artery atherosclerosis. Among these, 157 (27.1%) had an MCA stroke. After excluding patients with tandem stenotic lesions at the carotid artery and MCA branch, those with MRA data that did not allow WSS assessment, and those who received reperfusion treatment prior to the MRI, 64 patients with symptomatic MCA stenosis were included in the analysis. In this final cohort, 32 patients had sMCA-AAE and the remaining 32 had sMCA-LBO. Overall, 46 patients with aMCA during the study period were included (Supplementary Figure 1).
The mean age of the 110 patients was 63.4┬▒12.8 years old, and 54.5% were male. There were no significant intergroup differences in terms of demographics, risk factors, or the degree of stenosis.
Plaques were evenly distributed among the patients with aMCA. Plaques were more frequently observed in the middle MCA of patients with sMCA-LBO, whereas plaques were more frequently observed in the distal MCA of patients with sMCA-AAE (P=0.013). Plaque enhancement was observed more often in patients with sMCA-AAE (100%) or sMCA-LBO (90.6%) than in those with aMCA (32.6%; P<0.001). Plaque enhancement was most commonly observed in the minimal lumen area (87.5%) in those with sMCA-LBO, while it was frequently noted in the upstream point (75%) in those with sMCA-AAE (P<0.001) (Table 1). The inter-rater reliability of MCA plaque enhancement was 0.935 (P<0.001).
The maximal WSS at the initial, downstream, and terminal points differed among the three groups. The SD and CoV of the maximal WSS were significantly different among the three groups. The SD and CoV were higher in patients with sMCA-AAE than in those with aMCA or sMCA-LBO (SD: 2.56┬▒1.15 vs. 1.98┬▒0.79 or 1.59┬▒0.96, respectively; CoV: 0.45┬▒0.17 vs. 0.29┬▒0.14 or 0.25┬▒0.11, respectively). After normalization, the highest/initial maximal WSS ratio was the highest and the lowest/initial maximal WSS ratio was the lowest in those with sMCA-AAE.
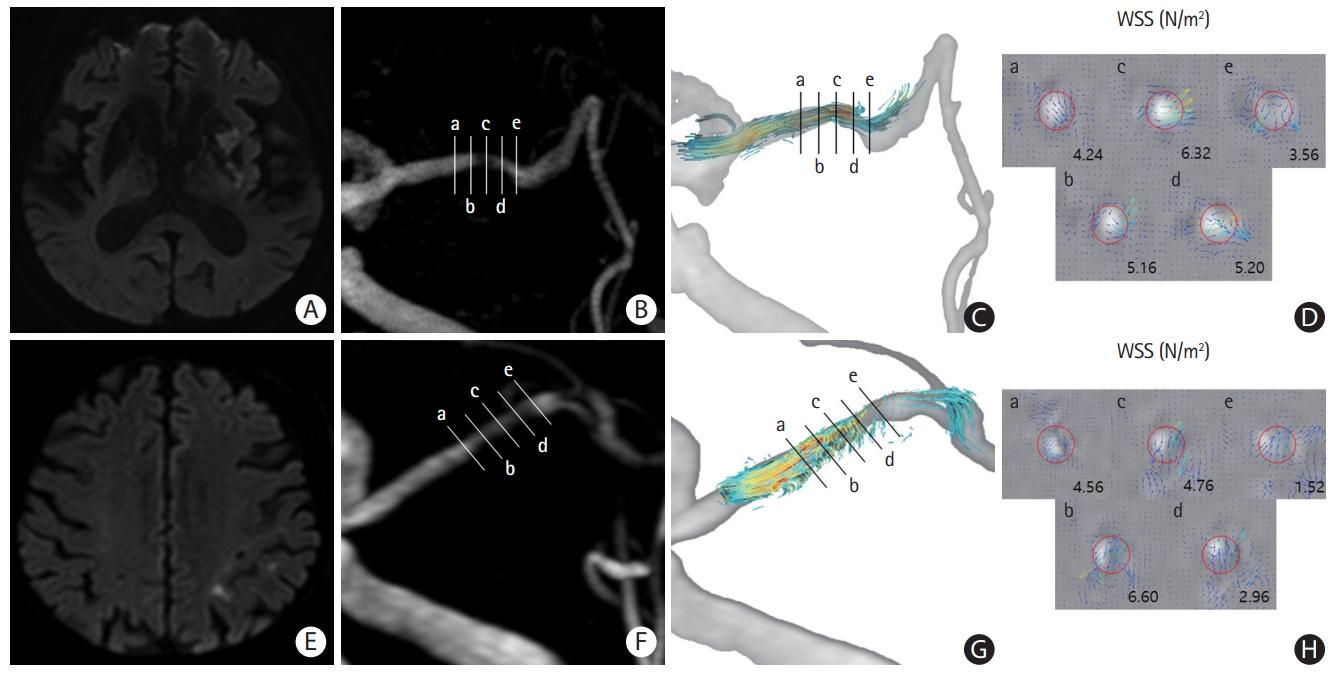
The location of the highest maximal WSS differed among the three groups (P<0.001); the highest maximal WSS was most commonly observed in the minimal lumen area in those with aMCA (34.8%) and those with sMCA-LBO (56.3%) in contract to the upstream point (59.4%) in those with sMCA-AAE (Table 2 and Figure 2). Analysis of the mean time-averaged WSS showed a similar trend (Supplementary Table 1). Furthermore, plaque enhancement location was highly correlated with the highest maximal WSS location (Žü=0.472, P<0.001).
After adjustment, multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the variability of the maximal WSS was independently associated with sMCA-AAE (OR, 2.372; 95% CI, 1.264-4.449; P=0.007). Furthermore, the highest maximal WSS located at the upstream point was also associated with sMCA-AAE (reference highest maximal WSS located at the minimal lumen area: OR, 5.299; 95% CI, 1.343-20.906; P=0.017) (Table 3 and Supplementary Table 2).
In the present study, plaque location differed among the patients with aMCA, sMCA-AAE, and sMCA-LBO. Plaques were evenly distributed in the proximal, middle, and distal MCA of patients with aMCA; however, in those with sMCA-LBO, plaques were more frequently located in the middle MCA, where the majority of perforators branched. Plaques in the middle MCA may obliterate the perforator orifice, resulting in subcortical infarction, while distal MCA plaques were associated with AAE, in line with our previous report [6].
Within the MCA plaque, plaque enhancement was observed more commonly in symptomatic MCA disease than in aMCA disease. Plaque enhancement was observed in most of the symptomatic cases, but only half of the aMCA cases, which corresponds well with our results [23]. Moreover, plaque enhancement location within the plaque correlated well with the area having the highest maximum WSS. Plaque enhancement represents a vulnerable plaque with higher stroke recurrence rates and is associated with AAE [24]. According to experimental studies, a high WSS changes endothelial cell behavior, modifies gene expression of matrix metalloproteinase, and exacerbates inflammation to form a vulnerable plaque [25,26].
In patients with sMCA-AAE, the highest maximal WSS was located at the upstream point, where plaque rupture frequently occurs [27,28]. The highest WSS is usually observed in the minimal lumen area, where the flow velocity is the highest, such as in patients with aMCA or sMCA-LBO in our study [21]. However, in sMCA-AAE, the flow directly impacted the upstream area intruding into the lumen, with a localized high WSS. This may contribute to plaque instability, which is evidenced by plaque enhancement, finally leading to plaque rupture and AAE [22,27,29]. Our findings may at least partially explain the results of a previous study, which showed that increased WSS within the stenotic lesion has a higher risk of recurrent stroke [30].
Although several controversies regarding this point exist, low WSS and slow recirculatory secondary flows are believed to promote atherosclerotic plaque development [10]. However, it is also believed that decreased WSS can also cause thrombus formation. In our study, the maximal WSS at the downstream and terminal points in patients with sMCA-AAE was significantly lower than that in patients with sMCA-LBO. Thrombus formation and progression developed in the post-stenotic area, as the low WSS region provides sufficient time and chance for platelets to aggregate and form a thrombus [31-33]. Such thrombi can trigger distal embolization, in a mechanism distinct from plaque rupture, as described above. Future studies using CFD may strengthen our findings.
A previous study reported that the WSS of atherosclerotic MCA was 5-10 N/m2, which corresponds well with our results [34]. However, as the absolute values may be affected by a participantŌĆÖs flow status, we normalized the value using the WSS at the initial plaque point. The highest/initial maximal WSS ratio was the highest in patients with sMCA-AAE; This may explain the association between high WSS, plaque instability, and AAE. Furthermore, the lowest/initial ratio was lowest in patients with sMCA-AAE. The WSS gradient may also play an important role in plaque instability [35]. Previous studies have shown that even a significant deceleration in shear force may cause unfolding of the von Willebrand factor, thereby enhancing shear-induced platelet activation [36].
The current study has several limitations. First, although we attempted to enroll all relevant consecutive patients, selection bias stemming from patient consent cannot be excluded. Because patients with severe disability cannot undergo HRVWI evaluation due to poor condition or motion artifacts, tandem stenotic lesions at the carotid artery and MCA branch, and reperfusion treatment were excluded, it is not representative of the entire population of patients with MCA steno-occlusive lesions. Second, patients with stroke caused by LBO and AAE may also have a stenosis degree of less than 50% in the MCA. In the current study, we only included patients with MCA stenosis Ōēź50% who were diagnosed with stroke due to large artery atherosclerosis, to minimize the effect of stenosis degree on WSS [2,21]. Further studies focusing on patients with stenosis of less than 50% may also be valuable. Third, we analyzed plaque and WSS characteristics based on two-dimensional anteroposterior images of three-dimensionally reconstructed MRA images using only five points. Further three-dimensional analyses of plaque characteristics and WSS may strengthen our results. Fourth, we measured the WSS within the slice along the circumferential vessel wall at a selected point. However, there may also be differences in the WSS on the plaque side and on the normal side within the same slice of the wall at the selected point. Fifth, the plaque composition, vulnerability, embolus size, and composition of each stroke mechanism were not confirmed pathologically. Furthermore, we used the maximal WSS to analyze the association between the nature of the plaque, stroke mechanism, and hemodynamics. Analysis of other features, such as flow velocity, may also be informative. Finally, we focused on the spatial variability of WSS; however, the temporal variability of WSS may also affect the plaque nature and stroke mechanism. Despite these limitations, our study is the first to report an association between WSS, plaque nature, and stroke mechanism in patients with MCA disease.
The results of this study showed that stroke in the MCA territory caused by AAE was more related to enhancement and the highest maximum WSS at the upstream point, and was associated with elevated variability of maximum WSS. Overall, our results indicated that hemodynamics may alter plaque characteristics and platelet aggregation, leading to different stroke mechanisms in MCA.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2022.02754.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā1.
Hemodynamic parameters in patients with asymptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis, symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis with infarction due to artery-to-artery embolism, or symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis with infarction due to local branch occlusion
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā2.
Univariable analysis of factors associated with ischemic stroke caused by artery-to-artery embolisms
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā1.
Flow chart of the study design. MCA, middle cerebral artery; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; HRVWI, high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance image; AAE, artery-to-artery embolism; LBO, local branch occlusion.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Brain Convergence Research Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (no. 2020M3E5D2A01084576), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (no. 2020R1A2C2100077), and Kyung Hee University in 2022 (no. KHU-20220786).
Research conception and design, H.G.W., H.G.K., K.M.L., S.H.H., H.J., S.H.H., D.I.C., DS.L., B.J.K.; Data acquisition, H.G.W., H.G.K., K.M.L., S.H.H., S.H.H., D.I.C., B.J.K.; Data analysis and interpretation, H.G.W., H.G.K., K.M.L., H.J., DS.L., B.J.K.; Statistical analysis, H.G.W., S.H.H., D.I.C., DS.L., B.J.K.; Drafting the manuscript, H.G.W., H.G.K., K.M.L., S.H.H., B.J.K.; Critical revision of the manuscript, H.G.W., H.G.K., K.M.L., S.H.H., H.J., S.H.H., D.I.C., DS.L., B.J.K.; all authors approved the final manuscript.
Figure┬Ā1.
Illustration of representative case with plaque enhancement in the middle cerebral artery. (A) Atherosclerotic plaque and significant stenosis in the middle cerebral artery. (B) Plaque enhancement (white arrowhead) can be seen on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging. (C) Plaque enhancement (white arrowhead) and an atherosclerotic plaque (white arrow) are visible on high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging. (D) Within the plaque, the location of the enhancement was measured at five points (initial, upstream, minimal lumen area, downstream, and terminal).
Figure┬Ā2.
Representative cases of maximal wall shear stress (WSS) in patients with symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis (sMCA) with infarction caused by local branch occlusion (sMCA-LBO) and sMCA with infarction caused by artery-to-artery embolism (sMCA-AAE). (A) Infarction due to local branch occlusion. (B) Five points (initial, upstream, minimal lumen area, downstream, and terminal) of the sMCA. (C, D) The highest maximal WSS was observed from the minimal lumen area in patients with sMCA-LBO. (E) Infarction due to artery-to-artery embolism. (F) Five points (initial, upstream, minimal lumen area, downstream, and terminal) of sMCA. (G, H) The highest maximal WSS was observed from the upstream area in patients with sMCA-AAE. Five points: a, initial; b, upstream; c, minimal lumen area; d, downstream; e, terminal.
Table┬Ā1.
Baseline characteristics of the study participants
Values are presented as the mean┬▒standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range). The three groups were compared using PearsonŌĆÖs chi-square tests, one-way analysis of variance, or the Kruskal-Wallis test, as appropriate.
aMCA, asymptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis; sMCA, symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis; AAE, infarction due to artery-to-artery embolism; LBO, infarction due to local branch occlusion; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MCA, middle cerebral artery.
Table┬Ā2.
Hemodynamic parameters of the study participants
Values are presented as mean┬▒standard deviation or number (%). The three groups were compared using PearsonŌĆÖs chi-square tests or one-way analysis of variance, as appropriate.
aMCA, asymptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis; sMCA, symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis; AAE, infarction due to artery-to-artery embolism; LBO, infarction due to local branch occlusion; WSS, wall shear stress; SD, standard deviation; CoV, coefficient of variation.
Table┬Ā3.
Multivariable analysis of factors associated with ischemic stroke caused by artery-to-artery embolism
| Variable | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | P | Adjusted OR* (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio of maximal WSS | ||||
| ŌĆāHighest/initial | 4.467 (1.472-13.556) | 0.008 | 5.420 (1.538-19.096) | 0.009 |
| ŌĆāLowest/initial | 0.082 (0.009-0.711) | 0.023 | 0.118 (0.011-1.261) | 0.077 |
| Standard deviation of maximal WSS | 2.617 (1.404-4.880) | 0.002 | 2.372 (1.264-4.449) | 0.007 |
| Location of highest maximal WSS | ||||
| ŌĆāMinimal lumen area | 1 | 1 | ||
| ŌĆāUpstream | 4.071 (1.311-12.646) | 0.015 | 5.299 (1.343-20.906) | 0.017 |
| ŌĆāDownstream | 0.250 (0.027-2.347) | 0.225 | 0.676 (0.054-8.438) | 0.761 |
References
1. Kim JS, Nah HW, Park SM, Kim SK, Cho KH, Lee J, et al. Risk factors and stroke mechanisms in atherosclerotic stroke: intracranial compared with extracranial and anterior compared with posterior circulation disease. Stroke 2012;43:3313-3318.


2. Kim BJ, Kim JS. Ischemic stroke subtype classification: an Asian viewpoint. J Stroke 2014;16:8-17.



3. Tekle WG, Hassan AE. Intracranial atherosclerotic disease: current concepts in medical and surgical management. Neurology 2021;97(20 Suppl 2):S145-S157.


4. Wu F, Song H, Ma Q, Xiao J, Jiang T, Huang X, et al. Hyperintense plaque on intracranial vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of artery-to-artery embolic infarction. Stroke 2018;49:905-911.



5. Noh KC, Choi HY, Woo HG, Chang JY, Heo SH, Chang DI, et al. High-on-aspirin platelet reactivity differs between recurrent ischemic stroke associated with extracranial and intracranial atherosclerosis. J Clin Neurol 2022;18:421-427.




6. Ha SH, Chang JY, Lee SH, Lee KM, Heo SH, Chang DI, et al. Mechanism of stroke according to the severity and location of atherosclerotic middle cerebral artery disease. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2021;30:105503.


7. Li ZY, Taviani V, Tang T, Sadat U, Young V, Patterson A, et al. The mechanical triggers of plaque rupture: shear stress vs pressure gradient. Br J Radiol 2009;82 Spec No 1:S39-S45.


8. Fowkes FG, Rudan D, Rudan I, Aboyans V, Denenberg JO, McDermott MM, et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013;382:1329-1340.


9. Kim BJ, Yoon Y, Lee DH, Kang DW, Kwon SU, Kim JS. The shape of middle cerebral artery and plaque location: high-resolution MRI finding. Int J Stroke 2015;10:856-860.



10. Dhawan SS, Avati Nanjundappa RP, Branch JR, Taylor WR, Quyyumi AA, Jo H, et al. Shear stress and plaque development. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2010;8:545-556.



11. Ku DN, Giddens DP, Zarins CK, Glagov S. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 1985;5:293-302.


12. Cicha I, W├Črner A, Urschel K, Beronov K, Goppelt-Struebe M, Verhoeven E, et al. Carotid plaque vulnerability: a positive feedback between hemodynamic and biochemical mechanisms. Stroke 2011;42:3502-3510.


13. Park ST, Kim JK, Yoon KH, Park SO, Park SW, Kim JS, et al. Atherosclerotic carotid stenoses of apical versus body lesions in high-risk carotid stenting patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31:1106-1112.



14. Woo HG, Heo SH, Kim EJ, Chang DI, Song TJ, Kim BJ. Atherosclerotic plaque locations may be related to different ischemic lesion patterns. BMC Neurol 2020;20:288.




15. Zhang M, Peng F, Li Y, He L, Liu A, Li R. Associations between morphology and hemodynamics of intracranial aneurysms based on 4D flow and black-blood magnetic resonance imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2021;11:597-607.



16. Gaidzik F, Pravdivtseva M, Larsen N, Jansen O, H├Čvener JB, Berg P. Luminal enhancement in intracranial aneurysms: fact or feature?-A quantitative multimodal flow analysis. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2021;16:1999-2008.




17. Sekine T, Takagi R, Amano Y, Murai Y, Orita E, Fukushima Y, et al. 4D flow MR imaging of ophthalmic artery flow in patients with internal carotid artery stenosis. Magn Reson Med Sci 2018;17:13-20.



18. Ando T, Sekine T, Murai Y, Orita E, Takagi R, Amano Y, et al. Multiparametric flow analysis using four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging can detect cerebral hemodynamic impairment in patients with internal carotid artery stenosis. Neuroradiology 2020;62:1421-1431.



19. Youn SW, Lee J. From 2D to 4D phase-contrast MRI in the neurovascular system: will it be a quantum jump or a fancy decoration? J Magn Reson Imaging 2022;55:347-372.

20. Ko Y, Lee S, Chung JW, Han MK, Park JM, Kang K, et al. MRI-based algorithm for acute ischemic stroke subtype classification. J Stroke 2014;16:161-172.



21. Chen Z, Qin H, Liu J, Wu B, Cheng Z, Jiang Y, et al. Characteristics of wall shear stress and pressure of intracranial atherosclerosis analyzed by a computational fluid dynamics model: a pilot study. Front Neurol 2019;10:1372.



22. Lee JM, Choi G, Hwang D, Park J, Kim HJ, Doh JH, et al. Impact of longitudinal lesion geometry on location of plaque rupture and clinical presentations. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2017;10:677-688.


23. Wang E, Shao S, Li S, Yan P, Xiang Y, Wang X, et al. A high-resolution MRI study of the relationship between plaque enhancement and ischemic stroke events in patients with intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. Front Neurol 2018;9:1154.



24. Kim JM, Jung KH, Sohn CH, Moon J, Shin JH, Park J, et al. Intracranial plaque enhancement from high resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging predicts stroke recurrence. Int J Stroke 2016;11:171-179.



25. Eshtehardi P, Brown AJ, Bhargava A, Costopoulos C, Hung OY, Corban MT, et al. High wall shear stress and high-risk plaque: an emerging concept. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2017;33:1089-1099.




26. Corban MT, Eshtehardi P, Suo J, McDaniel MC, Timmins LH, Rassoul-Arzrumly E, et al. Combination of plaque burden, wall shear stress, and plaque phenotype has incremental value for prediction of coronary atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability. Atherosclerosis 2014;232:271-276.


27. Groen HC, Gijsen FJ, van der Lugt A, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS, van der Steen AF, et al. Plaque rupture in the carotid artery is localized at the high shear stress region: a case report. Stroke 2007;38:2379-2381.


28. de Weert TT, Cretier S, Groen HC, Homburg P, Cakir H, Wentzel JJ, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque surface morphology in the carotid bifurcation assessed with multidetector computed tomography angiography. Stroke 2009;40:1334-1340.


29. Thondapu V, Mamon C, Poon EKW, Kurihara O, Kim HO, Russo M, et al. High spatial endothelial shear stress gradient independently predicts site of acute coronary plaque rupture and erosion. Cardiovasc Res 2021;117:1974-1985.



30. Leng X, Lan L, Ip HL, Abrigo J, Scalzo F, Liu H, et al. Hemodynamics and stroke risk in intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Ann Neurol 2019;85:752-764.



31. Rana A, Westein E, Niego B, Hagemeyer CE. Shear-dependent platelet aggregation: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Front Cardiovasc Med 2019;6:141.



32. Ha H, Lee SJ. Hemodynamic features and platelet aggregation in a stenosed microchannel. Microvasc Res 2013;90:96-105.


33. Zhao YC, Vatankhah P, Goh T, Michelis R, Kyanian K, Zhang Y, et al. Hemodynamic analysis for stenosis microfluidic model of thrombosis with refined computational fluid dynamics simulation. Sci Rep 2021;11:6875.




34. Chen Y, Liu J, Li M, Yu Y, Yan Z, Shiu W, et al. Non-invasive assessment of intracranial wall shear stress using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in combination with computational fluid dynamics technique. Fundam Res 2022;2:329-334.